Course: RMPS, Level: National 4
advertisement

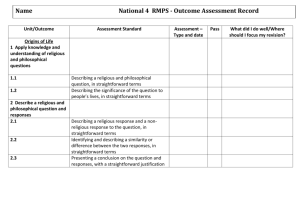
Course: RMPS Level: National 4 December 2012 This advice and guidance has been produced for teachers and other staff who provide learning, teaching and support as learners work towards qualifications. These materials have been designed to assist teachers and others with the delivery of programmes of learning within the new qualifications framework. These support materials, which are neither prescriptive nor exhaustive, provide suggestions on approaches to teaching and learning which will promote development of the necessary knowledge, understanding and skills. Staff are encouraged to draw on these materials, and existing materials, to develop their own programmes of learning which are appropriate to the needs of learners within their own context. Staff should also refer to the course and unit specifications and support notes which have been issued by the Scottish Qualifications Authority. http://www.sqa.org.uk Acknowledgement © Crown copyright 2012. You may re-use this information (excluding logos) free of charge in any format or medium, under the terms of the Open Government Licence. To view this licence, visit http://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-governmentlicence/ or e-mail: psi@nationalarchives.gsi.gov.uk. Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned. Any enquiries regarding this document/publication should be sent to us at enquiries@educationscotland.gov.uk. This document is also available from our website at www.educationscotland.gov.uk. 2 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 Contents Introduction 4 World Religion 11 Morality and Belief 14 Religious and Philosophical Questions 17 Added Value Unit 19 Links to resources 28 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 3 INTRODUCTION Introduction This resource provides advice and guidance for RMPS staff. There are four units of study: World Religion Morality and Belief Religious and Philosophical Questions Added Value Unit. Where learners are studying for a course award at National 4, they are required to complete all units. RMPS National 4 units do not have specified content. RMPS National 4 builds on the knowledge and skills learners will have experienced in the Broad General Education. Staff are therefore required to take account of a learner’s prior knowledge to plan for programmes of learning which promote progression and allow for challenge, breadth and application. Before embarking on this course, staff should be familiar with the contents of the religious and moral education (RME) principles and practice paper. http://www.educationscotland.gov.uk/learningteachingandassessment/curricul umareas/rme/nondenominational/principlesandpractice/index.asp Staff should also read the RMPS National 4 Professional Focus Paper produced by Education Scotland to ensure that they have familiarised themselves with the key areas of significant change and potential approaches to teaching and learning. http://www.educationscotland.gov.uk/nationalqualifications/professionalfocusp apers/index.asp 4 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 INTRODUCTION Guidance for staff Links to prior learning Entry to the course is at the discretion of the centre. However, learners would normally be expected to have attained the skills, knowledge and understanding required by one of the following: relevant experiences and outcomes from RME RMPS National 3 course or relevant component units. Progression in learning and skills The RMPS courses from National 3 through to Higher are organised in a hierarchical structure to allow for progression. The unit titles from National 3 to Higher are the same. This facilitates teaching situations where learners working at two or more levels are taught in the same class. The exception is the Added Value Unit, which is part of the RMPS National 4 course, but is not part of the RMPS course at any other level. Learning should be progressive and not repetitive. It is important that any content at one particular SCQF level is not repeated excessively as a learner progresses to the next level of the hierarchy. The range of options within each unit allows for skills progression in the context of new subject content. This will enrich the learning experience and offers opportunities to embed and extend skills. New and stimulating contexts for learning should be introduced throughout to encourage learners to achieve at their highest level. Aims of RMPS National 4 As stated in the SQA Course Specification document, the main aims of RMPS National 4 are to enable learners to develop: the ability to understand and reflect on religious, moral and philosophical questions and their impact a range of skills including investigating and describing religious, moral and philosophical questions and responses, making comparisons, and the ability to express reasoned views RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 5 INTRODUCTION straightforward knowledge and understanding of beliefs, practices and sources related to world religions straightforward knowledge and understanding of religious, moral and philosophical questions and responses to them. 6 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 INTRODUCTION Gathering evidence Assessment should be an ongoing process that permeates effective learning and teaching. As such, staff are encouraged to adopt imaginative and creative approaches to assessment that take account of a learner’s experience in terms of challenge, breadth and application. Whilst RMPS National 4 will have no final course assessment, the development of knowledge and skills remains a key factor in lesson planning. Staff are encouraged to develop approaches to learning and teaching that take account of a learner’s prior learning in the Broad General Education. Building on this, staff should be mindful of the need for progression within National 4 and should develop