Supplementary Material (doc 40K)
advertisement

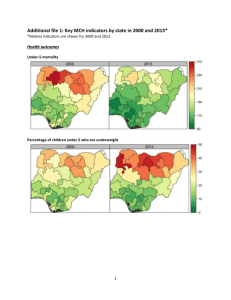
Kutzler et al. MI-14-355 1 Supplemental Fig. 1: Genetic diversity of constructs and immunization schedule. (a) 2 Schematic of the immunization and challenge regiments. RhMs were immunized on weeks 0, 6, 3 12, 18 and 48. After a 26 week rest, RhMs were challenged with multiple low dose SIVsmE660 4 swarm. (b) Genetic tree of SIV sooty mangabey Envelopes. The consensus envelope was made 5 using multiple different SIVsm envelopes. The open blue triangles show sequences from the 6 SIVsmE660 swarm stock used in the experiment. The red square represents the consensus 7 envelope used for immunization. 8 Supplemental Fig. 2: Cytokine production from CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after 4th 9 immunization. Intracellular cytokine staining was performed on PBMCs isolated at week 21 and 10 stimulated with peptides from Gag and Pol and totaled for CD4 (circles) and CD8 (triangles). 11 Bars indicate median. 12 Supplemental Fig. 3: Peripheral cellular responses do not correlate to challenge outcome or 13 peak viral loads. The percent of CD4+ (left) and CD8+ (right) T cells which secreted cytokines 14 after stimulated with Gag and Pol peptides was determined two weeks after 4th immunization (a) 15 and two weeks after final immunization (b) and plotted against peak viral load. There is not a 16 strong correlation between cellular responses, peak viral loads or challenge outcomes. 17 Supplemental Table 1: Genotype analysis of RhMs and challenge outcome. Genotype 18 analysis was performed on each RhM to insure it did not affect challenge outcome. RhMs were 19 grouped based on challenge outcome for all groups including naïve RhMs. Two RhMs in the 20 naïve group did not have TRIM5α analysis performed on them and have been not been included 21 in the table. 1