Intergenerational Gaps
advertisement

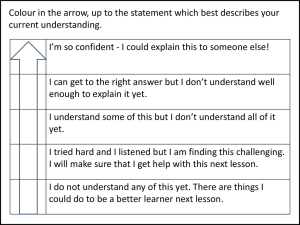
Generational filter, Intergenerational gap, And their impact on business By David Sarikhan BUS-8020 Strategic Information Alliance International Unvisited Spring 2009 Professor: Louise Kelly 1 Alliance International University Abstract Generational filter, intergenerational gap, Generational perception and their impact on business performance By David Sarikhan Narrowing the intergeneration gaps makes it easy to get the things done in the firm resulting to business success. 2 Table of Contents 1. I. Research Problem ...........................................................................................6 a. Generation ................................................................................................6 b. Intergenerational .....................................................................................7 2. II. Applicable Parading(s) (Literature) .............................................................9 3. III. Research Questions..................................................................................... 12 4. IV. Global Model ............................................................................................... 12 5. V. Research Model ........................................................................................... 12 6. VI. Research Strategy........................................................................................ 15 7. VII. Hypotheses / Propositions ..................................................................... 15 8. VIII. Intergenerational Gaps............................................................................ 16 9. IX. Variable Definitions .................................................................................... 17 10. X. Summary of this project .............................................................................. 21 List of figures Figure 1. Mr. Philip Goodman Generation Type Table Year 2004 Page 9 Figure 2. By Lynne C. Lancaster and David Stillman Intergenerational l gap & bridge work Page 10 Figure 3. The Global Model Page 13 Figure 4. The Research Model Figure 5. Performance and Intergenerational Gap Figure 6. Performance and Business Knowledge Transfer Figure 7. Performance and Product /Service Delivery, Revenue (REO) Figure 8. Performance and Communication Gap Page 14 Page 16 Page 16 Page 16 Page 16 3 Acknowledgments My thanks to Mr. Mr. Philip Goodman who spent his time and his effort contributing to this project. His decades of knowledge, experience, and relentless efforts in perusing and researching on generation study and helping the firms with his effective niche advertising methodology through his Genergraphic company. 4 Glossary Filters. Ansoff: (1994) classified filters as surveillance, mentality and power filters (see figure 1). A weak signal has to pass these filters in order to influence a strategy process. The surveillance filter defines the field of observation that an actor uses. The mentality filter hinders the recognition of new ideas by reducing information when it does not support the current mental model of an actor. The power filter explicates itself in the decision making process by holding back less powerful actors (e.g. organizational or expertise power) from expressing their perceptions. Gap. Ansoff: (1994) Current momentum. The Gap is the difference between extrapolation of the firm’s performance and performance projection based on environmental analysis. Current potential. The Gap is the difference between projection based on environmental analysis and performance possible if the firm optimizes its competitive posture. Diversification. The Gap is the difference between the optimal performance inherent in the firm’s present strategic portfolio and the objectives of the firm. Generation gap: Idioms: generation gap: A broad difference in values and attitudes between one generation and another, especially between parents and their children. For example, there is a real generation gap in their choice of music, restaurants, clothing--you name it (1960s). Science Dictionary: generation gap is the differences in customs, attitudes, and beliefs between any two generations, but especially between youths and adults. Generation: Wikipedia: A generation gap is a popular term used to describe big differences between people of a younger generation and their elders. This can be defined as occurring "when older and younger people do not understand each other because of their different experiences, opinions, habits and behavior." The term first came into prominence in Western countries during the 1960s, and described the cultural differences between the Baby Boomers and their parents. Although some generational differences have existed throughout history, during this era differences between the two generations grew significantly in comparison to previous times, particularly with respect to such matters as musical tastes, fashion, drug use, culture and politics. This may have been magnified by the unprecedented size of the young Baby Boomer generation, which gave it unprecedented power, influence, and willingness to rebel against societal norms. 