31 Abdominal distension
advertisement
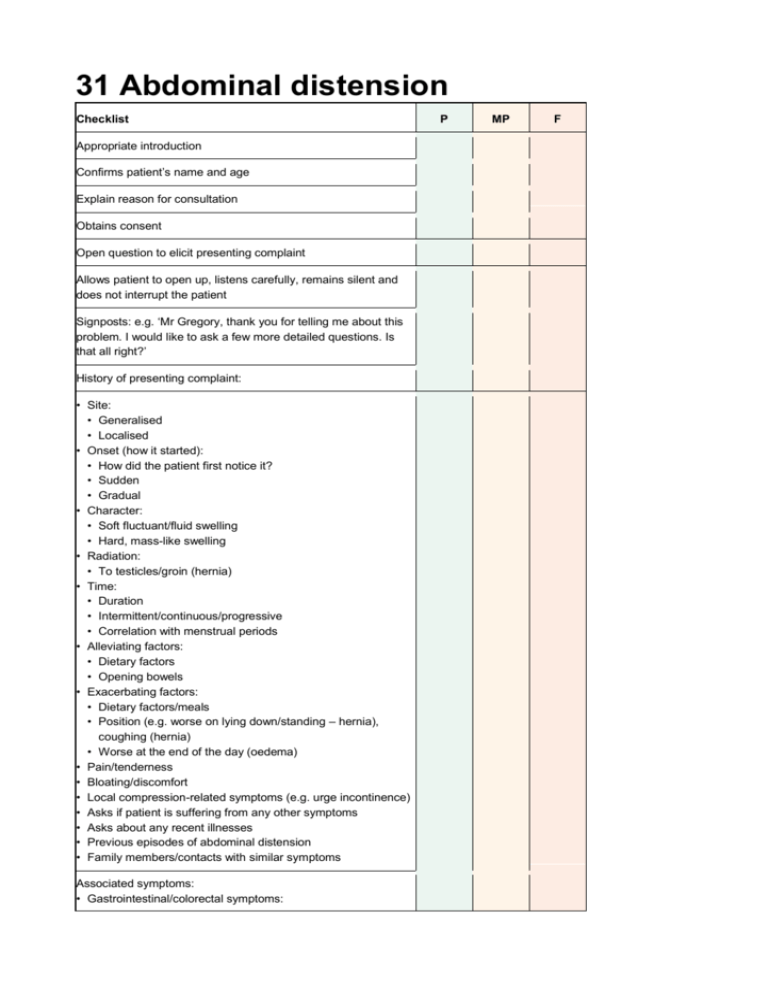
31 Abdominal distension Checklist Appropriate introduction Confirms patient’s name and age Explain reason for consultation Obtains consent Open question to elicit presenting complaint Allows patient to open up, listens carefully, remains silent and does not interrupt the patient Signposts: e.g. ‘Mr Gregory, thank you for telling me about this problem. I would like to ask a few more detailed questions. Is that all right?’ History of presenting complaint: • Site: • Generalised • Localised • Onset (how it started): • How did the patient first notice it? • Sudden • Gradual • Character: • Soft fluctuant/fluid swelling • Hard, mass-like swelling • Radiation: • To testicles/groin (hernia) • Time: • Duration • Intermittent/continuous/progressive • Correlation with menstrual periods • Alleviating factors: • Dietary factors • Opening bowels • Exacerbating factors: • Dietary factors/meals • Position (e.g. worse on lying down/standing – hernia), coughing (hernia) • Worse at the end of the day (oedema) • Pain/tenderness • Bloating/discomfort • Local compression-related symptoms (e.g. urge incontinence) • Asks if patient is suffering from any other symptoms • Asks about any recent illnesses • Previous episodes of abdominal distension • Family members/contacts with similar symptoms Associated symptoms: • Gastrointestinal/colorectal symptoms: P MP F Checklist • • • • Abdominal pain Flatulence Nausea/vomiting Bowel habit/diarrhoea/constipation: any correlation of distension with opening bowels? • Dysphagia/dyspepsia Ascites: • Facial swelling • Ankle swelling • Shortness of breath/orthopnoea Liver/hepatobiliary symptoms: right upper quadrant pain, jaundice, dark stools, pale urine Renal symptoms: urinary symptoms, frothy urine (nephrotic syndrome), lethargy, pruritus Heart failure symptoms: chest pain Hypothyroidism Females: gynaecological symptoms: • Correlation with menstrual periods • Irregular/painful periods • Intermenstrual/postcoital bleeding • Pelvic pain Females: obstetric symptoms: • Possibility of patient being pregnant • Last menstrual period • Unprotected sexual intercourse: must signpost before taking sexual history • Contraception ‘Red flags’: • Bleeding (rectal, melaena, vaginal) • Weight loss, loss of appetite, night sweats (malignancy) Review of systems Past medical history: • Constipation • Abdominal surgery –especially laparoscopic surgery • Gynaecological history: fibroids, ovarian cysts • Heart failure Family history: • Colorectal cancer • Ovarian cancer • Polycystic kidney disease • Hernia • Fibroids Drug history: • Laxative history: any recent changes, stopped taking • Oral contraceptive pill (OCP, if patient female) • Over-the-counter medication Allergies Social history: P MP F Checklist P MP F • Alcohol (peptic ulcer disease, gastritis) • Smoking • Illicit drug use (especially intravenous drug abuse for hepatitis B/C) • Diet: • Intake of fibre • Recent change in diet • Occupation • Activities of daily living Use of non-verbal cues, e.g. good eye contact, nodding head and good body posture Systematic approach Explores and responds to ICE: • Ideas • Concerns • Expectations Shows empathy Non-verbal skills Avoids technical jargon Devises holistic management plan and addresses psychosocial issues as well as medical problems Summarises Offers to answer any questions Thanks patient OSCEs for Medical Finals, First Edition. Hamed Khan, Iqbal Khan, Akhil Gupta, Nazmul Hussain, and Sathiji Nageshwaran. © 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Published 2013 by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.