4.12 - WMO
advertisement

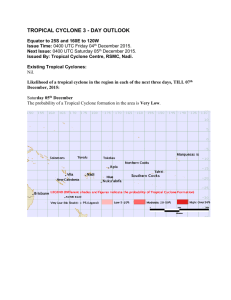
WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION _________________________ TCM-VI/Doc. 4.12 (12.X.2009) ___________ SIXTH TROPICAL CYCLONE RSMCs/TCWCs TECHNICAL COORDINATION MEETING ITEM 4.12 BRISBANE, AUSTRALIA 2 TO 5 NOVEMBER 2009 ENGLISH ONLY Review of terminology/classification of tropical cyclones (Submitted by the Secretariat) Summary and Purpose of Document This document provides the list of standardized terminology/classification of tropical cyclones adopted during previous coordination meetings to bring about better international coordination and understanding. ACTION PROPOSED The meeting is invited to review the list of terminologies and classifications for possible revision, if needed, and proposals, if any, for addition to the list. __________________ LIST OF STANDARDIZED TERMINOLOGY CENTRAL PRESSURE OF A TROPICAL CYCLONE – Surface pressure at the centre of the tropical cyclone as measured or estimated. CENTRE FIX OF THE TROPICAL CYCLONE – The estimated location of the centre of a tropical cyclone. CENTRE OF THE TROPICAL CYCLONE – The centre of the cloud eye or, if not discernible, the wind/pressure centre. CONFIDENCE IN THE CENTRE POSITION – Degree of confidence in the centre position of a tropical cyclone expressed as the radius of the smallest circle within which the centre may be located by the analysis. “Position good” – implies a radius of less than 30 nautical miles (55 kilometers) “Position fair” – implies a radius of 30 to 60 nautical miles (55 to 110 km) and “Position poor” – implies a radius of greater than 60 nautical miles (110 km). DIRECTION OF MOVEMENT OF THE TROPICAL CYCLONE – The direction towards which the centre of the tropical cyclone is moving. EXTRA-TROPICAL CYCLONE – Low –pressure system which develops in latitudes outside the tropics. EXTRATROPICAL TRANSITION – is an evolutionary process by which a symmetric warm-core tropical cyclone transforms to an asymmetric cold core extratropical cyclone. This process includes a change in the distribution of clouds, winds, and precipitation. Also, the primary energy source changes from latent heat release in deep convective clouds of the tropical cyclone to baroclinic conversion of available potential energy in the extratropical cyclone. EYE OF THE TROPICAL CYCLONE – The relatively clear and calm area inside the circular wall of convective clouds, the geometric centre of which is the centre of the tropical cyclone. GALE FORCE WIND – maximum sustained surface wind speed of 34 to 47 knots HURRICANE/TYPHOON FORCE WIND – maximum sustained surface wind speed of 64 knots or more. LOW PRESSURE AREA – Region of the atmosphere in which the pressures are lower than those of the surrounding region at the same level. *MAXIMUM SUSTAINED WIND SPEED – depending upon the regional practices. Averaging period of one, three or ten minutes RECONNAISSANCE AIRCRAFT CENTRE FIX OF THE TROPICAL CYCLONE, VORTEX FIX – The location of the centre of a tropical cyclone obtained by reconnaissance aircraft penetration. SPEED OF MOVEMENT OF THE TROPICAL CYCLONE – Speed of movement of the centre of the tropical cyclone. STORM FORCE WIND – maximum sustained surface wind speed of 48 to 63 knots STORM SURGE – The difference between the actual water level under influence of a meteorological disturbance (storm tide) and the level which would have been attained in the absence of the meteorological disturbance (i.e. astronomical tide). STORM TIDE – The actual sea level as influenced by a weather disturbance. The storm tide consists of the normal astronomical tide and the storm surge. SUB-TROPICAL CYCLONE – A low pressure system, developing over sub-tropical waters which initially contains few tropical characteristics. With time the sub-tropical cyclone can become tropical. TROPICAL CYCLONE – Generic term for a warm-core non-frontal synoptic scale cyclone originating over tropical or sub-tropical waters with organized deep convection and closed cyclonic surface wind circulation. The term is also used for a storm in the South-West Indian Ocean in which the maximum sustained wind speed is estimated to be in the range of 64 to 90 knots and in the South Pacific and South-East Indian Ocean with the maximum sustained surface wind speed greater than 33 knots. TROPICAL DEPRESSION WIND – maximum sustained surface wind speed less than 34 knots TROPICAL DISTURBANCE – A non-frontal synoptic scale cyclone originating in the tropics or sub-tropics with enhanced convection and light surface winds. TROPICAL STORM WIND – maximum sustained surface wind speed of 34 to 63 knots TROPICAL WAVE – A trough or cyclonic curvature maximum in the trade wind easterlies or equatorial westerlies. The wave may reach maximum amplitude in the lower middle troposphere, or may be the reflection of an upper-troposphere cold low or equatorial extension of a mid-latitude trough. ZONE OF DISTURBED WEATHER – A zone in which the pressure is low relative to the surrounding region and there are convective cloud masses which are not organized. WEATHER WARNING – Meteorological message issued to provide appropriate warnings of hazardous weather conditions.