5 I. Chapter 1 Research problem Generational mindsets and perceptions are affecting the business I Chapter 1-a performance and dampening the business growth. Generation: Generation Generation (from the Greek γενεά), also known as procreation, is the act of producing offspring. Here is an example: Here is an infant, his mother, his maternal grandmother, and his great-grandmother. Thus there are four generations of one family in this photograph. Intergenerational Gap is the difference in generation value, belief, attitude, and choice of music, clothing, and restaurant. 6 Intergenerational Gap Intergeneration gap is a broad difference in values and attitudes between one generation and another, especially between parents and their children. For example, there is a real generation gap in their choice of music, restaurants, clothing--you name it. 1920s During what was known as the 'Roaring Twenties' a large generation gap occurred due to the older generation having just fought in the war finding it inappropriate that the younger were out at dance halls and listening to jazz music. 1950s Teenagers prior to World War II were expected to take life seriously. Young males were expected to join the military and/or go out and get a job in order to help bring in money for their family. Young females were taught how to take care of the household and prepare themselves to be a dutiful wife and take care of children. Also, teenagers in the late 1930s had very little economic freedom, independence, and input into decision. In the 1950s, this changed. The United States emerged from the War the most powerful and affluent nation in the world. The economy picked up and teenagers began experiencing a great deal of economic freedom and independence. The "American Dream" was born, but at the same time there was a fear of losing America's prosperity and security. The focus for much of the fear over what America was becoming was youth - it was an adult obsession and shared assumption that young people lacked the discipline and get-up-and-go that had made America great. As the 40's ended and the 50's emerged, marked differences between teenagers and parents began to emerge. From a transformation of the dating system (going steady and early marriage become the norm as opposed to the "rating and dating" trend that was fashionable before the war), to the new medium of television gaining widespread popularity and often-portraying teenagers as juvenile delinquents. 'JD's' followed the standard black leather and denim jeans look set by Marlon Brando in 1953 film, The Wild One. The widespread adoption of rock and roll also helped foster differences between parents and teenagers. Rock was loud, rhythmic, and full of energy. Adults didn't get it and even FBI Director J. Edgar Hoover called the new music "a corrupting influence". [2] Holden Caulfield, the hero of J. D. Salinger's 1951 novel The Catcher in the Rye, was a literary embodiment of teenage angst and alienation further fueling adults perception of teens as rebels. 1980s When heavy metal music gained mainstream popularity in the 1980s, music became a touchpoint for the Generation gap between the parents, who were often teenagers in the 50's, and the younger generation. The 1980s saw Tipper Gore, wife of Democratic Presidential nominee Al Gore; launch a crusade against raunchy and violent rock lyrics, and heavy metal was one of her main targets. Cultural effects A seeming generation gap may be present between different generations, as well. Starting with the fear of childbirth, people may learn or otherwise impart a fear of children, fear of youth, 7 and/or fear of elderly people. Whether favoring the perspective of adults or actually solely allowing the perspective of adults, society may seem to also foster gerontocracy, which pits elderly people against children, youth and adults, as well. The largest generation gap, though, separated those born after 1940 from those born before 1935. It was summarized in 1967 with the slogan among the young: "Don't trust anyone over 30." As this gap moved through the decades, it separated those who appreciated rock music