Supplementary Figure Legends (doc 28K)
advertisement

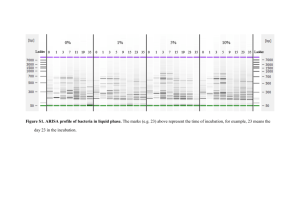
1 1 2 Figure S1 Exemplary bacterial automated intergenic spacer analysis (ARISA) profiles 3 obtained for gut walls of common earthworms and soils sampled from a wheat-barley field 4 (Johnstown Castle). ARISA profiles were obtained using DNA extracted from gut walls of 5 Aporrectodea longa (A), A. caliginosa (B), Lumbricus terrestris (C) and soil (0-20 cm depth) 6 collected from the earthworm sampling spots (D). All samples originated from the same 7 wheat-barley field. ARISA was conducted using the bacterial primer set 6-FAM tagged 8 ITSF/ITSReub (Cardinale et al., 2004) and products were analysed by capillary 9 electrophoresis with fluorescent laser detection. 10 11 Figure S2 Exemplary bacterial automated intergenic spacer analysis (ARISA) profiles 12 obtained for gut walls of common earthworms and soils sampled from a grass-clover field 13 (Johnstown Castle). ARISA profiles were obtained using DNA extracted from gut walls of 14 Aporrectodea longa (A), A. caliginosa (B), Lumbricus friendi (C) and soil (0-20 cm depth) 15 collected from the earthworm sampling spots (D). ARISA was conducted using the bacterial 16 primer set 6-FAM tagged ITSF/ITSReub (Cardinale et al., 2004) and products were analysed 17 by capillary electrophoresis with fluorescent laser detection. 18 19 Figure S3 Non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel (4% w v-1) electrophoresis profiles of partial 20 16S and 23S rRNA genes and intergenic spacer region defined bacterial community tightly 21 associated with gut walls of different earthworm species and soils collected from a wheat- 22 barley field (lanes: 1 to 5) and a grass-clover field (Lanes: 6 to 10) (Johnstown Castle Estate). 23 Lanes: 1, 2, Lumbricus terrestris; 3, 9, A. caliginosa; 4,10, A. longa; 5,6, soils (0-20 cm 24 depth); 7,8, L. friendi; L, 100 bp DNA marker (Invitrogen); B, blank PCR with loading dye. 2 25 The RISA bands marked by arrow pointers were excised for cloning and sequencing (See SI 26 Text).