Math Patterns - Saginaw Valley State University
advertisement

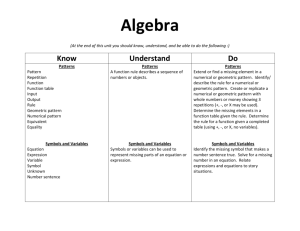
Unit Design For Math Patterns (Kindergarten) Developed by Renee Scott Pontiac Academy for Excellence UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 1 Unit Design Worksheet Unit Title: Math Patterns Subject/Course: Mathematics Topic: Patterns Grade(s): Kindergarten Staff Name: R. Scott Stage 1 - Desired Results Established Goals (GLCE’s, etc.): 1. G.GS.00.03 Create, describe, and extend simple geometric patterns 2. N.MR.00.10 Create, describe, and extend simple number patterns 3. N.ME.00.05 Count to 30 by 2’s, 5’s and 10’s using grouped objects as needed. Understandings: Essential Questions: Students will understand that... a pattern is a repetition of shapes, numbers, or any item selected. (#1) a pattern is a repetition of shapes, numbers, or any item selected. (#2) a pattern (grouped object) is a repetition of shapes, numbers, or any item selected. (#3) Students will know... how to create a geometric pattern. (#1) how to extend a simple number pattern. (#2) how to group objects to count. (#3) How can geometric shapes be used in the real world? (#1) What are patterns? (#2) How can you group numbers of objects to show a pattern? (#3) Students will be able to... use higher order thinking skills to predict what comes next and to find a missing element. recognize, copy, and predict how growing and repeating patterns will be extended. Unit Enduring Understanding: Unit Question: The student will understand that patterns are repetitive. What is a Pattern? UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 2 Stage 2 - Assessment Evidence Performance Tasks: (Summary in GRASPS form, end of the unit)(Summative)(After) GRASPS: Goal: To create an AB Pattern. The challenge will be to stick with the AB pattern. Role: The student will act as a T-Shirt Designer with the task of creating an AB pattern design on the Shirt. Audience: The teacher will act as the audience for the student creating the T-Shirt. Situation: The student will be provided a collection of geometric shapes as provided by the teacher. The student will then create an AB pattern in front of them. The student will use the geometric shape AB pattern to place on a T-shirt. Performance: Playing the role as a T-shirt designer, the student will create a hands on example by displaying an AB Pattern on a T-shirt as provided by the teacher. Standard: The student will be judged on the creation of their pattern. (or lack of AB pattern creation). If the student was not successful at first try, they will be given opportunities/prompts by the teacher to reach their goal. Key Criteria: (Rubrics, etc.) Patterns: 6 pts- shows clear understanding of math concepts; demonstrates use of basic skills independently with rare errors; uses multiple strategies to solve problems. 5 pts- communicates understanding of math concepts; demonstrates use of basic skills with few errors; may use more than one appropriate strategy to solve problems. 4 pts- shows proficient understanding of math concepts; demonstrates use of basic skills independently with occasional errors; uses an appropriate strategy to solve problems. 3 pts- shows some understanding of math concepts; demonstrates use of basic skills with some assistance; inconsistently uses an appropriate strategy to solve problems. 2 pts- shows minimal understanding of math concepts; demonstrates use of basic skills with frequent assistance; makes partial attempts to solve problems but little progress is made towards a solution. 1 pt- shows no understanding of math concepts; cannot demonstrate use of basic skills without assistance; is unable to apply strategies to solve problems Proficiency Levels: 6 Exceptional Proficiency 5 Advanced Proficiency 4 Proficient (demonstrates the student is consistently meeting the standard). 3 Developing Proficiency 2 Limited Proficiency 1 Minimal Proficiency Other Evidence: (Quizzes, Tests, Prompts, Observations, Dialogs, Work samples, etc.)(Before, During)(For learning) UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 3 Before Daily discussion questions (#1) Daily discussion questions (#2) Brainstorm/KWL (#1) Daily discussion questions (#3) Daily examples of showing groups of 2, 5, 10 (use students as props/models) (#3) During Extend geometric shape patterns by using pattern blocks/shape cards (#1) Use manipulatives to create AB Patterns (#1) Use a number chart to count to 100 by 2, 5’s, 10’s. (#2) Count by 2, 5, 10 using grouped objects/environmental items (people, items in classroom) (#3) Put manipulatives into groups (of 2, 5, 10) using counting bears, blocks or unifix cubes. (#3) After Create an AB pattern using manipulatives, pattern blocks (#1) Cut/paste to complete a geometric pattern (#1) Cut/paste to complete the missing numerical pattern. (#3) Quiz of counting by 2, 5, 10 (#2) Describe the assessment/s and state the prompt if applicable. XF XS What type of scoring tools will be used for evaluation? □ Analytic rubric □ Holistic rubric □ Criterion rubric X Checklist □ Answer Key □ Other Student Self-Assessment and Reflection: Draw a picture of what you know about patterns. Use crayons to make a pattern from their prior knowledge. UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 4 UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 5 Unit Design Worksheet Stage 3 - Learning Plan Differentiated Instruction (Layers, Tiered, etc.): Basic: What basic new knowledge do I need them to know/learn? What patterns do you see at school, outside, in your house, or anywhere else in your environment? How can you extend a variety of patterns by just looking at it? How do you know? If an element is missing in a repeating or growing pattern, how will you extend it? Applying: How can they apply this new information to previous information? Apply, compare, manipulate, demonstrate Compare patterns vs. non patterns Find patterns of objects in the room (students, shoes, crayons, markers). Manipulate objects to create patterns Demonstrate a repeated pattern by clapping, snapping, stomping Learning: What debatable issue in the real world deals with this topic? Current events, debates, leadership, decision? Students act as a T-Shirt designer Students act as book author, creating a counting book Learning Activities: Basic: Discuss patterns with examples Each student completes individual activities creating patterns Make a pattern using objects in the room (ex. crayon/marker/crayon/marker) Make a pattern using geometric shape patterns (ex. circle/triangle/circle/triangle) Apply: Students are actively engaged in creating numerical patterns Students manipulative hands on examples to create numerical