from those who did not, and the computer literate from the illiterate. Those on the old side of the gap could not wait to enlist in the military and fight World War II or the Korean War, while the young challenged the military draft during the Vietnam War. Despite the radical changes in the electronic and technological environment in the last several decades, a defined gap does not separate today's generations as it did in the sixties and seventies. The left/right political delineations in the U.S. at the present tend to mimic the generation gap of the sixties, as rich elders tend to be right-wing, and working youngsters tend to be left-wing. 8 II. Chapter 2 Literature Review 2.1, Genergraphic Website by Philip Goodman Generation gap in Nutshell, base on Mir Philip Goodman 30-years of imperial data indicates the following and I agree: There is no transfer of mindset between generation No generational mindset follows one another One size generation does not fit all Each generation brings their own mindset Each generation does not care about the previous generation Each generation has be treated differently Echoboomers generation is the first global generation in the history of mankind. Iranian Echoboomers generation distanced themselves from their culture There is an intergenerational filter that sets the generation apart from one another (intergenerational Filter) Generational mindset is established and locked in between 12 to 17 years of age Mindset is based on social circumstances, pear group. You can not bridge the gap between the generation Figure1: Mr. Philip Goodman Generation Type Table Year 2004 Generation Type Years 2006 Year Born old Oldest Population (Millions) Seniors The Forgotten Boomers Older Boomer Younger Generation X 69 5968 4859 2839 Echoboomers 22Older 27 Echoboomers Medium Echoboomers Younger Millennium 1-10 92 71 1915-1935 1936-1945 55 28 61 1946- 76.5 -1964 ~ 42 1965-1976 46 30 1977- 72 12 the The same generational mindset around the world. ~ -1994 Sandwiched between tow missing link Higher divorce rate ~ 1995-2005 9 Mr. Goodman description of the generation and their gaps give us a good foundation for gap analysis and recommend the gaps closure. I do agree the source of the gap and distinctive characteristics among them. His strategy is geared toward more particularly, the present invention relates to the creation and maintenance of data and presentations based on the generation-based mindsets of users or consumers and the use of those models to aid in presenting targeted content, such as advertising or special offers. Based on his view, most businesses is to target consumers with products and services that are of interest to the consumer based on their interests, preferences, or demographics. Thus many attempts have been made to determine consumer’s interests and provide content (e.g. promotions, advertisements) to products and services that match such interests. The field and study of Genergraphic is aimed at differentiating the attitudes, lifestyles, and buying patterns by generation. Using a unique method of psychographics differentiation based upon lifestyle questions, these studies have enabled major international companies to achieve major increases in brand awareness and sales. This field of study has shown that certain products and services appeal to all generations at different levels In short, his study and creation is designed towards making, promotion, and advertising and gives good foundation to my gap analysis. 2.2, “When Generation Collide”, By Lynne C. Lancaster and David Stillman. By Lynne C. Lancaster and David Stillman Strategy: Collection to generation: 65% says, “Generation Gap” makes it hard to get the things done. Figure 2. By Lynne C. Lancaster and David Stillman Intergenerational gap & bridge work Intergenerational Gap Bridge work Traditionalist Command / Control Boomers Play by the rules Generation X They want instant feedback, MTV, Tattoos, Punk attitude, spike hair style Millennium Digital Generation, Global Connection, global village, Scary place, world is not safe, realistic This seems to be a too general and they talk about the gap existence but do not give any kind of strategy for gap closures. And also talk about the strategy but only stapes of action to take to come up with a strategy for gap closure. 