Clinical Signs of Avian Influenza
advertisement

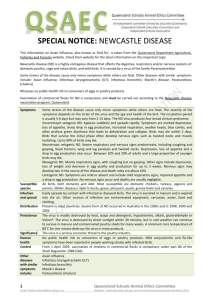
Bird Flu – Suppress the silent Killer of Poultry Economy What is Avian Influenza or Bird Flu? Avian Influenza (AI) or bird flu is an ‘infectious viral disease’ that can affect the birds. This disease can be well very prevented with the complete and suitable scientific approach. Here are some practical tips to prevent the disease. What is H5N1? There are different types of influenza viruses A, B & C but only type A viruses have been so far isolated from avian species. The strains of subtypes are determined by antigens H for Hemagglutin the substance that enables AI virus to bind and infect a specific type of cell; and N for Neuraminidase is another surface substance to that allows new copies of virus to escape infected cells and migrate to uninfected cells. There are 12 H subtypes and 9 N subtypes, and each virus has one of each subtype in any combination. Within this type, only a few strains containing H5 or H7 will cause the Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HAPI) called BIRD FLU Among them H5N1 and H5N7 are the most pathogenic strains. Recently H5N1 strain has been reported in West Bengal. Can AI virus target other species than poultry? No. However, all birds can be infected by AIV but wild birds especially wild ducks live near or around the long stored standing stagnant water areas like ponds, small lakes and temporary rain stored areas are more susceptible to the ‘Bird flu’. They spread the virus to the domestic birds. What are the general symptoms of Avian Influenza in poultry farming birds? Severe drop in egg production Swelling of the head, comb, wattles, eyelids and legs Cyanosis (blueness due to lack of oxygen) of the combs, wattles, and shanks edema of the head Respiratory disease, sneezing, coughs, nasal discharge Neurological signs, watery eyes Soft shelled and misshapen eggs In acute cases involving sudden death, clinical signs may not be seen. Wild birds’ carry the AI virus generally won’t show any signs of illness and are considered the major reservoir for AIV infections in domestic poultry. What could be the Mortality % in the flock? Mortality occurs in a flock as early as 24 hours after the first signs of disease, and frequently with in 48 hours, or can be delayed for as long as a week. Mortality rates starts from 10% and go up to 100% which, is possible and have been reported too. How AI Transmits? All avian (bird) species are susceptible to infection by AIV. However, most AIV are isolated from wild water fowls especially wild ducks.Mostly wild birds especially ducks and rarely Vectors (flies and insects) carry the AI virus They generally won’t show any signs of AI illness and are considered the major sources for AIV infections in domestic poultry. In live bird markets co-mingling of birds from different sources, and their fecal material are the important sources of AI virus ‘carried to the poultry farms. Can AI be spread to farm to farm through air? Airborne transmission of virus from farm to farm probably does not occur under normal circumstances. The spread of avian influenza between poultry premises is almost always by mechanical transmission of the movement of contaminated people and equipments. Wild birds often introduce AIV into domestic flocks through fecal contamination. The feces of infected birds are the most important source of avian influenza virus (AIV). Contact with infected fecal material is the most important mode of bird-to-bird transmission. Within a poultry house, transfer of the virus between birds can also occur via airborne secretions. AIV can also be found on the outer surfaces and inside of shell eggs. What is the favorable environment for the survival of AI virus? The virus can survive in the manure for up to 105 days, especially in high moisture and low temperature conditions. What are the recommendations to prevent the spread of AI virus? The following practical recommendations can prevent the spread of avian influenza between poultry premises. We have outlined these recommendations based on the three key principles. Stage 1: Disinfection Stage2 : Isolation Stage3: sanitation. STAGE 1 DISINFECTION MEASURES ON FARMS : FARM PROTECTION Simple Disinfection (Bio-security) model Practice "all in-all out" management of birds, with cleaning between restocking. Maintain and isolate equipment on the farm, do not share materials or vehicles Restrict traffic to essential movements in the poultry farm. Allow the personnel with a shower and a change of clothes only entering premises. Make sure that outsider’s vehicles including service persons’ and visitors including regular business people are strictly dealt outside the poultry farm. Anything that enters your premises should be properly and thoroughly disinfected with broad spectrum disinfectants. Wash and disinfect all egg trays, carts, and racks. Remove all feathers, feces, and eggs material. AIV can be transmitted at egg breaking facilities and processing plants. Equipments must be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected at these facilities STAGE 2 : ISOLATION : AVOIDING RISK FACTORS Mechanical transmission of AIV by anything that can walk, crawl, or fly from farm to farm should be strictly prevented by rising the fence height and proper vigilance. Clean out vegetation in and around poultry houses that can be shelter for possible carriers’ especially wild birds. Prevent and