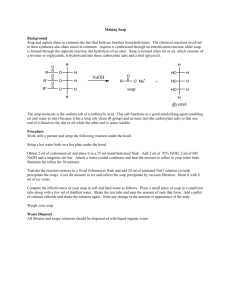
process and quality factors in laundary and toilet soap
advertisement

Process And Quality Factors In Laundry And Toilet Soap Production TABLE OF CONTENT Content Title page Letter of transmittal Approval page Dedication Abstract Table of content CAPTER ONE Introduction Scope and objective of projects Chapter two Literature survey History of soap making Raw materials used for soap making Soap manufacturing processes Processes and steps involved in production of soap Quality factors in soap production page Chapter three Experimental procedures Equipment and materials used General procedure Experimental procedure for laundry soap Experimental procedure for toilt soap Experimental analysis Determinations of saponification value Determination of free falty acid Determination of free caustic alkali Determination of moisture content Determination of PA of soap Chapter four Experimental results Discussion CHAPTER FIVE Conclusion Recommendation References Appendices CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION Soap is a class of products that serves for cleaning of human, property and surrounding. Hence, soap in its various forms, is in high demand in all society. For generations its use has increased until its manufacture has become an industry essential to the comfort and health of civilized man. In fact, modern civilization may be gauged by the per capital consumption of soap and detergents. Soap a classical example of detergent (cleaning agent) – differs from detergent in processes of manufacture and chemical composition. These result in differences in action. Soap depends for its washing action on the fact that its molecules possess one ionic (polar, water – attracting or hydrophilic) end and one covalent (nonpolar, water repelling or hydrophobic) end which attracts oils and greases. Thus, soap molecules can make water and oils come into an emulsion which can be washed away. This is the modern concepts of surface active agents or surfactants; soap, detergents, emulsifiers, wetting agents and penetrants. Soap is not, however, satisfactory, as it forms a scum (precipitate of insoluble calcium and magnesium salts) in hard and acidic waters. Synthetic detergents, on the other hand, do not form a scum in hard or acidic water as their calcium and magnesium salts are solute, are usually more soluble in water than soap is; enable water to spread and penetrate more fully over or through an article being cleaned and can generally be used equally well under alkaline or acidic conditions. Soaps are essentially the sodium or potassium salts of various fatty acids, while detergents are very complex mixtures of many substances, all chosen to impart a particular action in cleaning. The polar end of the detergent molecule consists of sulphonic acid ( - SO3H) or hydrogen sulphate (-OSO3H) group present in the form of its sodium salt to increase solubility. The non-polar end of the detergent molecule is a long alkyl – substituted benzene chain. Extensively branched chains are not biochemically degradable and such detergents cause pollution in rivers and sea wage waters. Soap also contains additives for some desired qualities. These include salt, soda ash, sodium silicate, sodium bicarbonate, perfume, colour, citric acid, borax, magnesium sulphate, and trisodium phosphate. A combination of inexpensive builders, e.g. soda ash with more effective (and expensive) tetrasoium pyrophosphate or sodium triphasphate, is sometimes superior to the phasphate used alone. Although the use of soap has declined since World War II, majority of the world’s toilet tablets are still soap, and in the developing countries hard soap bars are still the most important fabric washing products. Also, a substantial proportion of the fabric – washing powder used in the United Kingdom is soap powder. Other uses of soaps are in textile finishing, emulsion polymerization, cosmetics and polishes. Basically, all soap is made by saponification, that is the hydrolysis of naturally occurring fats and oil by sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) or potassium hydroxide (caustic potash). Various additives have been used to impart some specific characteristics to the products. The qualities and properties affecting soap and also the processing (which forms the basis of this project) depend on factors such as the nature and type of oil used, the type of alkali used and also on the proportion of mixture of both major raw materials. SCOPE AND OBJECTIVE OF PROJECT Soap can be produced with a variety of raw materials, using several processes and thus obtaining varying qualities. However, from the literature survey, it was found that various types of oils differed, consequently, their soap products different. In this work, soap is to be produced using palm oil and palm kernel oil respectively. The objective is to compare the qualities of the soaps made from these oils and also the processing involved for laundry and toilet soap production. The work entails working out the soap formulas and using the formulations to produce soap. The two soaps so produced will then be tested analytically to determine their various physical and chemical properties. From the results obtained from the various analytical test, distinguished process qualities of the two soap will then be deduced. Finally, recommendation will be made to aid further research on the project. *** INSTRUCTIONS *** Please Read The Below Instructions Carefully. ****************************** HOW TO ORDER THIS COMPLETE MATERIAL If you want to order the complete materials (Chapter One to Five, Including Abstract, References, Questionnaires, Proposal (where applicable)) of the above mentioned topic, please visit www.freeplace.org and click on “Order” (i.e. www.freeplace.org/order) ****************************** HOW TO BECOME OUR PARTNER To become our partner, visit www.freeplace.org and click on partnership. ****************************** TERMS OF USE This Material is for Academic Research Purposes only. On no account should you copy this material word for word. Copying this material “Word for Word” is against our “Terms of Use”. That you ordered this material shows you have agreed Our ‘Terms of Use’. ****************************** Better is not good enough, the best is yet to come! Endeavour to be the best!!