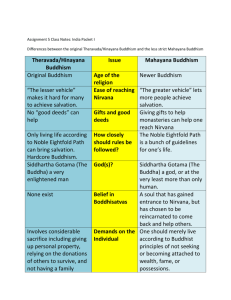
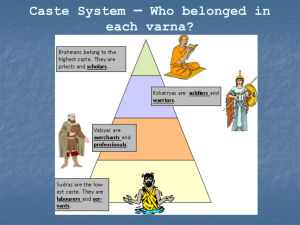
Buddhism - CLAS Users
advertisement

Ways to the Center, D.Carmody and T. Brink Questions on Chapter 8, Buddhism Identify the following individuals. Know when and where they lived, and which sect they are associated with, if applicable: Siddhartha Gautama Sakya King Srongsten Gampo Milarepa Dalai Lama Bodhidharma Hui-neng Tanluan Dengyo Daishi Kobo Daishi Ippen Nichiren Makiguchi Tsunesaburo Eisai Dogen Nagarjuna Identify the following entities: Amitabha, or Amida Maitreya Locate and identify the dominant Buddhist sect or school in each country or place: China Tibet Japan Burma Mount Shasta, California Know the meaning of the following terms: Samadhi Nirvana Mara Samsara Dharma Sangha Skandhas Arhat Tipitaka Sutras Stupas Hinayana Bodhisattvas Bodhi Sunyata Mahakaruna “twilight speech” Bonism chakras Abhidhmanna Lankavatara Sutra Koan Atman Sakyamuni karma Mudras jinguji Kami kazi zazen Ahimsa Know the significance of the following schools or sects, and their time periods: Yogacara Tantrism Indian guptadynasty Ge-lug Be able to answer the following questions: The Buddha What ends the cycle of rebirth? Who are Mara’s 3 daughters? Gautama’s enlightenment came after he sat under a _________tree and meditated for ____ days. In what way can the experience of enlightenment be conceived? What are the 4 stages of trance? What are the 4 Noble Truths? The Eightfold Path outlines what? Name all the parts of the 8-fold Path: The parts of the 8-fold path may be broken down into what three categories? The Dharma Dependent Co-Arising and the Eightfold Path Dependent Co-Arising is symbolized as a ___________ with _____ sections, or a chain to make _____ links (the first and last joined to make a circuit). Name all the parts of the Dependent Co-Arising: The Buddha’s Preaching In the Buddha’s first sermon after enlightenment, he prefaced it with a declaration of his____________ as an immortal enlightened one, which Buddhists conclude must be offered behind the dharma for it to have the intended effect. Buddhist Catechetics What are the 3 Marks of Reality? A fundamental difference between Hindus and Buddhists is: Name the 6 Realms or destinies (in order of lowest to highest). Which of these are punishment for bad and good deeds? Are punishments eternal? How may the human realm be reentered? Karma is meant to ____________ more than ____________. Early Buddhism After the Buddha’s death, what did he say should be the leader for his followers? Monasticism What are the 4 misdeeds that merited expulsion from the monastic order? Committing any of 13 lesser misdeeds led to what action? The Laity What color is a monk’s robe? Buddhist priests are more often involved in ___________services than in __________________ ceremonies. Name at least 3 symbols which represent the Buddha? Theravada Theravada is also known as, _______________ early Buddhism. because it claims ties with pristine Theravada stresses the importance of _____________for gaining freedom from illusions of self. Theravada Buddhism in Burma (Myanmar) focuses on what? Meditation What are the 3 Jewels of Buddhism? Mahayana Mark the following as either Mahayana or Theravada: Large raft Small raft Introduced concept of bodhisattva Buddha is “captain” of the boat Most like early Buddhist doctrine Hinayana The “Northern” tradition In which countries is Mahayana Buddhism dominant? In what countries is Theraveda Buddhism dominant? What are the two innovative teachings of the Mahayana school? Emptiness and Dialectics The Mahayana sutras known as ______________ centers on what doctrine? What is the fourth mark of all reality? The Diamond Sutra What is the lesson from the story in the Diamond Sutra? Mind-only Mind-only teaches what about reality? What is the school associated with Mind-Only? Mahayana Devotion Mahayana worked to change the Theraveda ideal of the arhat into what? What supreme compassionate act does a Bodhisattva commit for the unenlightened? Mahayanists saw Theravadan monks as too ______________? What are the 6 great “perfections” of Mahayanists in becoming a bodhisattva, which summarize Mahayana religious living? What are the 3 bodies the Buddha came to have? What happened to the distinction between buddhas and great bodhisattvas? Tantrism. In Tibet __________ combined with _________ to become the dominant Buddhist sect. What are Tantrism’s antecedents? Tantrism strove to symbolize the entire cosmic plan. For example, in Tantrism, stupa burial sites represented what? True or False: Tantrists were very open and vocal with their rites and teachings. What is the tantric term for the male sexual organs? What is the tantric term for the female sexual organs? Describe a typical Tantrist meditation: Tantrism stresses the relationship between ____________________, where the __________ represents tradition. Tibet Since the 8th century, Tibet owes more to _________ scholarship and philosophy than to ____________. The gradual penetration of enlightenment favored by Tibet and India, emphasizes what? What two things serve as the focus of Tibetan monastic life? Describe the typical day of a Tibetan monk: Prior to communist-Chinese occupation, what proportion of the population in Tibet lived in the monasteries? What is a Tibetan prayer wheel? What is its purpose? Tibetan Buddhism created its own version of the Tantrist doctrine that the _______________________________ are all potential sources of energy for enlightenment and wisdom. What are the two sects of Tantrism in