remove accumulation of long standing stagnant water. This is a great attraction to migrating waterfowl or wild birds. Implement a vector control program for insect, mammalian, and avian vectors. These vectors are important because they can mechanically carry infected feces from one house, pen, or premise to another. Rodent control and preventing their traffic between houses on a single premise are essential. Educate your employees about the dangers of wild and water fowls and advise them to avoid visiting live bird markets or other poultry premises. If it happens to be entered the premises after a bath or proper bio- secured measures. Advise your employees to avoid handling dead, wild and free-flying birds they find. Any such birds found in and around the premises must be treated cautiously. Handle them with gloves, place in a plastic bag, and seal it and should be disposed in the deep pit. Finally, a complete change of fresh clothes and shoes that are properly disinfected and a shower should happen before entering poultry premises. STAGE 3: SANITATION: PROTECTION WITH IN Removing organic material The first and foremost action is removing the organic material from the poultry house. Organic material can make the disinfectant ineffective and greatly increases the resistance of avian influenza viruses to disinfection. Hence, organic material must be removed before disinfection by any method which is effective. Cleaning protocols should include critical inspection. All the manures should be sprayed with broad spectrum disinfectants twice daily and should be removed at least once in a week completely. Scrape the sides and corners of the buildings to remove all residual organic material that might harbor virus or can be disinfected with fire guns. Practical tips for the better sanitation Spraying an anti viral disinfectant across the poultry house is a practical and effective method. Apply the disinfectant to all surfaces twice, allow the disinfectant to dry between applications. Avoid open sun drying of feed raw material as they can attract wild and freeflying birds. Droppings of the wild birds’ flying over the poultry house should be cleaned with broad spectrum disinfectant when they happen in the farm premises and water tank should be sanitized. At the same time a vector control program should be instituted, followed by removal of manure, cleaning of all surfaces followed by a second application of anti-viral spray. All dead birds to be disposed properly in the tightly closed plastic bags and into the deep pit. Disinfectants that can be used to protect the farm from AI virus Glutaraldehyde combinations Acid combinations Formaldehyde Iodine containing solutions Any reputed broad spectrum disinfectants can be used in the rotation method. What is rotation program? Any chemicals will have residual activity of particular period. On the continuous usage the micro pathogens will develop resistance to the particular medicines or chemicals by understanding their mechanism of action. This is called drug resistance. To avoid this we have to rotate the medicines periodically or at different sites of action. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT BIRD FLU Can we have chicken meat? Any one can have chicken meat freely without any psychological barrier. However, better to have cooked meat heated up to 100ºF at least for 30 min. Our, Indian cooking system is quite efficient to kill the AI virus. Who are vulnerable for AI virus? People live near the water as water fowls and wild birds are the potential carriers of AI virus and also the personnel who are working in the poultry farm or in close contact with the birds. If we take precautionary measures as mentioned above very well we can avoid AI infection and the disease spread. How and when AI occur? As we have discussed the incubation period is more 105 days for AI virus and the favorable environment for AI in India is onset of winter and early summer.To control the AI occurrence thrush should be given on the effective Bio-security programs through at the year in the farm houses. However, from the beginning of October month onwards our bio-security with vigilance program should be on the high alert. If so India can be free from the AI mania. What should I do if we find dead birds or huge mortality in a flock? Our advice is to avoid handling dead, wild and free-flying birds they find. Any such birds found in and around the premises must be treated cautiously. Handle them with gloves, place in a plastic bag, and seal it and should be disposed in the deep pit. Immediately should contact nearby veterinary centers and veterinarians and proper care Can I vaccinate my flocks for AI? Since vaccines strains specific and are not cross-protective for the 15 virus subtypes that can infect poultry. Its’ difficult to predict the strains as highly pathogenic sub types arise by mutation through re-assortment and recombination. Since there is no way to predict which type will infect a flock, vaccines can be used as a part of complex AI prevention program. What should I do if I suspect avian influenza in my birds? You should contact your veterinarian if you observe any of the signs of AI, especially if they are accompanied by a drop in feed consumption and/or a significant drop in egg production. Because the signs of AI are so variable, it is important to get the help of an expert for diagnosis. And the action should be taken under veterinarian’s supervision.