Advanced Structural Modeling: UML Classes & Relationships
advertisement
Advanced Structural Modeling
1. Advanced Classes
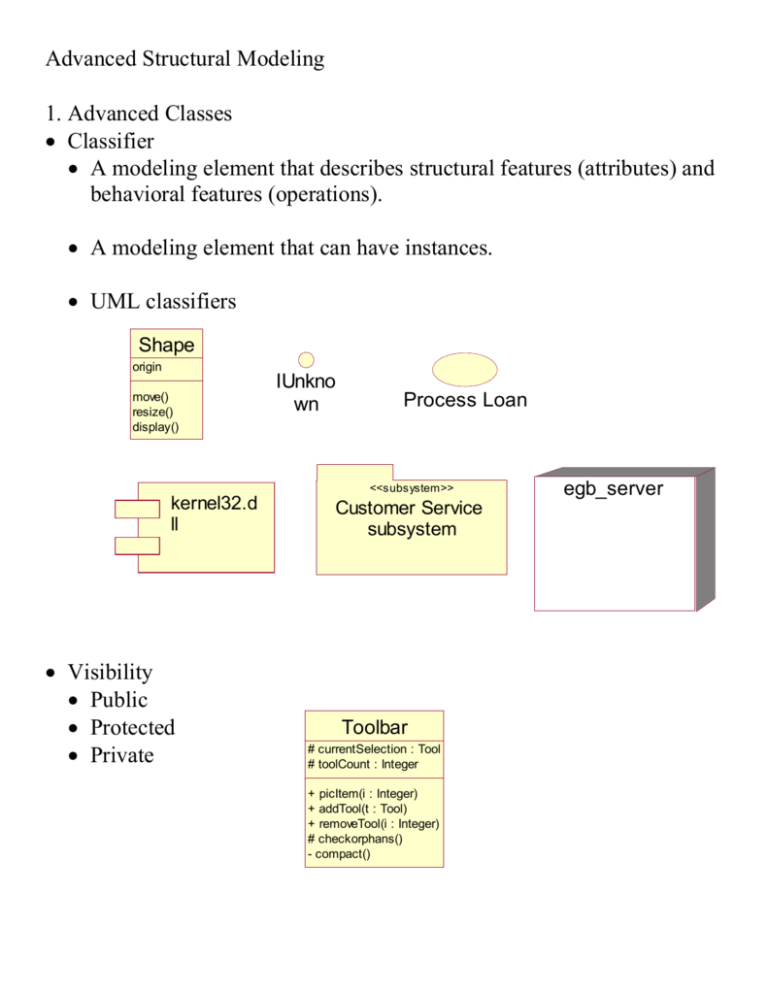
Classifier
A modeling element that describes structural features (attributes) and
behavioral features (operations).
A modeling element that can have instances.
UML classifiers
Shape
origin
move()
resize()
display()
IUnkno
wn
Process Loan
<<subsystem>>
kernel32.d
ll
Visibility
Public
Protected
Private
Customer Service
subsystem
Toolbar
# currentSelection : Tool
# toolCount : Integer
+ picItem(i : Integer)
+ addTool(t : Tool)
+ removeTool(i : Integer)
# checkorphans()
- compact()
egb_server
Scope
Instance
Each instance of the classifier holds its own value for the feature.
Classifier
There is just one value of the feature for all instances of the classifier.
Frame
header : FrameHeader
$ uniqueID : Long
Abstract, Root, Leaf, and Polymorphic Elements
Abstract class: no instance, unimplemented operation(s)
Concrete class: has instance(s) and all operations are implemented.
Abstract operation: no implementation
Root class: no parent class or super class
Leaf class: no subclasses
Leaf operation: cannot be overridden or redefined by subclasses
Polymorphic operation: can be overridden or redefined by
subclasses.