approaches that allow learners to be challenged at the appropriate level. For unit assessment purposes, a variety of methods of assessment should be used to gather a rich range of evidence such as digital presentations, recorded DVD/video, written work, podcasts, wall displays and oral presentations. Staff should share learning and assessment criteria with learners, provide effective feedback, encourage peer and self-assessment, and use effective questioning techniques. There should be opportunities for evidence to occur naturally as part of learning activities. Units can be assessed individually or, if learners are undertaking more than one unit or the RMPS National 4 course, may be assessed by combined assessment covering more than one unit, or by portfolio. Interdisciplinary learning Parts of the course may be suitable for teaching using interdisciplinary learning (IDL) approaches. IDL involving RMPS has the potential to offer valuable opportunities for learners to apply skills to new contexts, to experience learning that is broad and deep, and to experience the enrichment of connecting learning across disciplines. Good IDL should enhance learning in each of the disciplines involved and offer an appropriate level of challenge. RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 7 INTRODUCTION Where IDL approaches are used it will be important to have a good balance of activities and ensure that learners are supported to reflect on their learning and make specific connections to their learning in RMPS. IDL offers opportunities for learners to generate evidence required for unit assessment and, for example, could be an appropriate method of generating evidence for a portfolio. Skills, knowledge and understanding The skills, knowledge and understanding required for RMPS National 4 are shown in the box below. This list, from page 3 of the Course Support Notes, separates out the skills, the knowledge and understanding, and the added value of the course, which is contained in the Added Value Unit. Added value Researching and using information to present findings about straightforward, mainly factual, elements of religious, moral and philosophical topics or issues in a reasoned manner. Skills Describing and commenting on the meaning and context of sources related to world religions, in straightforward terms. Expressing views about contemporary moral questions and responses, in straightforward terms. describing religious and philosophical questions and responses, in straightforward terms Knowledge and understanding Straightforward factual knowledge and understanding of the impact and significance of religion today through studying some beliefs, practices and sources found within one of the world’s six major religions (Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism or Sikhism) and the contribution these make to the lives of followers. Straightforward knowledge and understanding of contemporary moral issues and responses. Straightforward knowledge and understanding of religious and philosophical questions and responses. Careful consideration of appropriate learning, teaching and assessment methodologies is necessary in order to ensure that learners have an opportunity to develop the range of skills necessary to be successful in RMPS National 4. 8 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 INTRODUCTION Where learners are undertaking the RMPS National 4 course, staff should ensure that skills development is embedded across the whole experience of the course and that, as learners develop skills, they are also able to articulate an awareness of the skills they are developing and are able to identify appropriate opportunities to apply particular skills. Assessment of skills In designing learning opportunities for learners, staff should seek to ensure that they build in opportunities for learners to develop skills. For the purposes of unit assessment each unit has an assigned skills focus, as described in the table below (see the Course Support Notes, page 6). World Religion Morality and Belief Religious and Philosophical Questions Describing and commenting on the meaning and context of religious sources Expressing views about moral questions and responses Describing religious and philosophical questions and responses Particular skills have been allocated to individual units for assessment purposes only. Where learners are undertaking the RMPS National 4 course, staff should ensure that learners have opportunities to develop and integrate skills across all the units. Integrated skills development RMPS National 4 offers opportunities to develop skills in an integrated way. Learners should be encouraged to explore and develop links across their learning. There are many opportunities for learners to apply what they have learnt in one area of learning to other contexts and situations. This enhances learning, helps to prepare learners for the Added Value Unit and can be used to provide appropriate challenge for learners at this level. The table below indicates where skills can be developed and gives examples of the sort of activities that may be used to develop the skills. This skill is an assessable skill for this unit This skill is not an assessable skill for this unit but there are many opportunities to develop this skill in this unit This skill is not an assessable skill for this unit but there are opportunities to develop this skill in this unit RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 9 INTRODUCTION Skill Researching and using information Presenting findings in a reasoned manner 10 Religious and Added Philosophical Value Unit Questions Religious and World Morality and Added Philosophical Religion Belief Value Unit Questions An example from the Added Value Unit Being able to choose two appropriate sources on the moral issue of capital punishment, identifying statements in the sources presenting arguments or evidence about capital punishment, organising the