Lesson 6 – 8 questions – Conservation of Momentum
advertisement

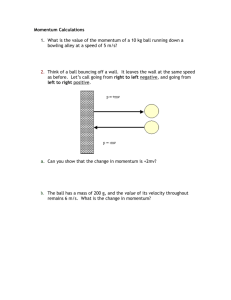
Lesson 6 – 8 questions – Conservation of Momentum ( /53)…………..%……….. ALL 1. State the principle of conservation of momentum and explain what is meant by elastic collisions and inelastic collisions. …………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………… (3) 2 In the fission of a uranium 235 nucleus a neutron collides with the nucleus causing it to break up. The particles formed are two smaller nuclei and three neutrons. Is the linear momentum of the system conserved during the collision? Explain your answer. ………………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………… (2) MOST 3A ball of mass 210 g moving at a speed of 23ms–1 hits a wall at right-angles and rebounds at the same speed. The ball is in contact with the wall for 0.31 s. a) Calculate the change in momentum of the ball. change in momentum = …………..…………..(2) b) Is the momentum of the ball conserved? Explain your answer. …………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………(2) c) Calculate the magnitude of the average force acting on the ball. Average Force = ………………….(3) 4 A ball mass 2 kg moving left to right at 1.5 ms -1 collides with a ball of mass 3 kg moving from right to left at 0.2 ms-1. After the collision the 2 kg ball moves from left to right at 1 ms-1. Draw a diagram. Calculate: (a) the change of momentum of the 2 kg ball Change in momentum = …………………… (2) (b) the momentum of the 3 kg ball after the collision momentum = ………… ………… (2) (c) the velocity of the 3 kg ball after the collision velocity = …………………… (2) 5 A 1 kg ball of plasticene moving at 4 ms-1 collides with another ball of mass 2 kg initially at rest. They stick together and move off. Draw a diagram Calculate: (a) the total momentum of the system before the collision total momentum =……… ……………… (2) (b) the velocity of the combined balls after impact velocity = ……………… (2) SOME (c) the kinetic energy converted to other forms kinetic energy = ……………… (2) 6 A radium 226 nucleus decays by the emission of an alpha particle into a radon 222 nucleus. If the velocity of the alpha particle is 2x106 ms-1 what is the recoil velocity of the nucleus? Recoil velocity = ………………… (2) 7The diagram shows two toy trains T and R held in place on a level track against the force exerted by the compressed spring. When the trains are released, R moves to the right at a speed of 3.8ms–1. The spring takes 0.25 s to uncoil to its natural length. Calculate: a) the velocity of train T; velocity = …………… (4) b) the average force exerted by the spring on each train. average force = …………. (4) 8 850kg cannon fires a 20kg shell at a velocity of 180ms–1. a) Calculate the final momentum of the shell. final momentum = ………………….(2) b) What is the magnitude of the momentum of the cannon immediately after the shell is fired? (You may assume that the cannon is initially at rest.) magnitude of the momentum = ……………………(2) c) Calculate the recoil velocity V of the cannon. recoil velocity = ……………………[3] 9The diagram shows flour falling onto a horizontally moving conveyor. The flour falls vertically onto the conveyor belt at a constant rate of 3.2kg s–1. The conveyor belt is moving at a constant speed of 1.5ms–1. Calculate the horizontal force required to keep the belt moving. Horizontal force = ………………(4) 10A stationary radioactive nucleus of mass M ejects an alpha particle of mass m at a speed of 2.0x107ms–1. Given M = 55m, calculate the kinetic energy of the alpha particle as a percentage of the final total kinetic energy. kinetic energy of the alpha particle = ……………..% [6]