14L final -revised 02-13 Geological Time
advertisement
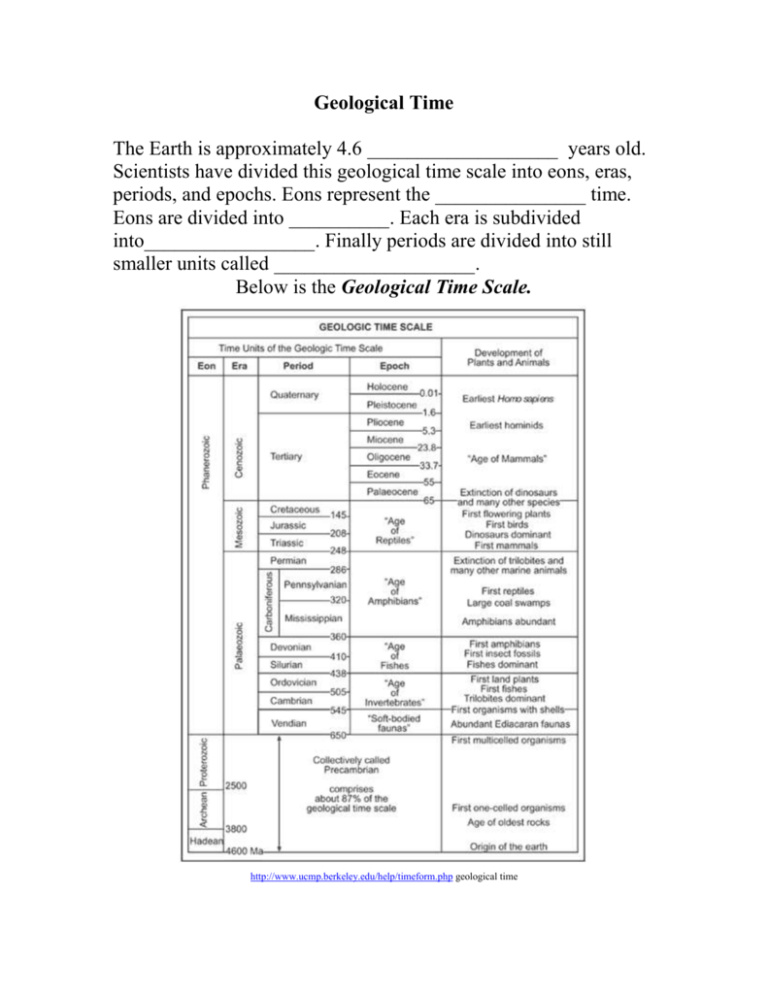
Geological Time The Earth is approximately 4.6 ___________________ years old. Scientists have divided this geological time scale into eons, eras, periods, and epochs. Eons represent the _______________ time. Eons are divided into __________. Each era is subdivided into_________________. Finally periods are divided into still smaller units called ____________________. Below is the Geological Time Scale. http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/help/timeform.php geological time The geologic time scale is a visual record of Earth’s history, with the individual units based on changes in the _______ and_______. Notice that the geological time scale before 650 million years doesn’t have epochs but has a super eon called the Precambrian which includes 3 eons. This is because Precambrian time, there were fewer _______________ forms. These life forms are more difficult to identify and the rocks have been disturbed often. (9,200,000 years equal one minute of time) Measuring the Age of Earth and the Events That Shaped It Time line of earth history of major events pictures http://exploringorigins.org/timeline.html Time line hour clock 1 hour - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H2_6cqa2cP4 How understanding the principles of rock layers help to determine the age of rocks. In geology the principal laws are: Principle of Uniformitarianism: Processes that are happening today also happened in the __________________. Principle of Superposition – The rock on the __________________ are older than the rock on the _____________. Principle of Cross-Cutting Relations: A rock is _________________________ than any rock it cuts across. In the above picture a vertical column of magma called a dike cooled into _____________ rock. The magma that cooled into igneous rock that cut across the other three layers of rock is ____________________ than the three other layers. Looking at the picture to the right arrange rock layers A, B, C, E, F, G, H, J, K in order from the oldest to the youngest. Ignore letters D and I. Rock layers from the oldest to the youngest: ________________________________________________ Rock layer D (red) going into layers A and B is _____________________ than A and B but ____________________ then _____, ______, _____and _______. Rock layer D represents a pocket of magma that traveled up from beneath layers A and B which hardened into igneous rock. Order the rock layers in order from the oldest to youngest. _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ __________________________________ Unconformity: Is a place where _____________ layers are missing. After a rock layer is formed, the area can be uplifted to the Earth’s surface (uplifting can be caused by ______________________ and plate tectonics). After, the process of __________________ and _____________ can wear the rock layer away. Rock layers often occur above the unconformity, but they are not the kind of rock that would have formed in the same way as the _______________ layer beneath the unconformity. Example: Order the rock layers in order from the oldest to youngest. _______________________________________________ Order the rock layers in order from the oldest to youngest. _______________________________________________ Two Types of Dating Relative Age Dating: Is a way to describe the age of one event compared to another object or event. Relative age dating is based on comparisons of the age of_____________. Thus, this method of dating objects always