information into arguments and evidence in favour of capital punishment, and arguments and evidence against, and using the information to explain why some people support capital punishment and some do not. An example from Religious and Philosophical Questions Being able to investigate two different Christian views on the Genesis creations stories, searching for sources of relevant information, selecting and recording relevant information from sources, and using that information to describe the differences between those two different Christian views on the Genesis creation stories. Religious and World Morality and Added Philosophical Religion Belief Value Unit Questions An example from the Added Value Unit Being able to present (in any suitable format, eg spoken presentation, written report, information poster) in an ordered manner arguments and evidence that would be used on both sides of the debate on capital punishment. An example from World Religion Being able to present (in any suitable format, eg spoken presentation, written report, information poster) the results of research about the origins of the Khalsa in a clear and logical manner. World Religion RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 Morality and Belief INTRODUCTION Describing and commenting on the meaning and context of sources related to world religions Expressing views about contemporary moral questions and responses Describing religious and philosophical questions and responses Religious and Added Philosophical Value Unit Questions An example from World Religion Being able to describe the content and context of a quote from the Torah, and being able to comment on the meaning of the passage for Jews today. Religious and World Morality and Added Philosophical Religion Belief Value Unit Questions An example from Morality and Belief Being able to articulate a view on the question of whether or not gender stereotyping is harmful, understanding and being able to express a view on a feminist assertion that gender stereotyping limits the life choices of both women and men and is thus harmful. Religious and World Morality and Added Philosophical Religion Belief Value Unit Questions An example from Religious and Philosophical Questions Being able to describe the nature of suffering, providing examples of suffering and the causes of suffering, being able to explain why the existence of suffering might be a challenge to theistic belief, understanding and being able to explain responses to this challenge that may be given by theists. World Religion Morality and Belief Approaches to learning and teaching When considering approaches to learning and teaching it will be important to build on the diverse range of methodologies that learners will have experienced in the Broad General Education. A wide range of learning activities supports learner motivation and choice, as well as providing good opportunities for appropriate challenge and skills development. In addition, a wide range of learning activities, for example the sample activities provided in the following guidance, will provide opportunities for capturing naturally occurring evidence to support unit assessment. RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 11 WORLD RELIGION World Religion The World Religion unit has one outcome. Outcomes and assessment standards Outcome 1 The learner will: World Religion Unit Specification 1 Apply knowledge and understanding of the significance and impact of religion today by: 1.1 Describing the meaning of a source related to a world religion today, in straightforward terms Describing one key belief and one key practice related to the source, in straightforward terms Describing how the source informs the belief and practice, in straightforward terms Providing a straightforward comment on the significance of a religious belief, practice and source to people’s lives today 1.2 1.3 1.4 In this unit learners will study beliefs and practices, and relevant sources of authority from one of the following religions: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, Sikhism. A key part of facilitating successful learning in this unit is in helping learners to see connections between beliefs, practices and sources of authority. One way of visualising this is as a triangle with beliefs, practices and sources of authority making up the three sides of the religion triangle, each contributing, each related to the other two and the triangle incomplete without all three. 12 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 WORLD RELIGION Key questions to discuss will be: How is this belief/practice/source related to other beliefs, practices and sources that we have studied? What is the importance for believers of this belief/practice/source? What has been and what is today the impact, on believers and on the world, of this belief/practice/source? Example activity Giant mind map This activity is designed to help learners to see connections between beliefs, practices and sources. Provide learners with sticky notes or small slips of paper. Working together, learners think of as many beliefs, practices and sources as they can and write each one on a separate sticky note. To develop an understanding of the difference between beliefs and practices, learners could be instructed to write beliefs, practices, and sources on different coloured sticky notes. Learners are then asked to think about the relationship between the beliefs, practices and sources they have written down. On a large sheet of flip-chart paper or directly onto a noticeboard learners work together to discuss the links between the things they have written on the sticky notes. At this level learners may need support in identifying links between ideas. Learners then use the beliefs, practices and sources on the sticky notes and the relationships they have discussed to create a giant mind map. It may be suitable to allow learners to do this directly onto desks with dry-wipe