Study Guide 4 Bio 4 C
advertisement

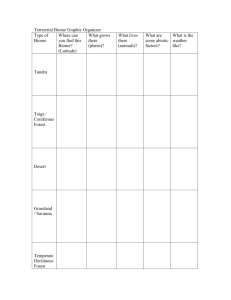
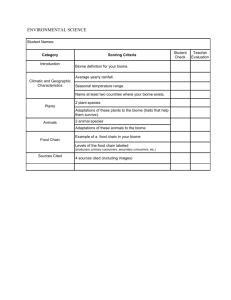
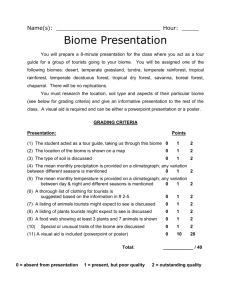
Study Guide 4 Bio 4 C. Shannon F14 (10th edition) Chapters: 22, 24, 25, 26, 30, 32, 33. 34, 52 Ch. 22 Evolution evolution, microevolution, macroevolution, Darwin, Galapagos Islands, speciation, Plato, conventional view, Cuvier, catastrophism, Hutton, gradualism, Lyell, uniformitarianism, Lamarck, Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics, Basic concepts of Darwin, natural selection, evidence for evolution from biogeography, molecular biology, taxonomy, paleontology, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology Ch. 24 The Origin of Species Prezygotic vs. postzygotic isolating mechanisms, allopatric, sympatric, allopatric speciation, sympatric speciation, adaptive radiation, punctuated equilibrium, speciation Ch. 25 Early Earth & The Origin Of Life and Ch. 26 Tracing Phylogeny endosymbiosis theory, big bang theory, Earth's formation, origin of life, Miller's experiments, first atmosphere compared to current atmosphere, first cells (approximate time when arose), evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Cambrian, Precambrian, important events on geological time scale (such as first birds and mammals, extinction of the dinosaurs), Cenozoic: quaternary, tertiary, Mesozoic: cretaceous, jurassic, triassic, Paleozoic: permian, carboniferous, devonian, sulurian, ordovician, Cambrian, Precambrian, continental drift, plate tectonics, pangaea, laurasia, gondwana, landbridge, mass extinction, homology, analogy, convergent evolution, taxonomy, Linnaeus, taxonomic levels (kingdom, phylum, class, etc.), taxon (taxa), DNA comparison, schools of taxonomy, phenetics, cladistics, serial endosymbiosis model Handout & Ch. 30 Plants major characteristics of plants (ie. sessile, autotrophs, etc), cuticle, stomata, vascular vs. nonvascular, gymnosperms, angiosperms, parts of a flower, monocot, dicot, anther, filament, stamen, carpel, pollen, ovule, ovary, stigma, style, petal, sepal, dendrochronology, Division Bryophyta, xylem, phloem, plant diversity is a nonrenewable resource Handouts, Ch. 32 & 33 Animals general characteristics of animals (ie. motile, heterotrophs, etc), vertebrate, invertebrate, 9 major Phyla and their major characteristics and types of organisms in each, : (Porifera, Cnidaria (Coelenterata), Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Annelida, Mollusca, Arthropoda, Echinodermata, Chordata), chitin, exoskeleton, molting, class Crustacea, class Insecta, class, Arachnida, radial symmetry, bilateral symmetry, asymmetrical, acoelomate, pseudocoelomate, coelom, complete digestive system, incomplete digestive system, sessile, cephalization, water vascular system, invertebrates that fly?, largest number of animal species in what phylum and what class? entomology, complete vs. incomplete metamorphosis, protostome, deuterostome Ch. 34 Vertebrates 4 characteristics of phylum Chordata, class Osteichthyes, class Chondrichthyes, class Amphibia, class Reptilia, class Aves, class Mammalia, hemipenis, cloaca, Archaeopteryx, marsupials, placentals, cetaceans, primates, swim bladder, ungulates Ch. 52 Ecology---Biomes handout, films and slides ecology, abiotic, biotic, population, species, community, ecosystem, biosphere, niche, habitat, biome, dominance (dominants), tundra biome, coniferous forest biome, deciduous forest biome, environmental grain (fine-grained and coarse-grained), grassland biome, desert biome, tropical rain forest biome, chaparral, basic characteristics of biomes; such as temperature, examples of vegetation found there, examples of animals and adaptations also permafrost, arboreal, 2 parts of our desert, causes of deserts, desertification, vertical stratification--layers of vegetation in tropical rain forest, tropical dry forest estuary, regulators vs. conformers Sample Essays 1. Draw and label the parts of a flower. 2. Write a paragraph explaining three evolutionary trends found in the phyla of the kingdom Animalia. (vertebrates or invertebrates) 3. List the general characteristics that distinguish plants from animals: (list general characteristics of animals vs. general characteristics of plants--like in 2 columns) 4. Discuss the six major biomes. What are the characteristics of each, what are examples of 3 species of plants and 3 species of animals found at each one, what are 2 special adaptations found at each area? 5. Explain the difference between mass extinctions of the past and current extinctions. 6. Draw one biome and write a paragraph explaining it. 7. Explain the threats to plant diversity. (end of Ch. 30, p. 645) !enod tsomla er'ew