Dramatic Conventions
advertisement

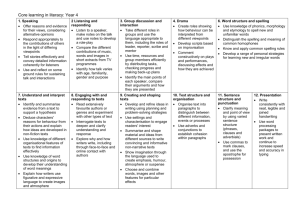
Literacy Unit Summary Plan Name: Class: Year Group: Five / Six Narrative Unit 6 Dramatic Conventions Term: Week Beginning: Outcome: Objectives Children write their own scripts and perform or record them. In order that children make effective progress in core skills across the year, it is important that these Strands are planned for in every unit: Strand 5 – Word Recognition: decoding (reading) and encoding (spelling) at KS1 Strand 6 – Word Structure and Spelling at KS2. Strand 11 – Sentence Structure and Punctuation at both key stages. Overview Demonstrate and illustrate the use of prepared scripts as the basis for a wide range of features on television, radio and other media. Consider these broadcasts, establishing and comparing purpose. Children listen to or watch and analyse broadcast information to identify techniques and styles. Demonstrate the application of playwriting skills (developed in previous years) to the writing of other forms of script. Children write own scripts and perform/record them. These are in addition to the Objectives listed below. 1. Speaking Y5: Present a spoken argument, sequencing points logically, defending views with evidence and making use of persuasive language Y6: Participate in whole-calss debate using the conventions and language of debate, including stadnrad English 2. Listening and responding Y5: Identify some aspects of talk that vary between formal and informal occasions Y6: Listen for langauge variation in formal and informal contexts. 3. Group discussion and interaction Prior Learning Check that children can already recognise that: Plays are divided into sections called scenes. The setting is often briefly described at the beginning of a scene. Every speech by a character starts on a new line. Each speech starts with the character's name. Speeches are not punctuated with speech marks. Stage directions are used to show actions or how characters are to speak. Stage directions may be written in brackets or italics. Characters arriving and leaving are described as entrances and exits. Y5: Plan and manage a group task over time using different levels of planning Y6: Consider examples of conflict and resolution, exploring the language used. Y5: Understand different ways to take the lead and support others in groups Y6: Understand and use a variety of ways to criticise constructively and respond to criticism. 4. Drama Y5: Perform a scripted scene making use of dramatic conventions Y6: Devise a performance considering how to adpat the performance for a specific audience. Y5: Use and recognise the impact of theatrical effects in drama Y6: Consider the overall impact of a live or recorded performance, identifying dramatic ways of conveying characters’ ideas and building tension. 6. Word structure and spelling Y5: Spell words containing unstressed vowels Y5: Know and use less common prefixes and suffixes such as im-, ir-, -cian Y5: Group and classify words according to their spelling patterns and their meanings 7. Understanding and interpreting texts Y5: Compare different types of narrative and information texts and identify how they are structured Y6: Understand how writers use different structures to create coherence and impact. Y5: Explore how writers use language for comic and dramatic effects Y6: Recognise rhetorical devices used to argue, persuade, mislead and sway the reader. 8. Engaging with and responding to texts Y5: Compare how a common theme is presented in poetry, prose and other media Y6: Compare how writers from different times and places present experiences and use language. 9. Creating and shaping texts Y5: Reflect independently and critically on their own writing and edit and improve it Y6: Set their own challenges to extend achievement and experience in writing. Y5: Adapt non-narrative forms and styles to write fiction or factual texts, including poems Y6: In non-narrative, establish, balance and maintain viewpoints. 10. Text structure and organisation Y5: Experiment with the order of sections and paragraphs to achieve different effects Y6: Use varied structures to shape and organise text coherently. 11. Sentence structure and punctuation Y5: Adapt sentence construction to different text-types, purposes and readers Y6: Express subtle distinctions of meaning, including hypoethesis, speculation and supposition, by constructing sentences in varied ways. Y5: Punctuate sentences accurately, including using speech marks and apostrophes Y6: Use puctuation to clarify meaning in complex sentences. 12. Presentation Y5: Use a range of ICT programs to present texts, making informed choices about which electronic tools to use for different purposes Y6: Select froom a wide range of ICT programs to present text effectively and communicate information and ideas. Phase 1 – approx 3 days Phase 1 Learning outcomes Resources The teacher illustrates the use of prepared scripts as the basis for a wide range of features on TV, radio and other media. Children consider these, establishing and comparing purpose. The following resources are to support the learning and teaching of Literacy Range of examples from radio or TV of non-fiction material presented from prepared scripts Phase 2 – approx 3 days Phase 2 and 3 Learning outcomes Children listen to or watch and analyse broadcast information to identify techniques and styles. Phase 3 and 4 – (Phase 3 - approx 3 days and Phase 4 approx 6 days) Phase 4 Learning outcomes Writing flier 4 - Writing playscripts, Ref: 0532/2001 Word 434KB The teacher demonstrates the application of playwriting skills (developed in previous years) to the writing of other forms of script. Children write their own scripts and perform or record them. Recall the basic features of playscripts (teacher observation). Analyse a range of broadcast material (feedback from other children, teacher observation). Write a script; use scriptwriting techniques to guide performers on how the script is to be presented (marking and feedback against agreed success criteria). Take part in a performance or recording of a script, performing confidently and accurately (teacher observation, self-evaluation).