pens. A photo could be taken of the finished mind map before it is dismantled. In the course of this activity staff may observe or gather naturally occurring evidence that meets the outcomes and assessment standards of this unit for individual learners. The results of this activity or reflection on this activity may form part of a learner’s portfolio. A good source of other learning activities suitable for this unit is the resource Skills development in the study of a world religion, published on the Education Scotland website. The World Religion Unit Specification states that sources should be ‘extracts from sacred or official texts, accurate re-tellings of sacred texts, or non-textual sources which clearly describe aspects of the religion concerned’. The non-textual sources used could come from a visiting speaker, a visit to a place of worship or a video of a person of faith describing the importance of a particular religious artefact. An important part of this unit is understanding the significance and impact of religion today. The use of contemporary sources RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 13 WORLD RELIGION (such as visiting speakers or a video of a recorded debate) will support learners in understanding the contemporary significance of religion and the impact that religious belief has on believers and the world today. Helping learners to understand the differing nature of a range of sources of authority from within a religious tradition will be important. For example, in Islam understanding the different nature of authority contained in sources from the Qur’an, the Hadith or the rulings of Islamic scholars will be important. This can then be developed to consider the impact that sources from different authorities have on believers and on various groups of believers. 14 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 MORALITY AND BELIEF Morality and Belief The Morality and Belief unit has two outcomes. Outcomes and assessment standards Morality and Belief Unit Specification Outcome 1 The learner will: 1 Apply knowledge and understanding of contemporary moral questions and responses by: 1.1 Describing a contemporary moral question, in straightforward terms 1.2 Describing a religious and a non-religious response to the question, in straightforward terms Outcome 2 The learner will: 2 Express reasoned views about religious and non-religious responses to contemporary moral questions by: 2.1 Describing one possible consequence of a religious and a non-religious response to a contemporary moral question, in straightforward terms 2.2 Describing a possible strength and a possible weakness of a religious and a non-religious response to a contemporary moral question, in straightforward terms 2.3 Expressing a viewpoint on the question and responses, with a straightforward justification All learners should study the two moral perspectives, one which is religious and one which is non-religious. Learners should to be able to apply these two modes of thinking about morality to the option chosen for study. The focus in this unit must be on the study of morality and how morality and belief interact. While areas of knowledge and understanding in relation to particular moral issues must be covered, the moral issues chosen for study should be seen as the context for learning about morality and belief rather than as the subject of study itself. RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 15 MORALITY AND BELIEF Example activity Causing offence Ask learners to gather examples of situations reported in the media of instances where something that someone has said or written has led to controversy or caused offence. Examples could include a religious leader making unpopular statements about sexuality, a member of the public revealing information about or making offensive comments about the victim of a crime on social media or a celebrity making a statement perceived to be offensive. Learners should work together to select a particular case and to compile a list of facts about the case. Learners should choose or be assigned perspectives on the issue. The perspectives should include both religious and non-religious views, and some should be defending and some criticising the action being studied. Once they are familiar with the perspectives they are considering, learners can prepare contributions for a debate or produce a display or presentation Nondescribing the different perspectives Religious religious and the reasons someone may have response response for holding that position. Alternatively, learners could be given Defending a grid like the one shown and attempt the action to find responses that fit each set of Criticising criteria. If reading newspaper reports the action on the issue, the responses could be cut from the article and stuck on, or a large whole-class grid could be completed with all learners contributing. In the course of this activity staff may observe or gather naturally occurring evidence that meets the outcomes and assessment standards of this unit for individual learners. The results of this activity or reflection on this activity may form part of a learner’s portfolio. Note: This example is appropriate for this unit at RMPS National 4 and may be appropriate at RMPS National 5 where Morality and Belief is undertaken as a free-standing unit, but would not be appropriate for learners studying for the RMPS National 5 course. In RMPS National 4 there is no specified unit content so staff are free to choose topic areas of interest to their learners, provided that learners are addressing the unit outcomes. This flexible and responsive approach is encouraged. This is also true where RMPS National 5 units are taken as free-standing units. However, as there is set content for the RMPS National 5 course assessment, learners who are studying for the RMPS National 5 course will be required to study the specified content as described in the RMPS National 5 Course Assessment Specification. 