CASE STUDY ON COASTAL MANAGEMENT
advertisement

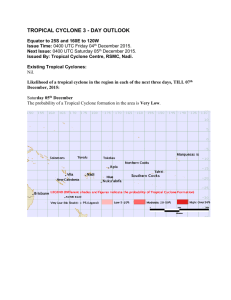
Case Study: “Coastal Management in Australia.” Student Name: Class: 1 CASE STUDY OF A CONTEMPORARY AUSTRALIAN GEOGRAPHICAL ISSUE. 2. COASTAL MANAGEMENT Background to the problem: Australia has 60,000 kilometres of coastline with over 10,000 separate beaches. Approximately 80% of Australia’s population live in cities and towns that are in close proximity to the coast. Over 50% of Australia’s Gross Domestic Product is produced in coastal areas. Human activities, as well as natural causes, impact enormously on our coastal environments. Go to: http://www.planetware.com/i/map/AUS/australia-distribution-of-population-map.jpg Copy and paste this Image into the space below. 2 1. Briefly describe this distribution of Australia’s population. Most of Australias population is in costal regions in Australia. And most are around the capital citys because most of the capital citys are on the water. 2. - List 3 problems this would cause to Australia’s coastline. Litter in the ocean Disturbing ocean life Killing ocean life The majority of Australia’s World Heritage sites are located in our coastal zone. These cultural and natural heritage sites include: The Great Barrier Reef Lord Howe Island Fraser Island Shark Island “Fraser Island.” Go to: http://www.tourfraserisland.com.au/un_np.php read the web page and respond to the questions below: 1. Outline why Fraser Island is a World Heritage Site. Because it is the worlds largest sand island and to protect the fragile environment. 2. When did Fraser Island become a World Heritage Site? 1992 3. What did UNESCO see as being the biggest threat to Fraser Island’s fragile environment? Being overrun by vistors 4. Copy and paste an appropriate THREE Images of Fraser Island that represents the unique and fragile environment into the space below. 3 4 Problems with our Coastal Zone: Natural Problems Man Made Problems * Coastal Erosion * Coastal Storms * King Tides and Cyclones * Mining * Water Pollution * Building too close to the coast To maintain our coastal environments we have to manage them in a sustainable manner. “Our use of coastal resources must meet the needs of the present population without endangering the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” Natural Problem: Environmental Effects of Tropical Cyclone Larry (2006). Go to: http://www.gbrmpa.gov.au/corp_site/info_services/publications/sotr/latest_updat es/environmental_effects_of_tropical_cyclone_larry_-_prcis read the “Summary” on the web page and respond to the following questions in the space below: Nature of the problem (causes): 1. Copy and paste the path of Cyclone Larry. 2. When did Tropical Cyclone Larry cross the Queensland coast? 5 7am on the 20th March 3. Which town was the closest to the Tropical Cyclone? Babindia and Silkwood 4. What Category was the Cyclone? 4 5. How damaging were the winds? Very damaging 6. Where were the winds most destructive? Between Carins and Tully Impacts (problems): 7. What environmental problems did Tropical Cyclone Larry create for the coral reefs? Coral breakage, Matrix exfoliation, torn soft coral, rubble filled gutters 8. Copy and paste the photograph of dislodged and broken coral. 9. What environmental damage was evident to the flora and fauna on Russell Island? Damage to vegetation, broken branches, erosion, debris were deposited. 6 10. Copy and paste THREE appropriate Images of Cyclone Larry. Responses (solutions): 11. What solution, if any, is there to the environmental damage caused by Tropical Cyclones such as Larry in 2006. Portable homes will be pieced together and trucked or trained into the Innisfail region for up to 50 families still without a place to live. Recovery task force leader General Peter Cosgrove referred to the figure as "a handful of families" on ABC Radio. The temporary homes will not have the amenities of a permanent dwelling, such as basic kitchens. The rush is now on to complete rebuilding work within nine months, before the start of the next 'wet' season, when rains are at their heaviest and the area becomes prone once more to cyclones. More than 10,000 tarps still cover damaged roofs. Broken windows in hundreds of homes are boarded up with plastic sheeting, sheets of plywood and corrugated iron. Posted by Darryl Mason at 12:50 AM Man Made Problems: Water Pollution of Sydney’s Beaches. 7 Go to: http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/beach/waterpollution.htm read the web page and respond to the following questions: Nature of the problem (causes): 1. What problems are caused to Sydney’s Beaches by: a. Stormwater: When it rains contaminates including litter, cigarette butts, oil ect. flow into the water b. Sewerage overflow: I cant contaminate the ocean c. People’s usage of the beach: “ Plastic litter, food scraps and fishing waste left by beach users can impact on beach amenity for a considerable time, particularly at busy times of year. ” d. Google, copy and paste THREE appropriate Images of “stormwater and sewage overflow on Sydney’s beaches” into the space below. Impacts (problems): 2. How would these examples of water pollution on Sydney’s beaches affect people’s use of the beach? 8 It can encourage people to change there ways and improve the way they treat the beach Responses (solutions): 3. How do Sewerage Treatment Works help to resolve the problem? “ Treatment classifications range from 'primary' treatment which involves removing solids from liquid waste to 'tertiary', the highest level, which involves removal of solids, dissolved and suspended organic and inorganic solids, inorganic compounds, and substances such as the plant nutrients nitrogen and phosphorus. Disinfection, to kill pathogens, can also be added to all levels of treatment. ” 9