pattern examples Students use workmats to create, practice, and share numerical patterns Learning: Practical example of a geometric pattern Classroom project to portray numerical pattern UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 6 UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 7 Unit Design Worksheet Essential Vocabulary (Identify and define) Create: to cause to come into being, as something unique that would not naturally evolve or that is not made by ordinary processes. Describe: to tell or depict in written or spoken words; give an account of. Extend: to increase the length or direction of. Pattern: A plan, diagram, or model to be followed Color: That aspect of the appearance of objects and light sources that may be specified in terms of hue, lightness, and saturation. Number: a word or symbol, or a combination of words or symbols, used in counting or in noting a total. Manipulative: Any of various objects designed to be moved or arranged by hand as a means of developing motor skills or understanding abstractions, especially in mathematics. Sequencing the Learning Monday Basic (C) Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Present lesson on sequences of shapes, colors, movements, letters, and objects. Educate students how patterns can be represented in a variety of ways. Activities of using patterns in the room: (teacher led) Show and discuss a story about patterns “Patterns Patterns Everywhere”. Discuss the story and how it’s linked to what we are doing in class. Introduce repeating and growing patterns and show examples of each. Activities of manipulating objects in the room to create patterns: Students work individually at their desks by: Students use colored chips to create an AB pattern at their seat. Use cut out shapes to create a pattern. Example: (circle/ triangle/circle triangle etc…) Students cut/glue their pattern on a piece of construction paper. Use counting bears of various colors to lay out an AB Pattern on a workmat. Students then color in the corresponding worksheet to show colored bears according to the pattern they created. Have students practice identifying the core of a pattern, or a part, of the pattern that repeats. (Teacher led-whole group practice using shapes) Have them practice extending a pattern. By using shape cards. (individual practice at desk) Boy/girl pattern Shoes pattern (black/ brown/black/ brown) Glue stick/ crayon/glue stick/crayon Book/pencil/book Counting Bears (large/small/large/ small) Clap a pattern Stomp a pattern Use color cards to create a pattern (individual work at desk) UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University Students take turns calling out the color patterns they created in front of them. Display work in the room. Use unifix cubes of various colors to lay out an AB pattern on the workmat. Students then color in the corresponding worksheet which shows unifix cubes according to the pattern they created. 8 Sequencing the Learning Monday Apply (B) Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Introduce repeating patterns using numerical values. Discuss how counting by 10’s shows a numerical pattern. Introduce repeating patterns using numerical values. Discuss how counting by 5’s can be an example of a numerical pattern. Introduce repeating patterns using numerical values. Discuss how counting by 5’s can be an example of a numerical pattern. Introduce repeating patterns using numerical values. Discuss how counting by 2’s can be an example of a numerical pattern. Introduce repeating patterns using numerical values. Discuss how counting by 2’s can be an example of a numerical pattern. Students clap out counting by 10’s to 100. Students snap together as a whole class as they count together by 5’s to 100. Students trace foot including 5 toes. (depicting 5 toes) Use students as examples to count by two’s to 30 by using the students’ eyes as a numerical pattern. (call students to the front of the room to demonstrate counting by 2’s ) Discuss how a bicycle has two wheels and how the wheels could be used as a numerical pattern to count by 2’s. Use 100 chart to highlight the tens to 100 (10, 20, 30). Students are given handprints (depicting 5 fingers) to put up on the board. As each handprint is placed on the board, the teacher writes each five number. (5,10,15…100) The class then reviews the number pattern as the teacher points to each handprint and counts to 100 by 5’s. Monday Learning (A) Students stand behind the foot they traced. Students then step on and call out the number pattern by 5’s until they reach number 100. Give students a quiz on counting by 5’s to 100. Discuss how different body parts can be used to show a numerical pattern. Have students give examples of body parts that have “2” and use examples to count by 2’s. Provide student with a worksheet filled with pictures of bicycles. Students number the wheels by 2’s, cut them out, and glue them in a sequential order depicting a numerical pattern of 2’s to 30. Display student work. Tuesday Students use hands on manipulative to create a geometric pattern. Students use hands on manipulative to create a numerical pattern. The student acts as a T-Shirt Designer. Students act as an author of a children’s counting book. The student will be provided a collection of geometric shapes as provided by the Students then place their foot in a circle in the front of the room. Students use cutouts to create a classroom book depicting a UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 9 teacher. The student will then create an AB pattern by displaying the pattern in front of them as a model. Playing the role as a T-shirt designer, the student will create a hands-on example by displaying an AB Pattern on a T-shirt as provided by the teacher. The student will be judged on the creation of their pattern. (or lack of AB pattern creation). If the student was not successful at first try, they will be given opportunities/prompt s by the teacher to reach their goal. numerical pattern of counting by 2’s. Each student will be given a peace sign of 2 fingers to decorate, cut out, and glue onto a page. Students will then stand in front of the class to line up their peace sign (2 fingers) to show how numerical values can represent a pattern. The class will count out by 2’s as the peace signs are held up and counted to 30. The students will then create a classroom book by joining each peace sign page together. The correct number of counting by 2’s will be added under the peace sign to indicate how many 2’s (fingers) have been counted in the book. The end result will produce a numerical pattern book of counting by 2’s. UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 10