16 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 MORALITY AND BELIEF A source of other active learning methodologies which are adaptable for this unit is the resource Skills development in the study of a world religion, published on the Education Scotland website. RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 17 RELIGIOUS AND PHILOSOPHICAL QUESTIONS Religious and Philosophical Questions The Religious and Philosophical Questions unit has two outcomes. Outcomes and assessment standards Religious and Philosophical Questions Unit Specification Outcome 1 The learner will: 1 Apply knowledge and understanding of religious and philosophical questions by: 1.1 Describing a religious and philosophical question, in straightforward terms Describing the significance of the question to people’s lives, in straightforward terms 1.2 Outcome 2 The learner will: 2 Describe a religious and philosophical question and responses by: 2.1 Describing a religious response and a non-religious response to the question, in straightforward terms Identifying and describing a similarity or difference between the two responses, in straightforward terms Presenting a conclusion on the question and responses, with a straightforward justification 2.2 2.3 This unit requires learners to be able to work with abstract ideas and concepts. Learners will at some point in this unit be required to describe and analyse positions that they themselves do not hold. In this unit learners may be presented with questions such as ‘If God exists, would he choose to let people suffer?’, ‘If there is no Creator, does my life have any purpose?’ or ‘If miracles do not happen, can I still believe in God?’ It is important for learners to be able to deal in a philosophical manner with such ‘if’ questions regardless of their own position. 18 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 RELIGIOUS AND PHILOSOPHICAL QUESTIONS Example activity Questionnaire This activity is designed to help learners to think about the significance of the question they are studying to people’s lives. Learners should consider the question they are studying, for example ‘Does God exist?’, and work in groups to generate a questionnaire based on that issue. For example, learners might come up with questions such as: 1 Do you believe in God? 2 Have you always believed that or have you changed your mind at some point? If you have, what made you change your mind? 3 If you answered yes to question 1, what is the main reason why you believe in God? 4 If you answered no to question 1, what is the main reason why you don’t believe in God? 5 If you answered yes to question 1, how would your life change if you saw proof that convinced you that God doesn’t exist? 6 If you answered no to question 1, how would your life change if you saw proof that convinced you that God does exist? 7 Do you think that believing in God makes life more meaningful? Why? 8 If you could meet God and ask God one question, what would you ask? Learners will benefit from creating the questionnaire in itself, but it would greatly enhance learning if learners had opportunities to ask people the questions they have generated. It may be possible to find one or more guest speaker willing to visit and answer the learners’ questions. Alternatively, the learners themselves could role-play a situation where a researcher was asking members of the public (with a range of views) the questions or where a presenter was asking contributors to a TV debate programme about the issue. In the course of this activity staff may observe or gather naturally occurring evidence that meets the outcomes and assessment standards of this unit for individual learners. The results of this activity or reflection on this activity may form part of a learner’s portfolio. A further source of other active learning methodologies which are adaptable for this unit is the resource Skills development in the study of a world religion, published on the Education Scotland website. RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 19 ADDED VALUE Added Value Unit The Added Value Unit has one outcome. Outcomes and assessment standards Added Value Unit Specification Outcome 1 The learner will: 1 Research and use information relating to a religious, moral or philosophical topic or issue by: 1.1 Choosing, with support, a religious, moral or philosophical topic or issue for study Collecting relevant evidence from at least two sources of information, including at least one religious viewpoint Organising and using the evidence collected to address the topic or issue Drawing on factual knowledge and understanding to describe and briefly explain some key features of the topic or issue Providing a straightforward description of the significance of the topic or issue to the contemporary world Presenting findings in response to the chosen topic or issue 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 This unit, as with all the other units, may be studied as a free-standing unit or as part of the RMPS National 4 course. Due to the flexibility, personalisation and choice inherent in this unit, as well as the focus on skills that are transferable to many other curricular areas, this unit may be a choice for staff who wish to offer the option of certification to learners in core RME for whom National 4 is an appropriate level. Education Scotland has produced a resource to support the delivery of the RMPS National 4 Added Value Unit, which can be found on the Education Scotland website or by following this link: RMPS National 4 Added Value Unit. 20 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 ADDED VALUE Qualifications The requirements for a qualification in RMPS National 4 are laid out in the SQA documentation, which can be accessed from: http://www.sqa.org.uk/sqa/47420.html. RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 21 ADDED VALUE Comparison across levels The following tables are