File
advertisement

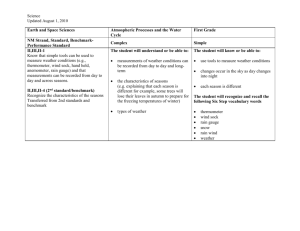
1 Subject: Earth Science (Four Seasons/Weather) Grade Level: 1st Grade Standard: E.ES.01.22 – Describe and compare weather related to the four seasons in terms of temperature, cloud cover, precipitation, and wind. Objectives/Targets: Given a four seasons cycle wheel/circle the learner will be able to answer a question about a season by evaluating the weather that occurs during each season with 90% accuracy. - I can compare weather related to the four seasons in terms of temperature and precipitation. The objective will be formatively assessed by students holding up their four seasons cycle wheel to answer each question. Anticipatory Set: Read The Four Seasons by Melvin Berger on the floor. - - - - Teacher asks questions about the spring section of the book. What are the days like in the spring? Why do you think flowers grow in the spring? (Warmer temperatures, rain) Which season comes next? Teacher asks questions about the summer section of the book. What are the days in the summer? Which season comes next? Teacher asks questions about the fall section of the book. What are the days like in the fall? Why do you think leaves fall during autumn? (Colder temperatures) Which season comes next? Teacher asks questions about the winter section of the book. What are the days like in the winter? Why do you think plants don’t grow during the winter? (Colder temperatures, Snow) Which season comes next? 2 Prior Knowledge: Students learned about the order of the seasons and some ‘signs’ that tells us what season it is by learning the “Four Seasons” song. Students have also been learning about fall since we are currently in that season. Practice(s): Read aloud to Students; Real life applications; Collaborative Interaction; Hand’s on activity; Connections to students’ lives Input: Task Analysis: Have students go back to their assigned seats. Tell students they will be making a Four Seasons Wheel (picture attached) Teacher models how to create the Four Seasons Wheel (worksheet attached) - Cut out the arrow - Glue spring item (plant) onto one section of the circle and label it “Spring” with a black crayon Glue summer item (sun) onto one section of the circle and label it “Summer” - with a black crayon Glue fall item (leaf) onto one section of the circle and label it “Fall” with a - black crayon Glue winter item (snowflake) onto one section of the circle and label it “Winter” - with a black crayon - Use brad/fastener to connect the arrow and circle - Write name on the back of the Four Season Wheel Teacher will hand out the Four Seasons Wheel plate, four season items, arrow cut out, and one fastener to each student. Teacher will allow one student from each group to grab a scissor caddy. Students will individually make their Four Seasons Wheel quietly while the teacher walks around to help (teacher might have to help poke the brads/fasteners through). Teacher will model how to move the arrow to answer the series of questions that will be asked. Teacher will ask a series of questions and students need to point the arrow to which season they think is the answer and be ready to explain why. - Which season is usually the warmest? Why? 3 - Which season is usually the coldest? Why? - Which season does it rain the most? Why? - Which season can you jump into a pile of leaves? Why do leaves fall during autumn? - Which season do you wear sandals? Why can you wear sandals in the summer? - Which season do you wear a hat and gloves? Why do you need to wear hat and gloves? - Which season do flowers blossom? Why do flowers blossom in the spring? - Which season are most baby animals born? Why? - Which season do you pick apples? Why? - Which season do you carve pumpkins? Why? - Which season can you make a snowman? Why can you only make a snowman during winter? - If time allotted, have students practice the “Four Seasons” song and add dance moves. Each season has different weather and weather affects what we wear and what activities we do outside. Weather is what the sky and air are like each day. The sky might be sunny or cloudy and the air might be rainy or snowy. This affects the temperature and makes it either warm or cold outside. Thinking Levels: - Remember: Recall the four seasons and the order of their cycle. Describe things that are the ‘signs’ of a season. - Understand: Recognize characteristics of seasons by answering a series of questions. (Ex. Carve pumping is a sign/characteristic of fall) - Apply: Illustrate the four seasons by using pictures that describe them. (Ex. Sun for summer) - Evaluate: Explain why you chose that season for the characteristics within the question. (Ex. Why do flowers blossom in the spring? – Rain, Warmer temperature) - Create: Construct a wheel with the four seasons to represent that they occur as a cycle. Accommodations: Remediation: Student does not need to label the season if they are unable to write. Extension: Students will think of dance moves to add to the “Four Seasons” song (movement must match the season). Learning Styles (Multiple Intelligences): 4 - Visual/Spatial: Ability to recognize seasons by items that represent them and then construct a wheel of the season cycle. - Intrapersonal: Understand what you can do (activities) during that season. - Bodily/Kinesthetic: Add dance movements to the “Four Seasons” Song. (if time allotted) - Musical/Rhythmic: Practice sing the “Four Seasons” Song (if time allotted) Managing the Lesson: Instructional Methods: - Teacher Modeling Collaborative Learning Engagement Strategies: - Sing and Dance to “Four Seasons” Song (if time allotted) - Read Aloud - Construct Four Seasons Wheel Materials Needed: - The Four Seasons by Melvin Berger (Big Book) - Four Seasons Wheel Plate (1 per student) – Picture Attached - Wheel Arrow Cut-out (1 per student) – Worksheet Attached - Brads/Fasteners (1 per student) - Glue sticks - Black crayons Modeling: Teacher models how to create the Four Seasons Wheel (picture attached) Teacher will model how to move the arrow to answer the series of questions that will be asked. Teacher will model how to add dance moves to our “Four Seasons” song. (if time allotted) Checking for Understanding: Teacher will ask questions about each section of The Four Seasons by Melvin Berger. o Teacher asks questions about the spring section of the book. What are the days like in the spring? Why do you think flowers grow in the spring? (Warmer temperatures, rain) 5 Which season comes next? o Teacher asks questions about the summer section of the book. What are the days in the summer? Which season comes next? o Teacher asks questions about the fall section of the book. What are the days like in the fall? Why do you think leaves fall during autumn? (Colder temperatures) Which season comes next? o Teacher asks questions about the winter section of the book. What are the days like in the winter? Why do you think plants don’t grow during the winter? (Colder temperatures, Snow) Which season comes next? Guided Practice: Teacher will ask a series of questions and students need to point the arrow to which season they think is the answer. Teacher will say which season is the correct answer and explain why (by using weather terms (temperature, sun, rain, snow, etc.). - Which season is usually the warmest? Why? - Which season is usually the coldest? Why? - Which season does it rain the most? Why? - Which season can you jump into a pile of leaves? Why do leaves fall during autumn? - Which season do you wear sandals? Why can you wear sandals in the summer? - Which season do you wear a hat and gloves? Why do you need to wear hat and gloves? - Which season do flowers blossom? Why do flowers blossom in the spring? - Which season are most baby animals born? Why? - Which season do you pick apples? Why? - Which season do you carve pumpkins? Why? - Which season can you make a snowman? Why can you only make a snowman during winter? 6 Closure: Each season has different weather and weather affects what we wear and what activities we do outside. Weather is what the sky and air are like each day. The sky might be sunny or cloudy and the air might be rainy or snowy. This affects the temperature and makes it either warm or cold outside. Assessment: Teacher will ask a series of questions and students need to point the arrow to which season they think is the answer. The teacher will formatively assess during this activity. Reflection: How well did the students perform? Were all students engaged? How was my timing? How was my instruction received? What should be modified? 7 Four Seasons Four Seasons Four Seasons 8