48KB - NZQA
advertisement
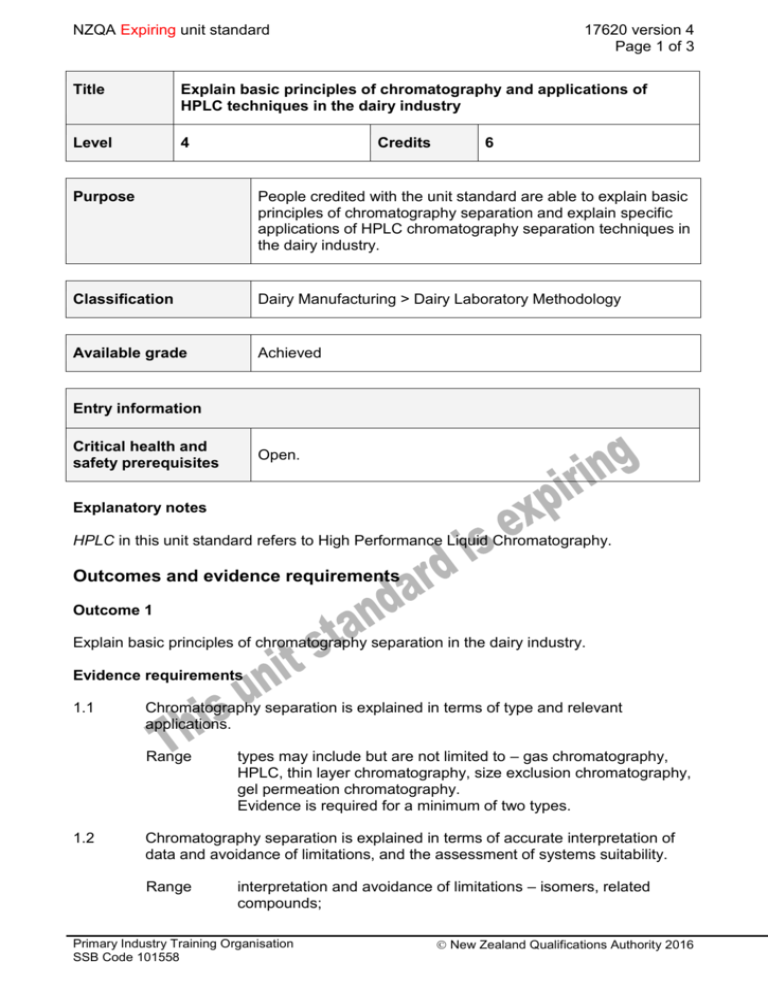
NZQA Expiring unit standard 17620 version 4 Page 1 of 3 Title Explain basic principles of chromatography and applications of HPLC techniques in the dairy industry Level 4 Credits 6 Purpose People credited with the unit standard are able to explain basic principles of chromatography separation and explain specific applications of HPLC chromatography separation techniques in the dairy industry. Classification Dairy Manufacturing > Dairy Laboratory Methodology Available grade Achieved Entry information Critical health and safety prerequisites Open. Explanatory notes HPLC in this unit standard refers to High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Outcomes and evidence requirements Outcome 1 Explain basic principles of chromatography separation in the dairy industry. Evidence requirements 1.1 Chromatography separation is explained in terms of type and relevant applications. Range 1.2 types may include but are not limited to – gas chromatography, HPLC, thin layer chromatography, size exclusion chromatography, gel permeation chromatography. Evidence is required for a minimum of two types. Chromatography separation is explained in terms of accurate interpretation of data and avoidance of limitations, and the assessment of systems suitability. Range interpretation and avoidance of limitations – isomers, related compounds; Primary Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 101558 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA Expiring unit standard 17620 version 4 Page 2 of 3 systems suitability – height equivalent theoretical plate count, resolution, plate symmetry. 1.3 Chromatography equipment components are explained in terms of essential and practical requirements for accurate analysis. Range 1.4 essential requirements – polarity, flow rate, pressure; practical requirements – waste processing, elution, gradient elution, ambient versus elevated oven temperature. Methods used for signal measurement are identified and explained in terms of limiting factors in the conversion of signals to quantifiable results. Range methods of signal measurement – ultraviolet/visible, flame ionisation, spectro flurometric, electron capture; limiting factors – symmetry, superposition, retention times, resolution. 1.5 The use of internal standards is explained in terms of purpose and interpretation of variance. 1.6 Column structure is explained in terms of separation and causes and remedies of common problems. Range separation – mechanism, reverse phase, normal phase; common problems – back pressure, variable pressure, dead volumes, column wear. Outcome 2 Explain specific applications of HPLC chromatography separation techniques in the dairy industry. Evidence requirements 2.1 HPLC applications are explained in terms of fit with, and result variations from, traditional methods. Range applications may include but are not limited to – vitamin analysis, lactose analysis. 2.2 HPLC separation is explained in terms of the need to clean up milk component matrices. 2.3 HPLC separation and analysis is explained in terms of commonalties and differences in procedure and detection for fat soluble versus water soluble vitamins. 2.4 HPLC separation and analysis of lactose is explained in terms of identification and correction of profile variations between product batches. Primary Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 101558 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA Expiring unit standard 17620 version 4 Page 3 of 3 This unit standard is expiring. Assessment against the standard must take place by the last date for assessment set out below. Status information and last date for assessment for superseded versions Process Version Date Last Date for Assessment Registration 1 25 November 2000 31 December 2017 Revision 2 13 June 2003 31 December 2017 Rollover 3 26 January 2007 31 December 2017 Review 4 15 October 2015 31 December 2017 Consent and Moderation Requirements (CMR) reference 0022 This CMR can be accessed at http://www.nzqa.govt.nz/framework/search/index.do. Please note Providers must be granted consent to assess against standards (accredited) by NZQA, before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be granted consent to assess against standards by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Providers and Industry Training Organisations, which have been granted consent and which are assessing against unit standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those standards. Requirements for consent to assess and an outline of the moderation system that applies to this standard are outlined in the Consent and Moderation Requirements (CMR). The CMR also includes useful information about special requirements for organisations wishing to develop education and training programmes, such as minimum qualifications for tutors and assessors, and special resource requirements. Primary Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 101558 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016