designed to help staff to compare statements made in the SQA documents on skills, knowledge and understanding across levels and the outcomes and assessment standards across levels. The comparator statements for National 4 and the levels on either side of National 4 are shown side by side. National 3 National 4 Added value Researching and using information to present findings about straightforward, mainly factual, elements of religious, moral and philosophical topics or issues in a reasoned manner National 5 Added value Researching, processing and analysing information to draw conclusions and present findings about factual and theoretical elements of religious, moral and philosophical topics or issues in a reasoned manner, taking account of different ideas and viewpoints Skills Understanding and commenting on the meaning of sources related to world religions, in basic terms Expressing views about contemporary moral questions and responses, in basic terms Outlining religious and philosophical questions and responses, in basic terms Skills Describing and commenting on the meaning and context of sources related to world religions, in straightforward terms Expressing views about contemporary moral questions and responses, in straightforward terms Describing religious and philosophical questions and responses, in straightforward terms Skills Explaining and commenting on the meaning and context of sources related to world religions, in detail and referring to relevant abstract ideas Expressing reasoned views about contemporary moral questions and responses, in detail and referring to relevant theoretical ideas Analysing religious and philosophical questions and responses, in detail and referring to relevant theoretical ideas Skills, knowledge and understanding See: N3 Course Support Notes, page 3 N4 Course Support Notes, page 3 N5 Course Support Notes, page 3 22 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 ADDED VALUE Knowledge and understanding Basic knowledge and understanding of the impact and significance of religion today through studying some beliefs, practices and sources found within one of the world’s six major religions (Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism or Sikhism) and the contribution these make to the lives of followers Basic knowledge and understanding of contemporary moral issues and responses to them Basic knowledge and understanding of religious and philosophical questions and responses Knowledge and understanding Straightforward factual knowledge and understanding of the impact and significance of religion today through studying some beliefs, practices and sources found within one of the world’s six major religions (Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism or Sikhism) and the contribution these make to the lives of followers Straightforward knowledge and understanding of contemporary moral issues and responses Straightforward knowledge and understanding of religious and philosophical questions and responses Knowledge and understanding Detailed factual and theoretical knowledge and understanding of the impact and significance of religion today through studying some beliefs, practices and sources found within one of the world’s six major religions (Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism or Sikhism) and the contribution these make to the lives of followers Detailed factual and theoretical knowledge and understanding of contemporary moral issues and responses Detailed factual and theoretical knowledge and understanding of religious and philosophical questions and responses RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 23 ADDED VALUE Unit outcomes and assessment standards: World Religion National 3 Outcome 1 The learner will: 1 Apply knowledge and understanding of the impact and significance of religion today by: National 4 Outcome 1 The learner will: 1 Apply knowledge and understanding of the significance and impact of religion today by: National 5 Outcome 1 The learner will: 1 Apply knowledge and understanding of the impact and significance of religion today by: 1.1 Outlining the meaning of a source related to a world religion today, in basic terms 1.1 Describing the meaning of a source related to a world religion today, in straightforward terms 1.1 Explaining the meaning of a source related to a world religion today, in detail and with reference to relevant abstract ideas 1.2 Outlining one key belief and one key practice related to the source, in basic terms 1.2 Describing one key belief and one key practice related to the source, in straightforward terms 1.2 Explaining one key belief and one key practice related to the source, in detail and with reference to relevant abstract ideas 1.3 Providing a basic comment on the significance of a religious belief, practice or source to peoples’ lives today 1.3 Describing how the source informs the belief and practice, in straightforward terms 1.3 Explaining how the source informs the belief and practice, in detail and with reference to relevant abstract ideas 1.4 Providing a straightforward comment on the significance of a religious belief, practice and source to people’s lives today 1.4 Providing a detailed comment on the significance of a religious belief, practice and source to people’s lives today See: N3 World Religion Unit Specification N4 World Religion Unit Specification N5 World Religion Unit Specification 24 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 ADDED VALUE Unit outcomes and assessment standards: Morality and Belief See: N3 Morality an Belief Unit Specification N4 Morality and Belief Unit Specification N5 Morality and Belief Unit Specification National 3 Outcome 1 The learner will: 1 Apply knowledge and understanding of contemporary moral questions and responses by: National 4 Outcome 1 The learner will: 1 Apply knowledge and understanding of contemporary moral questions and responses by: National 5 Outcome 1 The learner will: 1 Apply