includes words such as before, after, earlier, later, older, and younger. Example using the principal of superposition: If you found an arrow head in one sedimentary layer of rock and a saber tooth tiger skull in a lower layer of rock, you can use the law of superposition to conclude that the skull is ________________ than the arrow head. Absolute Age: This describes the _______________ age of an object or event. The absolute ages of objects from long ago are found by analyzing the ____________________ in the object or the rock layers in which they were found. Radiometric Dating – This is the most accurate form of dating. This method measures the ____________ (decrease in size and/or energy) of naturally occurring ___________________ isotopes. Example: Carbon-14 Dating (The 14 is the total number of ________________ and _____________ in the nucleus of the atom). http://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/earth/ge ology/carbon-14.htm Most atoms of carbon have 6 _____________ and 6 _______________ in the nucleus of atom. A very few carbon atoms have a different number of ___________________ and are called isotopes. In conclusion, an isotope is an atom of the same element with a different amount of _________________in the___________________. Carbon-14 is an _____________ of carbon and is radioactive. Carbon-14 is produced in the upper atmosphere when the ________ element nitrogen-14 is hit by cosmic radiation from the sun forming the ___________ radioactive element carbon-14. The carbon-14 will _________ eventually back into the stable element nitrogen-14. Radioactive describes an element that gives off tiny particles and _____________from inside its atom. Only about 1 in a 1,000,000,000,000 (_____________) carbon atoms are__________________, the majority of the atoms are carbon-12. This means that it tends to give off _____________________ and energy from its nucleus. Above picture show the decay of carbon-14 to nitrogen-14. The antineutrino will destroy itself and give off energy. The carbon-14 atom changes back into an atom of nitrogen14, which is not ___________________ but stable. This change is called radioactive decay. The ________________ process compares the ratio of carbon-14 to carbon-12 in an object. All living things contain very small amounts of carbon-14. The amount of carbon-14 remains about the same as we live our lives. This amount remains steady throughout our lives as we eat and obtain carbon-14 but at the same time the carbon -14 is decaying to nitrogen-14. This carbon is recycled as we live our lives (carbon in food is released as ________________ __________________ as we burn food for___________________). When an organism dies no more carbon-14 is obtained and the carbon-14 __________________ to a the stable element nitrogen-14. As the carbon-14 decays, the ratio of carbon-14 to carbon12 in the organic object _____________ at a steady rate, because the amount of carbon-14 decreases. Scientists have figured out that it takes about 5730 ___________________ for half of the carbon-14 to change to nitrogen-14. Picture of how carbon-14 is renewed or produced on the Earth. Another important radioactive isotope is Uranium which decays into the stable element______________. This method has let scientists to determine the approximate age of the Earth as ______ _______________ years old. Below are 3 common radioactive isotopes that are used to date objects. The parent or mother isotope is the radioactive_______________ isotope and the daughter isotope is the _____________________ element that forms from decay.