Rectangle
height : Integer
width : Integer
Button
display()
Icon {root}
ArbitraryIcon
origin : Point
edge : LineCollection
<<abstract>> display()
getID() : Integer {leaf}
isInside(p : Point) : Boolean
OkButton {leaf}
display()
Multiplicity
Number of class instances
Number of elements of an array attribute
NetworkController
consolePort[2..*] : Port
1
ControlPad 3
Attribute specification
Full form
[visibility] name [multiplicity] [:type] [=initial-value] [{property}]
Standard properties
changeable
addOnly: add element(s) only, no remove
frozen: no value change
Operation specification
Full form
[visibility] name [(parameter-list)] [:return-type] [{property}]
Standard properties
leaf: cannot be overridden
isOuery: does not change state
sequential: semantics of concurrent calls cannot be guaranteed.
guarded: sequencing and synchronizing concurrent calls
concurrent: semantics of concurrent calls are guaranteed
Parameter specification
Full form
[direction] name : type [=default-value]
Standard directions
in: an input parameter with input value, may not be modified
out: an output parameter, without input value, may be modified
inout: an input parameter with input value, may be modified
What is a utility class
A class with stereotype <<utility>> whose all attributes and
operations have classifier scope (i.e. static).
Example: <<utility>> Math
2. Advanced Relationship
Association
Navigation
Association (role) visibility
Public: can be seen outside of the association
Private: cannot be seen outside of the association
Protected: can be only seen by subclasses of the association
UserGroup
+ user
+user User +owner
-key
- key
Passward
+ owner
Qualification through Qualifier
Bank Account
0..*
accountNumber : Integer
owner
(bankAccount, accountNumber) 0 or 1 person
person many(bankAccount, accountNumber)
0..1
Person
Association class
Company
1..*
*
employer
Person
employee
Job
description
dateHired
salary
Realization
What
A realization is a semantic relationship between classifiers in which
one (target) classifier specifies a contract that another (source)
guarantees to carry out.
Where to use
A class realizes an interface
<<Interface>>
IRuleAgent
AccountBusinessRules
addRule()
changeRule()
explainAction()
A component realizes an interface
AcctRule.
dll
IRuleAgent
A use-case realization realizes a use case or realization
Validate user
Validation-Analysis
Validation-Design
3. Interfaces
What is an interface
An interface is a collection of operations that are used to specify a
service of a class or component.
An interface does not specify any structure (attributes) nor any
implementation of the operations in the collection.
An interface defines a line between the specification of what an
abstraction does and the implementation of how that abstraction does
it.
Relationships between interfaces and other classifiers
A class can realize one or more interfaces
An interface can be realized by one or more interfaces
A class can depend on an interface
Inheritance relationship between interfaces
Tracker
TargetTracker
Observer
java::util::Observable
Target
id
currentPosition
<<Interface>>
Observer
TargetTracker
setPosition()
setVelocity()
ExpectedPosition()
Interface for role
Company
1..*
*
e: Employee
employer
<<Interface>>
Empolyee
gwtEmploymentHistory()
getCompensation()
getBenefits()
Person
4. Packages
What is a package
A package is a general-purpose mechanism for organizing elements
into groups.
Owned elements
A package can own other elements, even other packages.
Every element is uniquely owned by exactly one package.
A package forms a name space. Two elements owned by two
different packages may have the same name.
Examples:
BuyerPackage::Information class
SellerPackage::Information class
Elements of different kinds may have the same name
Example:
BuyerPackage::Information class
BuyerPackage::Information component
Path names in nested packages
Example:
CustomerPackage::BuyerPackage::Information class
Visibility of owned elements
Public (+)
Private (-)
Protected (#)
A package exports all its public elements
Server
+ Database
+ LoggingService
Client
+ OrderForm
+ TrackingForm
- Order
GUI
Policies
+ Window
+ Form
# EventHandler
+ OrderRules
- GUI::Window
Subsystem – a stereotyped package
It is a package of elements treated as a unit, including a specification
of the behavior of the entire package contents as a coherent unit.
A subsystem is modeled both as a package and as a class.
A subsystem has a set of interfaces that describe its relationship to the
rest of the system
<<design subsystem>>
Buyer's Invoice Managemenr
InvoiceReceiver
<<service subsystem>>
Payment Scheduling management
PaymentScheduling
<<design subsystem>>
Account Management
Transfer
<<design subsystem>>
Buyer's Invoice
Management
InvoiceReceiver
<<service subsystem>>
Payment Scheduling
Management
<<design subsystem>>
Account
Management
Transfer
PaymentScheduling