knowledge and understanding of contemporary moral questions and responses by: 1.1 Outlining a contemporary moral question, in basic terms 1.1 Describing a contemporary moral question, in straightforward terms 1.1 Explaining a contemporary moral question, in detail and with reference to relevant theoretical or abstract ideas 1.2 Outlining a religious and a non-religious response to the question, in basic terms 1.2 Describing a religious and a nonreligious response to the question, in straightforward terms 1.2 Explaining a religious and a nonreligious response to the question, in detail and with reference to relevant theoretical or abstract ideas Outcome 2 The learner will: 2 Express reasoned views about religious and nonreligious responses to contemporary moral questions by: Outcome 2 The learner will: 2 Express detailed and reasoned views about religious and non-religious responses to contemporary moral questions by: 2.1 Describing one possible consequence of a religious and a non-religious response to a contemporary moral question, in straightforward terms 2.1 Explaining one possible consequence of a religious and a non-religious response to a contemporary moral question, in detail and with reference to relevant theoretical or abstract ideas 1.3 Outlining a potential consequences of a religious and a nonreligious response, in basic terms RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 25 ADDED VALUE 1.4 Expressing a viewpoint on the question and responses, in basic terms 26 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 2.2 Describing a possible strength and a possible weakness of a religious and a non-religious response to a contemporary moral question, in straightforward terms 2.2 Explaining a possible strength and a possible weakness of a religious and a nonreligious response to a contemporary moral question, in detail and with reference to relevant theoretical or abstract ideas 2.3 Expressing a viewpoint on the question and responses, with a straightforward justification 2.3 Expressing a detailed and reasoned viewpoint on the question and responses, with reference to supporting evidence and contrasting viewpoints ADDED VALUE Unit outcomes and assessment standards: Religious and Philosophical Questions See: N3 Religious and Philosophical Questions Unit Specification N4 Religious and Philosophical Questions Unit Specification National 3 Outcome 1 The learner will: 1 Apply knowledge and understanding of religious and philosophical questions and responses by: National 4 Outcome 1 The learner will: 1 Apply knowledge and understanding of religious and philosophical questions by: National 5 Outcome 1 The learner will: 1 Apply knowledge and understanding of religious and philosophical questions by: 1.1 Outlining a religious and philosophical question, in basic terms 1.1 Describing a religious and philosophical question, in straightforward terms 1.1 Explaining a religious and philosophical question, in detail and referring to relevant theoretical or abstract ideas 1.2 Outlining the significance of the question to people’s lives, in basic terms 1.2 Describing the significance of the question to people’s lives, in straightforward terms 1.2 Explaining the significance of the question to people’s lives, in detailed terms Outcome 2 The learner will: 2 Describe a religious and philosophical question and responses by: Outcome 2 The learner will: 2 Analyse a religious and philosophical question and responses by: 2.1 Describing a religious response and a non-religious response to the question, in straightforward terms 2.1 Explaining a religious response and a non-religious response to the question, in detail and referring to relevant theoretical or abstract ideas 2.2 Identifying and describing a similarity or difference between the two responses, in 2.2 Comparing and contrasting the two responses, in detail and referring to relevant N5 Religious and Philosophical Questions Unit Specification 1.3 Outlining the key features of a religious response to the question, in basic terms 1.4 Outlining the key features of a nonreligious response to the question, in basic terms RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 27 ADDED VALUE 28 RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 straightforward terms theoretical or abstract ideas 2.3 Presenting a conclusion on the question and responses, with a straightforward justification 2.3 Presenting a reasoned conclusion on the question and responses, with reference to supporting evidence and contrasting viewpoints ADDED VALUE Links to resources RME Principles and Practice RERC Principles and Practice Skills development in the study of a world religion: This resource offers guidance on methodologies for effective teaching and learning focused on skills development in the study of a world religion: National Qualifications support for RMPS. Testimony: This online resource is designed to support learners and RME staff within the senior phase. The site focuses on the importance of faith, belief and values to the lives of individuals and how these beliefs and values have impacted on their lives and influenced their actions. RMPS National 4 Added Value Unit: These materials have been created to support the teaching and delivery of the RMPS National 4 Added Value Unit (the RMPS assignment). Making Good Assessment Decisions 3–18 poster Advice and Support listed on the Education Scotland website. Some of these resources relate to previous qualifications (eg Intermediate 2) but staff may find helpful content within them. Staff will need to assess these against the new arrangements to ensure they are appropriate. Archive resources: A collection of RMPS resources that have been removed from the National Qualifications online database, but are still available for archive use and contain some relevant content. Staff will need to assess these against the new arrangements to ensure they are appropriate. RMPS (NATIONAL 4) © Crown copyright 2012 29