EGEE102 Solutions Chap5
advertisement

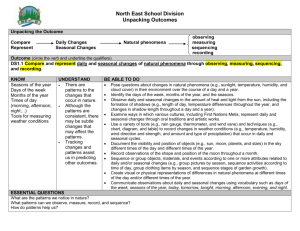
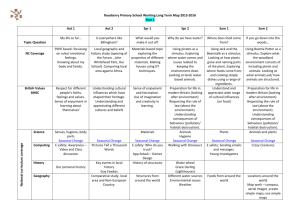
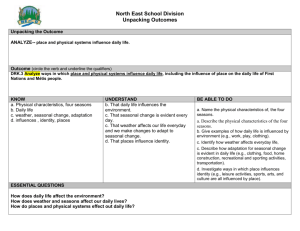
CHAPTER 5 SOLUTIONS Heating Degree-days 1. Step 1: Identify the equation to calculate heating degree days, in which HDD is heating degree days, Tbase is the base temperature or inside temperature, usually 65°F, and Ta is the average outside temperature. HDD Tbase Ta Step 2: Substitute the known variables and solve for heating degree days. HDD 65F 13F HDD = 52 Degree-days 2. Step 1: Convert the average outside temperature to degrees Fahrenheit. Recall the following equation: 5 C ( F 32) 9 2C ( F 32) 5 9 F 35.6 Step 2: Substitute the known variables and solve for heating degree days. HDD 65F 35.6F HDD = 29.4 Degree-days 3. Step 1: Calculate the heating degree days for each day of the week. Day Average Temperature Sunday 49°F Monday 47°F Tuesday 51°F Wednesday 60°F Thursday 65°F Friday 67°F Saturday 58°F HDD 16 18 14 5 0 0 7 Step 2: To calculate the HDD for the week add the HDD for each day of the week. HDDweek = 60 Degree-days 4. Step 1: Calculate the daily HDD. Then, multiply by the number days in the month of January to calculate the HDD for the month. HDD 65F 25F HDD = 40 Degree-days 40 Degree-days 31days 1,240 Degree-days 5. Step 1: Calculate the heating degree days for each month to determine the heating season. Then, multiply the number days in each month by its HDD to calculate the HDD for the month. Month January February March April May June July August September October November December Average Temperature 25°F 28°F 37°F 48°F 59°F 67°F 71°F 70°F 62°F 51°F 41°F 31°F HDD HDDmonth 40 1240 37 1036 28 868 17 510 6 186 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 90 14 434 24 720 34 1054 Step 2: Add the HDD for each month to calculate the HDD for the heating season. HDDheating season = 6,138 Degree-days 6. Step 1: Find the increase in HDD by subtracting Birmingham, AL HDD from State College, PA HDD. Then, divide the difference by the HDD for the location she is moving from and multiply by 100% to calculate the percent increase. (6,000 HDD 2,800 HDD ) 100% 114% 2,800 HDD Composite R-values 7. Step 1: Add the R-values of the materials the wall consists of to calculate the composite R-value of the wall. Composite R-value = 15.2 ft2 °F hr/BTU 8. Step 1: Add the R-values of the materials the wall consists of to calculate the composite R-value of the wall. Remember to multiply the R-value of the brick by its total thickness. Composite R-value = 2.94 ft2 °F hr/BTU 9. Step 1: Add the R-values of the materials the wall consists of to calculate the composite R-value of the wall. Remember to multiply the R-value of the fiberglass by its total thickness. Composite R-value = 19.76 ft2 °F hr/BTU 10. Step 1: Add the R-values of the materials the wall consists of to calculate the composite R-value of the wall. .94 (2in 5) (3in 3.7) 22.04 ft2 °F hr/BTU 11. Step 1: Add the R-values of the materials the wall consists of to calculate the composite R-value of the wall. (8in .08) (3in 6.25) .94 20.33 ft2 °F hr/BTU Heat Loss 12. Step 1: Recall that Area Length