Ray Optics numericals
advertisement
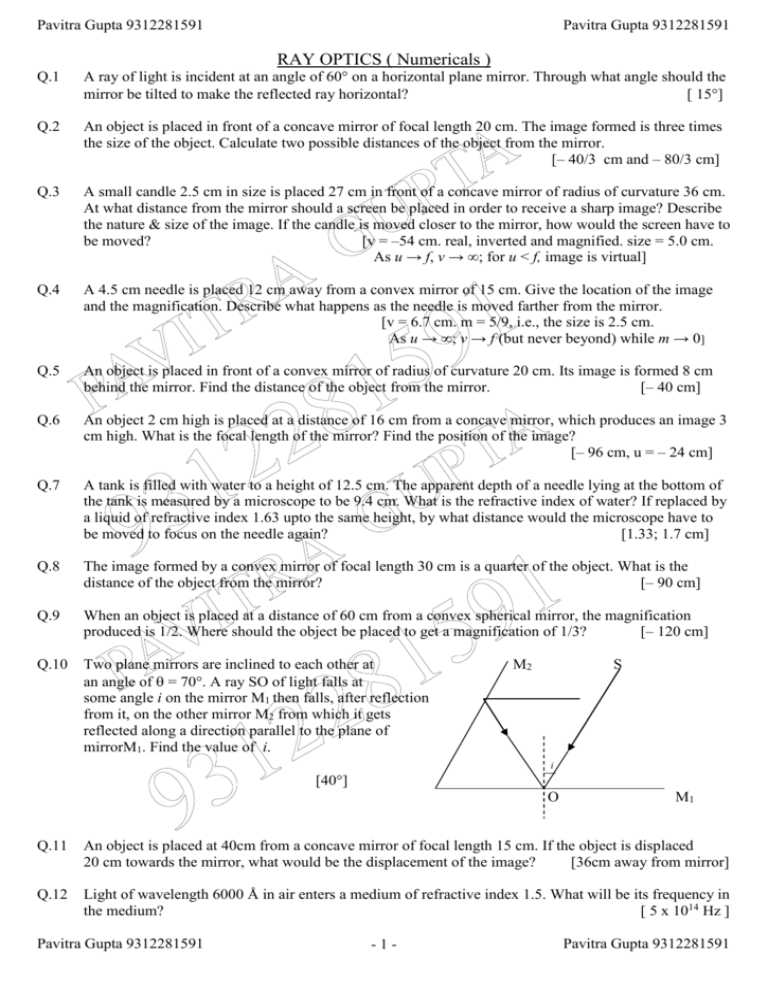
Pavitra Gupta 9312281591 Pavitra Gupta 9312281591 RAY OPTICS ( Numericals ) Q.1 A ray of light is incident at an angle of 60° on a horizontal plane mirror. Through what angle should the mirror be tilted to make the reflected ray horizontal? [ 15] Q.2 An object is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm. The image formed is three times the size of the object. Calculate two possible distances of the object from the mirror. [– 40/3 cm and – 80/3 cm] Q.3 A small candle 2.5 cm in size is placed 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to receive a sharp image? Describe the nature & size of the image. If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, how would the screen have to be moved? [v = –54 cm. real, inverted and magnified. size = 5.0 cm. As u → f, v → ∞; for u < f, image is virtual] Q.4 A 4.5 cm needle is placed 12 cm away from a convex mirror of 15 cm. Give the location of the image and the magnification. Describe what happens as the needle is moved farther from the mirror. [v = 6.7 cm. m = 5/9, i.e., the size is 2.5 cm. As u → ∞; v → f (but never beyond) while m → 0] Q.5 An object is placed in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm. Its image is formed 8 cm behind the mirror. Find the distance of the object from the mirror. [– 40 cm] Q.6 An object 2 cm high is placed at a distance of 16 cm from a concave mirror, which produces an image 3 cm high. What is the focal length of the mirror? Find the position of the image? [– 96 cm, u = – 24 cm] Q.7 A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope to be 9.4 cm. What is the refractive index of water? If replaced by a liquid of refractive index 1.63 upto the same height, by what distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again? [1.33; 1.7 cm] Q.8 The image formed by a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm is a quarter of the object. What is the distance of the object from the mirror? [– 90 cm] Q.9 When an object is placed at a distance of 60 cm from a convex spherical mirror, the magnification produced is 1/2. Where should the object be placed to get a magnification of 1/3? [– 120 cm] Q.10 Two plane mirrors are inclined to each other at an angle of = 70. A ray SO of light falls at some angle i on the mirror M1 then falls, after reflection from it, on the other mirror M2 from which it gets reflected along a direction parallel to the plane of mirrorM1. Find the value of i. M2 S i [40] O M1 Q.11 An object is placed at 40cm from a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. If the object is displaced 20 cm towards the mirror, what would be the displacement of the image? [36cm away from mirror] Q.12 Light of wavelength 6000 Å in air enters a medium of refractive index 1.5. What will be its frequency in the medium? [ 5 x 1014 Hz ] Pavitra Gupta 9312281591 -1- Pavitra Gupta 9312281591 Pavitra Gupta 9312281591 Pavitra Gupta 9312281591 Q.13 What is the ratio of velocities of light rays of wavelengths 4000 Å & 8000 Å in vacuum? Q.14 Monochromatic light of wavelength 600 nm, travelling in air, is incident on a glass surface. What are the wavelength, frequency and speed of refracted light, if refractive index of glass is 1.5? [ 400 nm, 5 x 1014 Hz, 2 x 108 m/s ] Q.15 A biconvex lens with both faces of same radius of curvature is to be made from a glass of refractive index 1.55. What should be the radius of curvature for focal length to be 20 cm? [20 cm ] Q.16 Calculate the refractive index of an equilateral prism for which minimum deviation is 60. Q.17 An astronomical telescope has two thin lenses 36 cm apart and has magnifying power 8 under normal adjustment. Find the focal length of lenses. [ f0 = 32 cm, fe = 4 cm ] Q.18 a glass prism of refracting angle 60 and refractive index 1.5 is completely immersed in water of refractive index 1.33. Find the angle of minimum deviation [ sin-10.56 = 34.3]. [8.6] Q.19 A glass has refractive index of 1.5. A convex lens made of this glass has a focal length of 20 cm in air. It is immersed in water of refractive index 1.33. Find the focal length of lens in water. [ 80 cm ] Q.20 A ray of light passes through an equilateral glass prism, such that angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence. If angle of emergence is ¾ times the angle of prism, find the refractive index. [ 2] Q.21 Calculate the speed of light in a medium whose critical angle is 45. Q.22 What is the focal length and power of a combination of a convex lens of focal length 30 cm in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm? Is the system a converging or a diverging lens? Ignore thickness of the lenses. [ a diverging lens of focal length 60 cm ] Q.23 A ray is to deviate through 90 by a right angled isosceles triangular prism. What should be the minimum refractive index of the prism? [ 2 ] Q.24 The radius of curvature of each face of a biconcave lens of refractive index 1.5 is 30 cm. Find the focal length of lens in air. [ 30 cm ] Q.25 The image obtained with a convex lens is erect and its length is 4 times the length of the object. If focal length of the lens is 20 cm, find positions of object and image. Q.26 A biconvex lens of refractive index 1.5 has both radii of curvatures 20 cm. An object 2 cm high is at 10 cm from the lens. Find the position, nature and size of the image. Q.27 An object is placed at 15 cm from a compound lens of two lenses having powers +12.5 D and –2.5 D. Find the position and nature of image. Q.28 Velocity of light in a liquid is 1.5 x 108 m/s and in air is 3 x 108 m/s. Find the critical angle for the liquid. [ 30 ] Q.29 A converging lens has both radii of curvature 24 cm and refractive index 1.6. (i) Find its focal length (ii) if the lens is split vertically into two identical parts, what is the focal length of each part? [20cm, 40cm] Pavitra Gupta 9312281591 -2- [ 3 ] [2.1 x 108 m/s] Pavitra Gupta 9312281591 Pavitra Gupta 9312281591 Pavitra Gupta 9312281591 Q.30 A bubble inside a glass slab appears to be at a depth of 3 cm from one face and 2 cm from opposite face. If refractive index of glass is 1.5, what is the actual thickness of slab? Q.31 A compound microscope has a magnification of 30. The focal length of eye – piece is 5 cm. Assuming final image to be at least distance of distinct vision, find the magnification produced by the objective. [5] Q.32 A beam of light converges at a point P. Now a lens is placed in the path of the convergent beam 12 cm from P. At what point does the beam converge if the lens is (a) a convex lens of focal length 20 cm, and (b) a concave lens of focal length 16cm? [ 7.5 cm, 48 cm ] Q.33 At what angle should a ray of light be incident on the face of a prism of refracting angle 60° so that it just suffers total internal reflection at the other face? The refractive index of the material of the prism is 1.524. [ 30 ] Q.34 A person with a normal near point (25cm) using a compound microscope with objective of focal length 8.0 mm and an eyepiece of focal length 2.5cm can bring an object placed at 9.0mm from the objective in sharp focus. What is the separation between the two lenses? Calculate the magnifying power of the microscope? [ 9.47, 88 ] Q.35 A small bulb is placed at the bottom of a tank containing water to a depth of 80cm.What is the area of the surface of water through which light from the bulb can emerge out? Refractive index of water is 1.33. (Consider the bulb to be a point source.) [ 2.6 m2 ] Pavitra Gupta 9312281591 -3- Pavitra Gupta 9312281591