10 2.3, Other Applicable Paradigm(s) (Literature) Strategic Information o Mentality Filter (page 60 on Implementing Strategic Management (by Dr. Igor Ansoff) Text Generation Gap: U R 2 Old (JK) (New York Times March 9, 2008) Closing the Generation Gap between Youth, Business School and Business through Learning–by-Sharing Combining Academic Rigor and Practical Relevance Closing Generation gap – BizTimes Tips offered to close the generation gap in the workplace Failure to communicate: Survey reveals big generation gap in the workplace. Bridge the generation gap in business 11 III. Chapter 3 Research Questions WHAT IS THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN DIVERSE GENERATIONAL PERCEPTIONS WITH PERFORMANCE OF THE FIRM? IV. Chapter 4 IV. The Global Model The environment containing technology, custom, music Socio-Economic and political trends, attitudes, values, and beliefs follows the Minded Filter create generation mindset. This mindset happens between twelve (12) to seventeen (17) years of age and gets lock in human mind mapping the human mind for the rest of remaining life personal life. See Figure 3. The mindset creates perception impacting both strategic formulation and performance of the firm concluding that the Periodic mindset sets tone for the rest of person’s life. It sets a tone for the kind of food to eat, the kind of music to listed, all likes and dislikes, the kind of technology to use, the kind of custom to follow as well as the kind of attitude, value and belief to have. These characteristics have tremendous impacts on the performance of the firms. V. The Research Model The Research Model shows the propositions from P-1 to p-5. See Figure 5. Proposition 1: The Environment Creates mindset filter resulting the Mindset. There are gaps between the mindsets, which we try to close. However it is not possible to close these gaps do to social-economical experience that the person had at the time of growing up. These gaps have almost impact on strategic formulation and the firm’s performance. The larger the gap the less the firm performs. The larger the gap is, the lesser firm’s performance. The gaps have inverse relationship with firm’s performance 12 Technology IV. The Global Model Attitudes Custom Values Socio-Economic and Political Trends Music Belief s Environment Filter Periodic Generational Mindset 1915-1935 1936-1945 Seniors Mindset Gap 1946-1964 1965-1976 The Forgotten Generations Echoboomers Mindset Mindset Gap Seniors Perception The Forgotten Generations Perception Boomers Mindset 1977-1994 Gap Gap Boomers Perception 1995-2009 Millenniums Mindset Gap Generation X Mindset Generation X Perception Strategic Formulation Echoboomers Perception Performance Of the Firm Figure 3: The Global Model. 13 Millenniums Perception V. The Research Model Environment Filter P-1 Seniors Mindset Gap The Forgotten Generations P-2 Mindset Echoboomers Mindset Millenniums Mindset P-4 Gap Gap Gap Seniors Perception The Forgotten Generations Perception P-3 Boomers Mindset Gap Boomers Perception Generation X Mindset Generation X Perception Strategic Formulation P-5 Echoboomers Perception Performance Of the Firm Figure 3: The Global Model. 14 Millenniums Perception VI. Chapter 6 Research Strategy The selected research is to research from available literature and interviews of the authors on the subjects of Generational gap. VII. Chapter 7 Hypotheses / Propositions 7.1, Propositions: Proposition 1: The Environment Creates filter subsequently creates the Generational Mindset Proposition 2: No two Generational Mindset are the same. Proposition 3: Knowledge does not transfer between generations. Proposition 4: The Generational Mindset Creates Generational Perception. Proposition 5: The size of the Intergenerational Gap has inverse relationship with Performance of the firm . 7.2, Generational Mindset Followings are the Generational Mindset: 1. Proposition: Seniors Generation Mindset 2. Proposition: The Forgotten Generation Mindset 3. Proposition: Boomers Generation Mindset 4. Proposition: Echoboomers Generation Mindset 5. Proposition: Millenniums Generation Mindset 15 VIII. Chapter 8 Intergenerational Gaps Here are the Intergenerational Gaps: Seniors and The Forgotten Generational Gap The Forgotten and Boomers Generational Gap Boomers and Generation X Generational Gap Generation X and Echoboomers Generational Gap Echoboomers and Millennium Generational Gap As we look at the Proposition 5. (The size of the Intergenerational Gap (See Figure 5) has inverse relationship with Performance of the firm.), we notice that when this gap is greater we see the followings: Less communication among the worker. See Figure 8. Business knowledge (even though this knowledge is sued by generational perception) does not delivered (See Figure 6). Resentment and animosity increase among the workers Products/Services do not get properly delivered. See Figure 7 Less revenue comes to the firm. See Figure 7 Firm performance suffers. See Figure 7 REO, Return on Investments suffers. See Figure 7 Performance Intergenerational Gap Figure 5 Performance Business Knowledge Transfer Figure 6 Performance Performance Product /Service Delivery, Revenue (REO) Figure 7 16 Communication Gap Figure 8 IX. Chapter 9 Variable Definitions 9.1, INDEPENDENT VARIABLE 1. Environmental Turbulence: Complexity and predictability of the environment; the degree of changeability and speed with which they developed. 