PDA Feeding Study Feeding Protocol
advertisement

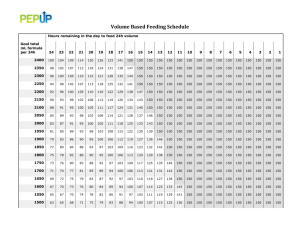
FINAL compromise feeding protocol: Day of Type of feed Birth Weight: Birth Weight: Birth Weight: Feeding 401 – 700 gm 701 – 1000 gm 1001 – 1250 gm ml/kg/day ml/kg/day ml/kg/day 1 EHM 15 15 15 2 EHM 15 15 15 3 EHM 15 15 30 4 EHM 15 30 45 5 EHM 15 45 60 6 EHM 30 60 80 7 EHM 45 80 100 8 EHM 60 100 120# 9 EHM 120* 80 120# 10 EHM 120* 140 100 11 EHM 140 160 120# 12 EHM 120* 160 160 13 EHM 140 160 14 EHM 160 15 EHM 160 EHM = expressed human milk or preterm formula 20 kcal/oz # Primary outcome achieved on the day baby takes 120 ml/kg/d * Human Milk Fortifier or Preterm Formula 22 kcal/oz initiated 1. Prior to the study, infants would be started on feedings and advanced according to individual center preferences. 2. During the study drug administration period (from first dose of study drug to 24 hours after last dose of study drug), infants that are randomized to the “feed through study drug administration period group” will receive a volume of 15 ml/kg/d 3. After study administration period, infants would be switched to the “study protocol feeding advance schedule” (which would be started immediately after the study drug administration period) 4. When to start the “feeding advance protocol”: We would like infants to start the “study protocol feeding advance schedule” immediately following the study administration period (the interval from the first dose of study drug to 24 hours after last dose of study drug). Therefore, ideally the feeding advance protocol should start 24 hr after the last dose of study drug. This may be inconvenient if the 24h point falls between 9pm and 5am, since many centers may not want to start new or increased feedings during the middle of the night. Therefore if the calculated start time for the first feeding of the “feeding advance protocol” falls between 9pm and 5am, we would permit the first feeding of the “feeding advance protocol” to occur as early as 16h after the last dose of study drug, or it could be delayed until the morning when normal feeding orders are usually written. 5. To determine feeding amounts, birth weight will be used for the first 7 days of life, after which feeds should be adjusted for daily weight. 6. The total volume of feeding per day is set by the protocol. On the other hand, the number of feedings per day will be at the discretion of each study center. Typical recommended feeding version (10/20/08) intervals are q 3 hour or q 4 hour for feeding volumes of 15 ml/kg/d, and q 2 hour or q 3 hour for feeding volumes ≥30 ml/kg/d. 7. For bolus feeds, round amount of weight based feeds to the nearest 0.5 ml for feeds ≤ 2.5 ml and to the nearest ml for feeds ≥ 2.6 ml. 8. When to advance to the next day on the “feeding advance protocol”: An infant’s feeding volume will be advanced each day according to the “feeding advance protocol”. In many centers, feeding orders are discussed and written once a day, on morning rounds. In order to advance to the volume designated for the next “Day of Feeding” on the feeding advance protocol, the infant would need to have received at least 61% of the previous day’s planned feeding volume before the change could be made. For example, an infant who weighed 1300 gm at birth and currently weighs 1200 gm and is currently on day 2 of the “feeding advance protocol” is scheduled to receive 15 ml/kg/d =18 ml/day. If the infant had only been given 10ml of the planned 18 ml that he was supposed to receive at the time feeding orders are being written (either because it had been made NPO for a while or because the feedings had been delayed in starting the day before), then either the change to the new feeding volume (for day 3 of the protocol it would be 30 ml/kg/d) would not be made until later in the day (when at least 11ml would have been taken at the current feeding rate) or the change would not be made until the next morning if daily feeding orders can only be written once a day in that nursery 9. For babies who never previously fed, who are randomized to the feeding group: the 15 ml/kg/day feedings during the study drug administration period would be counted as part of their feeding protocol advance 10. For babies who never previously fed, who are randomized to the non-feeding group, we would not start the first 15 ml/kg/day feeding until 24 hours after the last dose of study drug. 11. For study infants who have already been on a feeding advance prior to their entry into the study: please match the maximum daily volume of feeds (and the number of days that the infant has been on that volume, either prior to or during the study drug administration period) with the equivalent number of days on the study protocol feeding advance schedule and then continue to advance feedings according to the study protocol feeding advance schedule. 12. Total fluid intake will be at the discretion of the clinician and the partition between enteral and parenteral nutrition will be calculated daily. 13. Recommendations for feeding advance AFTER reaching 120 ml/kg/day.The infant is considered to achieve full enteral feeding when the volume reaches 120 ml/kg/day (of 20 cal/oz feed). Parenteral nutrition should be discontinued when the infant achieves full feedings of 120 ml/kg/day. 14. Recommendations for feeding advance AFTER reaching 120 ml/kg/day. Calorie fortification to 22 kcal/oz should occur when the baby is tolerating 120 ml/kg/day. The feed advance may be held on the day of calorie fortification so two changes are not implemented on the same day. version (10/20/08) Criteria for Feeding Intolerance and Management of Feeding Regimen. Signs of feeding intolerance Management*** Record as Episode of Gastric aspirate prior to Other signs Feed the feeding of feeding Intolerance intolerance* 1a*. if both ≤2 ml and ≤1/3 None Refeed aspirate as part of total No of previous feed volume volume, continue feeding 1b*. if ≤2 ml but >1/3 of None Check infant, then may refeed No previous feed volume aspirate as part of total volume, and continue feeding. Or may hold feeding and resume in 3 hours. 2. if >2 ml and > 1/3 of None Stop feeding and recheck Yes previous feed volume gastric aspirate in 3 hours. Resume feeding when conditions revert to 1 above. 3. Irrespective Present Stop feeding, perform appropriate Yes evaluation and resume when infant stable and conditions revert to 1 above. *: if continuous naso or orogastric feedings are used, check for residuals q3 – 4 hours. Tolerate benign-appearing residuals of ≤ 2cc or < 2 hours worth of feeds (whichever is more.) ** Evaluation of significant feeding intolerance should be performed by the primary clinical team according to the standard procedure at your institution: (Physical exam, KUB, CBC, culture, etc). Other signs will include one or more of the following: a) dark bile or blood stained gastric aspirate ≥1 ml; b) vomiting ≥ 1/3 of the previous feed volume; c) abdominal distension, discoloration or tenderness; d) visible bowel loops e) bloody stool; f) KUB showing signs of intestinal dilatation; g) metabolic acidosis or new thrombocytopenia; h) Evidence that the child is not well: apnea (new onset or increasing frequency), respiratory distress, lethargy, poor perfusion, temperature instability, etc. ***Recommendations: check feeding tube placement; position infant prone, right side down; consider glycerin suppository if no stools in 18-24 hrs; if recurrent episodes occur after a recent feed advance or fortification, consider returning to the previously tolerated feeding volume or concentration version (10/20/08)