Height . Area 20 ft 8 ft 160 ft 2 13. Step 1: Find the wall area of the room by adding the area for each wall. Area 16 ft 8 ft 128 ft 2 2walls 256 ft 2 Area 12 ft 8 ft 96 ft 2 2walls 192 ft 2 Total Area 256 ft 2 128 ft 2 448 ft 2 14. Step 1: Find the wall area of the room by adding the area for each wall. Area 20 ft 10 ft 200 ft 2 2walls 400 ft 2 Area 12 ft 10 ft 120 ft 2 2walls 240 ft 2 Total Area 400 ft 2 240 ft 2 640 ft 2 Step 2: Find the area of openings in the room by adding the area of both windows and the door. Area window1 3 ft 4 ft 12 ft 2 Area window2 6 ft 4 ft 24 ft 2 Area door 4 ft 7 ft 28 ft 2 Total Area 12 ft 2 24 ft 2 28 ft 2 64 ft 2 Step 3: Then, subtract the area of openings from the total area to calculate the total area of the wall space. 640 ft 2 64 ft 2 576 ft 2 15. Step 1: Identify the equation to calculate heat loss. Heat Loss (BTU/h) Area (Tinside Toutside) R value Step 2: Calculate the heat loss by substituting the known variables. Heat Loss (10 ft 8 ft ) (70 F 43 F ) 22 Heat Loss = 98.18BTU/h 16. Step 1: Calculate the heat loss by substituting the known variables. Heat Loss (12 ft 9 ft ) (72 F 27 F ) 19 Heat Loss = 255.79BTU/h 17. Step 1: Calculate the heat loss per hour by substituting the known variables. (360 ft 2 ) (65 F 37 F ) Heat Loss 22 Heat Loss = 458.18BTU/h Step 2: Calculate the heat lost through the room in 12 hours. 458.18BTU 12h 5,498.18BTU h 18. Step 1: Calculate the heat loss through windows, the walls, and the roof using their respective areas and R-values. Heat Losswindows (120 ft 2 ) (68F 33F ) 4,200 BTU h 1 Heat Losswalls (776 ft 2 ) (68F 33F ) 1,429.47 BTU h 19 Heat Lossroof (900 ft 2 ) (68 F 33 F ) 1,431.82 BTU h 22 Step 2: Calculate the heat lost through the house by totaling the heat loss values. Heat Losshouse = 7,061.29BTU/h 19. Step 1: Calculate the heat loss per hour by substituting the known variables. (246 ft 2 ) [70 F (4 F )] Heat Loss 19 Heat Loss = 958.11BTU/h Step 2: Calculate the heat lost through the wall during a 36 hour period. 958.11BTU 36h 34,491.79 BTU h 20. Step 1: Identify the equation to calculate seasonal heat loss. Seasonal Heat Loss (BTU) Area HDD 24h day R value Step 2: Calculate the seasonal heat loss by substituting the known variables. 184 ft 2 6,000 F day 24h day Seasonal Heat Loss 19 Seasonal Heat Loss = 1,394,526.32BTU 21. Step 1: Calculate the seasonal heat loss by substituting the known variables. Seasonal Heat Loss (2 ft 3 ft ) 11,000 F day 24h day 1 Seasonal Heat Loss = 1,584,000BTU 22. Step 1: Calculate the HDD for the 150 day heating season in Roanoke, VA. HDD 65F 47F 18 Degree-days 18 Degree-days 150days 2,700 Degree-days Step 2: Calculate the seasonal heat loss in Roanoke, VA. (176 ft 2 ) 2,700 F day 24h day 712,800 BTU Seasonal Heat Loss 16 23. Step 1: Calculate the HDD for the 220 day heating season in Fargo, ND. HDD 65F 27F 38 Degree-days 38 Degree-days 220days 8,360 Degree-days Step 2: Calculate the seasonal heat loss through the window. Seasonal Heat Losswindow (8 ft 6 ft ) 8,360 F day 24h day 1 Seasonal Heat Losswindow 9,630,720 BTU 24. Step 1: Add the R-values of the materials the wall consists of to calculate the