Physics I H: Momentum and Collisions Problem Set

Physics – I H
Chapter 6 Problem Set
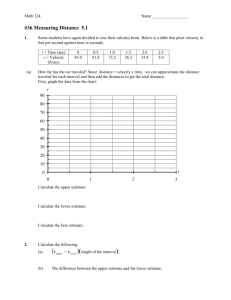
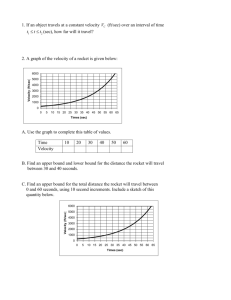
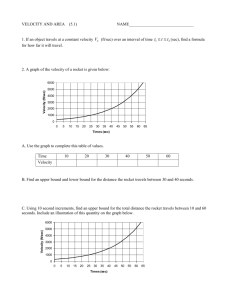
1.
A car weighs 7840 N. (a) What is its mass? (b) The car’s velocity is 25 m/sec eastward. What is its momentum? (c) The car was accelerated from rest to 25 m/sec by a force of 1000 N. How long did the force act to give it this velocity?
2.
A force of 6 N acts on a body for 10 sec. (a) What is the body’s change in momentum? (b) The mass of the body is 3 kg. What is its change in speed?
3.
A car weighing 15680 N and moving at 20 m/sec is acted upon by a 640-N force until it is brought to a halt. (a) What is the car’s mass? (b) What is the initial momentum? (c) What change in the car’s momentum does the force bring about? (d) How long does the braking force act on the car to bring it to a halt?
4.
A 300 g ball is struck by a bat with an impact that lasts 0.020 sec. If the ball moves through the air towards the bat at 50 m/s and leaves at 100 m/s in the opposite direction, calculate the average force exerted by the bat on the ball.
5.
A 40-kg projectile leaves at 2000-kg launcher with a velocity of 800 m/sec forward. What is the recoil velocity (speed and direction) of the launcher?
6.
A neutron of mass 1.67 X 10 -27 kg is ejected from a boron nucleus of mass 17.0 X 10 -27 kg. IF the neutron leaves the nucleus with a velocity of 2.0 X 10 4 m/sec, what is the recoil velocity of the nucleus?
7.
A 4.0 kg seagull flies at 15 m/s into the windshield of an airplane flying in the opposite direction at 180 m/s. If the impact lasts 1.0 ms, find the average force on the windshield. (-7.8 x 10 5 N)
8.
In each of the following collisions, find the unknown: a) v' = ________ b) m
1
= ________
5 kg
5 m/s 4 m/s m
1
2 kg
2 kg
5 kg m
1
2 kg
v' 6 m/s
2 kg
10 m/s 6 m/s 5 m/s 2 m/s c) v = __________
2 8 2 8 kg kg kg kg
30 m/s v 10 m/s 25 m/s
12. A 15 g bullet is fired horizontally into a 3 kg block of wood suspended by a long cord and the bullet remains embedded in the wood. Compute the velocity of the bullet if the impact causes the block to swing 10 cm above its initial level. (1.4 m/s)
13.
A radioactive nucleus at rest decays into a second nucleus, an electron, and a neutrino. The electron and neutrino are emitted at right angles and have a momenta of 9.30 x 10 -23 kg·m/s, and 5.40 x 10 -23 kg·m/s, respectively. What is the magnitude and direction of the momentum of the second (recoiling) nucleus?
(1.08 x 10 -22 kg·m/s; 30.1
o opposite the electron)
14.
An eagle (4.3 kg) moving with speed 7.8 m/s is on a collision course with a second eagle (5.6 kg) moving at 10.2 m/s in a direction at right angles to the first. After they collide, they hold onto one another. In what direction, and with what speed, are they moving after the collision? (60 o ; 6.7 m/s)
From p. 232 16, 36, 44, 45, 46, 52 44 (6.0 kg) 46 (29 s) 52 (2.36 x 10 -2 m)