9.1a, EXTERNAL ENVIORNMENT i. Technology: Technology deals with the knowledge of human tools and crafts. " Technology" is simply the application of knowledge. Humans from around the world find different ways to increase the efficenticy of different technology functions. ii. Custom: A custom (also called a tradition) is any thing, which lots of people do, and have done for a long time. Usually, the people come from the same country, culture, time or religion. If something is usually done the same way, you might say that is the "customary way" of doing thngs. iii. Music: Music is an art that puts sounds together in a way that people like or find interesting. Most music includes people singing with their voices or playing musical instruments, such as the piano, guitar, or drums. iv. Socio-Economic and Political Trends: It was distinguished by differences of economics, politics, and religion rather than by clear geography has less to do with geography and more to do with economics. v. Attitudes: A complex mental state involving beliefs and feelings and values and dispositions to act in certain ways. vi. Values: The value of something is how much it is worth. Often the best way to find the value of something is use the price that it can be sold for. In mathematics, a value is a number. vii. Beliefs: 1. In philosophy, attempts to analyze the nature of belief have been couched in terms of judgment. 2. In religious contexts, the word often implies that what is believed cannot be justified conclusively, but still holds personal and/or social value as valid (faith and rationality). 9.1b, INTERNAL ENVIONMENT viii. Mindset: A mindset is a state that usually a majority of people would have in a particular time or occasion. It is formed from things that people are convinced about. It is like a collective norm. ix. Perception: 17 1. In psychology and the cognitive sciences, perception is the process of getting, interpreting, selecting, and organizing sensory information. 2. Perception is essentially biological or physiological approaches, through psychological approaches through the philosophy of mind and in empiricist epistemology, and affirmation of perception as the basis of all science and knowledge. x. Seniors Generation: 1. Seniors Mindset: It is state of the people who were born within the years of 1915-1935. 2. Seniors Perception: It is the process of getting, interpreting, selecting, and organizing sensory information by the people who were born within the years of 1915-1935. xi. The Forgotten Generation 1. The Forgotten Generation Mindset: It is state of the people who were born within the years of 1936-1945. 2. The Forgotten Generation Perception: It is the process of getting, interpreting, selecting, and organizing sensory information by the people who were born within the years of 1936-1945. xii. Boomers Generation: 1. Boomers Generation Mindset: It is state of the people who were born within the years of 1946-1964. 2. Boomers Generation Perception: It is the process of getting, interpreting, selecting, and organizing sensory information by the people who were born within the years of 1946-1964. xiii. Generation X: 1. Generation X Mindset: It is state of the people who were born within the years of 1965-1976. 2. Generation X Perception: It is the process of getting, interpreting, selecting, and organizing sensory information by the people who were born within the years of 1965-1976. xiv. Echoboomers Generation: 1. Echoboomers Generation Mindset: It is state of the people who were born within the years of 1977-1994. 2. Echoboomers Generation Perception: It is the process of getting, interpreting, selecting, and organizing sensory information by the people who were born within the years of 1977-1994. xv. Millenniums Generation: 1. Millenniums Generation Mindset: It is state of the people who were born within the years of 1995-2005. 18 2. Millenniums Generation Perception: It is the process of getting, interpreting, selecting, and organizing sensory information by the people who were born within the years of 1995-2005. 9.2, MODERATING VARIABLES: 1. Power: Power is the ability to act or produce an effect. 2. Propensity To Use Power: An often intense natural inclination or preference to use power. 