Sed Rx Notes - Harnett County High School Wikispaces
advertisement

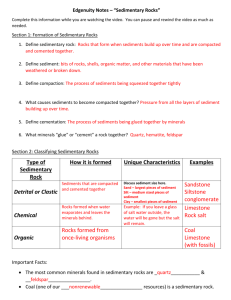
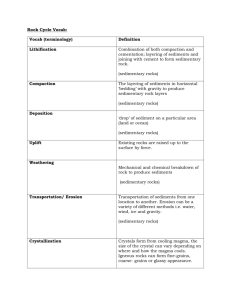
Sedimentary Rock Notes ________________ are pieces of solid material that have been deposited on Earth by wind, water, ice, gravity, or chemical precipitation. The formation of sedimentary rocks begins when weathering (breaking down) and erosion (transporting) of rocks to produce sediments. Weathering of existing rocks (igneous, metamorphic, or sedimentary) creates small fragments called ______________ sediments. The sediment particles range in size from _______________ to microscopic particles. See Table for particle sizes. After clastic sediments are transported (eroded) and deposited in a new location the process of lithification may begin if the conditions are favorable. The word lithify comes from the greek word lithos meaning “stone”. The first step of lithification is ________________. The weight of overlying sediments squeezes grains together forcing out any water or air present between the grains. Once the sediments are covered and buried deep enough underground (3-4 km) then the next step called _________________ can start to transform compacted sediments into rock. Cementation occurs when minerals grow between the grains causing them to become “stuck” together. As groundwater flows through compacted sediment, minerals such as calcite or iron oxide ________________ out of the water cementing the grains together. There are two major categories of sedimentary rock which are ________________ also known as detrital and ______________________ /biochemical. Overall classification of sedimentary rocks is based on how they are formed but each category has its own classification scheme. CLASTIC SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Clastic sedimentary rocks composed of loose sediments that have been cemented together are classified by _________________. Grain size ranges from clay-sized particles which cannot be seen when examining a rock to coarse-grained pebbles and gravel. The size, shape, and sorting of sediments within sedimentary rocks provides information about the environmental conditions at the time the sediments were deposited. When the particles are ____________ it suggests the sediment did not travel far, where if the particles are _______________ it could mean the particles were transported over long distances providing the time necessary to weather and round the grains. Sand-sized grains are indicative of beaches, river channels, deserts due to the constant transport that is needed to break sediment down to sand. CHEMICAL SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Chemical sedimentary rocks are formed by evaporation and precipitation. When water becomes _______________ with a particular mineral it means no more of that mineral can be dissolved in the water. When saturation is reached the mineral begins to crystallize (precipitate out of water) and settle to the bottom of the water body. This forms chemical sedimentary rocks called ____________________. These types of chemical rocks are normally found in __________ regions because little water flows in the area causing mineral concentrations to become high and crystallization to occur. Calcite, _________________ and gypsum are the three most common evaporites. Other types of chemical sedimentary rocks form as a result of _______________ material sinking to the bottom of the ocean or deep lakes. Living organisms makes their _______________ out of carbonate dissolved in the water. After the organisms ______ they sink to the bottom and a calcite layer forms resulting in the formation of __________________ after cementation and lithification occur. Limestone is the most common organic sedimentary rock. ___________________ is another form of organic sedimentary rock that is formed over a period of time after plant remains accumulate and become _______________ in swamp environments. Antarctica has ancient coal beds located under the layers of ice dating back to the ___________________ time period. This provides supporting evidence for scientists that the continents were once connected together near the ________________. Name of Particle Boulder Cobble Pebble Sand Silt Clay Size Range Loose Sediment >256 mm Gravel 64 - 256 mm Gravel 2 - 64 mm Gravel 1/16 - 2mm Sand 1/256 - 1/16 mm Silt <1/256 mm Clay Consolidated Rock Conglomerate or Breccia (depends on rounding) Sandstone Siltstone Claystone, mudstone, and shale (http://www.tulane.edu/~sanelson/geol111/sedrx.htm) Cross Bedding - Sets of beds that are inclined relative to one another. The beds are inclined in the direction that the wind or water was moving at the time of deposition. Boundaries between sets of cross beds usually represent an erosional surface. Very common in beach deposits, sand dunes, and river deposited sediment. . Graded Bedding - As current velocity decreases, first the larger or more dense particles are deposited followed by smaller particles. This results in bedding showing a decrease in grain size from the bottom of the bed to the top of the bed.