Notes_RotaEquil_2012

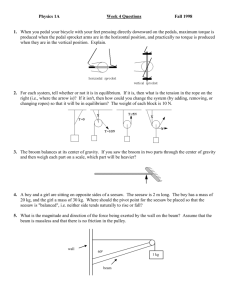
The Second Condition of Equilibrium
A net torque, Στ, is analogous to a net force (ΣF) when examining its influence on motion. Στ applies to rotational motion the same way ΣF applies to linear motion.
What is the ΣF if something is at rest?
What is the Στ if something is at rest?
At equilibrium, what is the relationship between the clockwise torques and the counterclockwise torques?
When is there a torque present on an object?
Where is the fulcrum located?
A few important notes about torque:
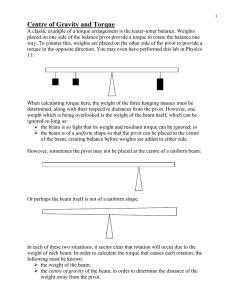
The exact position of where a force acts now becomes very important .
The weight of an object seems to act through its center of mass.
The words "balanced" or "equilibrium" or "at rest" imply Στ = 0
726946719
Practice Rotational Equilibrium Problem Solving:
1.
A weight of 2 N is placed 0.2 m from the pivot of a 0.5-N beam. If the beam is 1-m long and the pivot is in the exact center, where should you place a 1.5 N weight to balance the beam?
2.
A weight of 2 N is placed 0.2 m from the pivot of a 0.5-N beam. If the beam is 1-m long and the pivot is in the exact center, how much weight should be placed at 0.4 m from the pivot to balance the beam?
3.
A weight of 2 N is placed 0.2 m at the 0.1-m mark of a 0.5-N beam. If the beam is 1-m long and the pivot is at the 0.4-m mark, where should you place a 1.5 N weight to balance the beam?
4.
A uniform bridge span weighs 50,000 N and is 40.0 m long. An automobile weighing 15,000 N is parked with its center of gravity located 12.0 m from the right pier. a.
What upward support force is provided by the left pier? b.
How do you think the force from the right pier compares to that of the left? c.
There are 2 ways to solve for the force on the left: what are they?
726946719