9.3, INTERVENING VALIABLES: 1 Seniors Generation: The people who were born within the years of 1915-1935. 2. The Forgotten Generation: The people who were born within the years of 1936-1945. 3. Boomers Generation: The people who were born within the years of 1946-1964. 4. Generation X: The people who were born within the years of 1965-1976. 5. Echoboomers Generation: The people who were born within the years of 1977-1994. 6. Millenniums Generation: The people who were born within the years of 1995-2005. 7. Seniors and The Forgotten Generation Mindset Aggressiveness Gap: Degree of discontinuity between Seniors and The Forgotten Generation Mindset. 8. The Forgotten Generation and Boomers Mindset Aggressiveness Gap: Degree of discontinuity between Forgotten Generation and Boomers Mindset. 9. Boomers and Echoboomers Mindset Aggressiveness Gap: Degree of discontinuity between Boomers and Echoboomers Mindset 10. Echoboomers and Mindset Generation X Mindset Aggressiveness Gap: Degree of discontinuity between Echoboomers and Mindset Generation X Mindset. 11. Generation X and Millenniums Mindset Aggressiveness Gap: Degree of discontinuity between Generation X and Millenniums Mindset. 12. Aggressiveness Gap: It is the discontinuity between the two. 13. Strategic Investment Gap: A firm’s investment in its strategic posture in an SBA (strategic Business Area) difference between the optimal performance and inherent in the firm’s present strategic. 9.4, DEPENDENT BALIABLES: 1. Gap: Gap was defined as the space between variable and environment turbulences. Misalignment with the Environment. 2. Intergenerational Gap: The gap between tow generations. 1 Current Momentum Gap: The difference between extrapolation of the firm’s performance and performance projection based on environmental analysis. 19 2 Diversification Gap: The difference between the optimal performance and inherent in the firm’s present strategic portfolio and the objective of the firm. 3 Growth Thrust Gap: A component of competitive strategy with specifies the source of the firm’s future growth. 3. ROI: This is the amount money (profit) the investors receive as a result of investing. 20 X. Chapter 10 Summary of this Project A generation gap is the differences between people of a younger generation and their elders. This can be defined as occurring "when older and younger people do not understand each other because of their different experiences, opinions, habits and behavior. The differences between the two generations grew significantly in comparison to previous times, particularly with respect to such matters as musical tastes, fashion, drug use, culture and politics. This may have been magnified by the unprecedented size of the young Baby Boomer generation, which gave it unprecedented power, influence, and willingness to rebel against societal norms. Knowing that there is no transfer of Mindset and perception between the generations, the mindset of previous generation has no value to the recent generation, and it is difficult if not impossible to bridge the generations’ gap, how can we close the intergenerational gaps? The best way to close the gap between the generation is not closes the gap (not possible). But to be present where the other generations are coming from, understanding and taking proper actions that how the communication is going to land on recipient side that happens to be from another generation. The information transfer would be colored with proper generational characteristics then the intergenerational gap is narrowed. Unless the intergeneration gaps are narrowed, it makes it difficult to get the things done in the firm. 21 Bibliography Igor Ansoff. Strategic Management, Classic ed. Palgrave Macmillan 1979 Igor Ansoff. Implanting Strategic Management, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall International (UK) Ltd, 1990. Philip Goodman. Genergraphic Website, McNichols Randick O’Dea & Tooliatos, November 28, 2005 Tomas Thijssen, Closing the Generation Gap between Youth, Business School and Business through Learning–by Sharing, Spruts 2007. BuzTimes. Closing Generation gap, BuzTimes.com, April 2009. Mark Larson. Failure to communicate: Survey reveals big generation gap in the workplace, Financial Week, February 2008. Laura M. Holson. I R 2 Old (JK), New York Times March 9, 2008. Lynne Lancaster and David Stillman. When Generation Collide. HarperCollins publishers, 2002. 352 pp J.P.T. Thijssen and W. Gijselaers. Closing the Generation Gap between Youth, Business School and business through Academic Rigor and Practical Relevance, Spruts 2007. Beverly Stencel. Tips offered to close the generation gap in the workplace, Beverly Stencel, Feb. 2001 22