Tibet, and to which does the Dalai Lama belong? What did the text compare the ancient Tibetan bon (“he who invokes the gods”) to? Based on a belief in ______________, there’s a practice of seeking to identify small boys as the next reincarnation of the Buddha, in Tibet. The one identified as the reincarnation will be the next _____________. What is the significance of the Tibetan Book of the Dead, and what does it describe? The Demise of Indian Buddhism When did Buddhism decline in India? What two factors contributed to its decline? In India, with the demise of Buddhism, _____________, became the native tradition that opposed the Muslims. Buddhism in China True or False: Buddhism was immediately adopted when introduced in China. The Chinese saw the human body as _________________, while Indian monks called it a ___________________________. In China, Buddhism was considered similar to _______________, that is, more as a philosophy. The Chinese, attracted more to ____________________, were interested in bridging the gap between the present and the time of Buddha by constructing what? Chan Name the 3 most popular sects of Buddhism in China: Explain why Chan Buddhism is the most mystical school in all of Mahayana. What is “wall gazing”? Pure Land What was probably the most popular sect of Buddhism in China? Which Buddha does it focus on? What does this sect stress as a way to achieve salvation? Popular Buddhism Why did the government of China build a network of official temples? What significance did the temple grounds have? Chinese Philosophy Compared with other Buddhist sects, Chan and the other native schools stressed living close to nature. Why? Conceptually, for Buddhism to be adopted, Indian ________________ had to be adapted to Chinese _______________. Government relations The golden age of Buddhism in China was during the ________ dynasty, from ___________ C.E. Name a regulation imposed by the government during the Sui and Tang dynasties that follows Buddhist doctrine: Why did the Sui and Tang dynasties build temples at the scene of foreign battles? Chinese society Supported by the Tang dynasty government, name some of the social services that Buddhist monks provided? Circle the correct answer: Buddhism in China attempted to increase/downplay social differences. Cite an example of this: Buddhism in Japan Buddhism co-existed with what native religion in Japan? Syncretism led to Japanese _________ seen as manifestations of Buddhist ___________. Tendai The new monastic foundation for Tendai was founded where? Which Sutra did it focus on? What was its primary emphasis? Tendai was important, as during the______________ era (1185-1333), came the leaders of which sects: Shingon The word Shingon means what? What did Shingon focus on? Amida Amida bodhisattva became the most influential form of devotional Buddhism during the Kamakura period. Amida Buddha is also known as ____________, and is worshipped in the ____________ sect. This form of Buddhism required a _________ commitment, rather than _____________________________. Nichiren Nichiren, founder of the Nichiren sect, focused on which sutra, which he considered of what significance? What was Nichiren’s apocalyptic message? What did he demand must be built, and what were some of his predictions? Tracing its roots to Nichiren, the _______________ leaders refused the Japanese government’s request during WWII to support the military effort, arguing that compliance would compromise the truth of the Lotus Sutra. This movement has been criticized as being ____________. Has been exported to west under name, _________________. Japanese Zen Eisai introduced to Japan, the __________ school of Zen, which used __________ as help to sudden enlightenment. Dogen sought to establish the _________ school of Zen, which concentrated on the ________________ and led him to a practice of simple meditation called ____________. Japanese society Japan was a culture of ____________ to which Buddhism offered a sense of _______________. Contemporary Buddhist Rituals It is insulting to place a statue of the Buddha where? Which side of a house is most auspicious? A Buddhist rosary contains _(how many?) beads, one for each of the marks on the ________ of the Buddha, which represent his ______________. What is the major difference between the monastic ritualism of Mount Shasta and the lay ritualism of Burmese Buddhism? What is the view of Nature in Buddhism? How does this change with a reanalysis of Samsara and Nirvana? The most popular Buddhist movements were built on the Indian traditions of ____________. Popular Buddhism fixed on which 3 bodhisattvas? How did devotion to them change the popular religious imagination? What was the Buddha’s stance on both the Vedas and caste system of India? What is the status of women in Buddhism? What was the relationship between the monasteries and laity? What influenced this relationship? The concept of ahimsa is fundamental to Buddhism. What is ahimsa, and how do Buddhist political leaders resolve the conflict of ahimsa when in a position of war? Is there capital punishment in Buddhist countries? What is the conflict of the self in Buddhism? How does Buddhism counsel to regard family members? How is society then, ideally viewed? Is Buddhism a theistic religion? How do each of the two major schools of Buddhism answer this question? When we realize that reality is a seamless cloth, we can enjoy all its various designs. At that point, Buddhist selfhood will be properly achieved. It will then be found to be what? ____________