Geology Review
advertisement

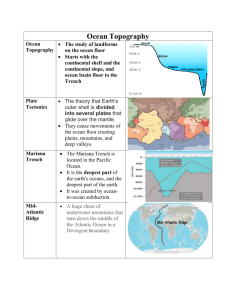
Geology Review 1. Which of the following is a bottom-dweller? F. tuna G. whale H. sea stars J. dolphin 2. What must plankton have to reproduce? A. sunlight B. C. sunlight and nutrients D. nutrients sunlight and oxygen 3. A scientist wants to study the impact of tide on the population of local clams which are harvested for food. Where is the best place to set up the testing equipment? A. shoreline B. coral reef C. open ocean D. deep continental shelf 4. What part of the ocean is a deep, narrow valley? A. ridge C. slope B. trench D. rise 5. The beach where people swim is usually part of F. the ocean basin. H. the continental shelf. G. the continental slope. J. an ocean ridge. 6. Which structure in the ocean builds up as an underwater mountain, sometimes forming an island? A. a trench C. rise B. a volcano D. continental shelf 7. The gradually sloping part of the ocean floor that is made of sediment below the continental slope is F. the rise. H. a ridge. G. the shelf. J. the ocean basin. 8. Which part of the ocean is usually the deepest? A. a volcano C. a trench B. the continental shelf D. the ocean basin 9. What is the name for a deep, somewhat flat area of the ocean floor? F. basin H. rise G. slope J. ridge 10. The area between the continental shelf and the ocean floor is called the A. ridge. C. continental slope. B. volcano. D. basin. 11. The place where water meets the land is called F. the shoreline. H. the ocean basin. G. the continental slope. J. the continental rise 12. What is a wave? A. a river of water moving through the ocean B. the rise and fall of the surface level of the ocean C. a disturbance seen on the surface of the ocean D. a warm current moving north along the east coast of the United States 13. What causes tides? F. the currents in the surrounding water G. the pull of the moon on the Earth H. the pull of the Earth on the moon J. the height of nearby waves 14. How does ocean depth affect pressure? A. As depth increases, pressure decreases. B. As depth increases, pressure increases. C. As depth decreases, pressure increases. D. Depth does not affect pressure. 15. Do currents affect the weather? A. No, weather is affected by tides. B. Yes, currents can cause changes in the weather. C. Currents only affect water temperature. D. Weather is not affected by any changes in the ocean. 16. The __________ is solid iron and is covered by melted iron and nickel. F. inner core H. mantle G. outer core J. crust 17. The __________ is the thickest layer of the Earth. A. inner core C. crust B. mantle D. outer core 18. The __________ is the thinnest layer of the Earth. F. inner core H. mantle G. outer core J. crust 19. One kind of boundary between plates is __________. A. glacial movement C. sea-floor spreading B. divergent boundary D. lithosphere 20. A convergent boundary exists when __________. F. continental and oceanic H. plates come together G. new ocean floor is made J. both F and J plates slide away from each other 21. Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions are thought to be caused by __________. A. meteorological events C. tiny seismographic disturbances B. plate movement D. the oceanic crust 22. There are __________ major plates. F. six G. seven J. nine H. eight 23. __________ rocks are formed from magma. A. Sedimentary C. Metamorphic B. Igneous D. Sedimentary and Igneous 24. __________ rocks can become metamorphic rocks. F. Sedimentary H. Metamorphic G. Igneous J. Metamorphic, Sedimentary and Igneous 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. __________ rocks can change into magma. F. Sedimentary H. G. Igneous J. Metamorphic All Erosion is A. not a major problem. B. the evaporation of water. C. D. the carrying away of particles. runoff. Erosion can be caused by F. topsoil. G. wind. H. J. grass. the sun. An example of deposition is A. a river. B. a glacier. C. D. erosion. a delta. One way to stop or reduce erosion is to F. plant grass, trees, and shrubs. G. remove grass, trees, and shrubs. H. J. The greatest cause of erosion and deposition is A. cutting grass. C. ice. B. running water. D. waves. rake leaves. pick up litter.