composite R-value of the wall. (3in .2) 1.89 (2in 3.7) .45 10.34 ft2 °F hr/BTU Step 2: Calculate the heat lost through the wall during the heating season in State College, PA. Seasonal Heat Losswall (160 ft 2 ) 6,000F day 24h day 10.34 Seasonal Heat Losswall 2,228,239.85BTU 25. Step 1: Add the R-values of the materials the wall consists of to calculate the composite R-value of the wall. .81 .94 (3in 3.7) (1.5 6.25) 45 22.68 ft2 °F hr/BTU Step 2: Calculate the seasonal heat loss through windows, the walls, and the roof using their respective areas and R-values. Seasonal Heat Losswindows (580 ft 2 ) 6,000 F day 24h day 1 Seasonal Heat Losswalls (1,920 ft 2 ) 6,000 F day 24h day 22.68 Seasonal Heat Lossroof (2,750 ft 2 ) 6,000 F day 24h day 22 Step 3: Calculate the seasonal heat lost through the house in State College, PA by totaling the seasonal heat loss values. Seasonal Heat Losshouse = 113,710,476.2BTU 26. Step 1: Find the wall area for the room by adding the area for each wall. Area 50 ft 8 ft 400 ft 2 2walls 800 ft 2 Area 70 ft 8 ft 560 ft 2 2walls 1,120 ft 2 Total Area 800 ft 2 1,120 ft 2 1,920 ft 2 Step 2: Find the area of openings in the single-story house by totaling the area of the six windows. Area windows 4 ft 6 ft 24 ft 2 6windows 144 ft 2 Step 3: Then, subtract the area of openings from the total area to calculate the total area of the wall space. Area walls 1,920 ft 2 144 ft 2 1,776 ft 2 Step 4: Add the R-values of the materials the wall consists of to calculate the composite R-value of the wall. .81 (2in 6.25) (4in 3.7) .45 28.56 ft2 °F hr/BTU Step 5: Calculate the seasonal heat loss through windows, the walls, and the roof using their respective areas and R-values. Seasonal Heat Losswindows (144 ft 2 ) 11,000 F day 24h day 1 Seasonal Heat Losswalls (1,776 ft 2 ) 11,000 F day 24h day 28.56 Seasonal Heat Lossroof (1,920 ft 2 1.1) 11,000 F day 24h day 30 Step 6: Calculate the seasonal heat lost through the house by totaling the seasonal heat loss values. Seasonal Heat Losshouse = 73,018,406.72BTU Heating and Fuels 26. Step 1: Convert CCF to BTUs of natural gas. Recall that 1 CCF is equal to 100,000BTU. 34CCF 100,000 BTU 3.4MMBTU 1CCF 27. Step 1: Convert gallons to BTUs of natural gas. Recall that 1 gallon is equal to 130,000BTU. 83gal 130,000 BTU 10.79MMBTU 1gal 28. Step 1: Convert the seasonal heating requirement from BTUs to CCF. 236MMBTU 1CCF 2,360CCF 100,000 BTU 29. Step 1: Convert the heating requirement from BTUs to gallons of fuel oil. 173MMBTU 1gal 1,330.77 gal 130,000 BTU 30. Step 1: Convert CCF to BTUs of natural gas. 106CCF 100,000 BTU 10.6MMBTU 1CCF Step 2: Convert BTUs to Kilowatt-hours of electricity. 10.6MMBTU 1kWh 3,106.68kWh 3,412 BTU 31. Step 1: Calculate the seasonal heat loss through windows, the walls, and the roof using their respective areas and R-values. Seasonal Heat Losswindows Seasonal Heat Losswalls (580 ft 2 ) 6,000 F day 24h day 1 (1,920 ft 2 ) 6,000 F day 24h day 19 Seasonal Heat Lossroof (2,750 ft 2 ) 6,000 F day 24h day 22 Step 6: Calculate the seasonal heat lost through the house by totaling the seasonal heat loss values. Seasonal Heat Losshouse = 116,071,579BTU