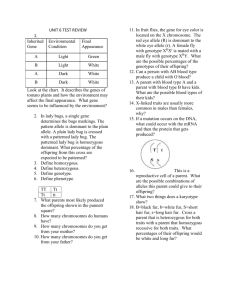
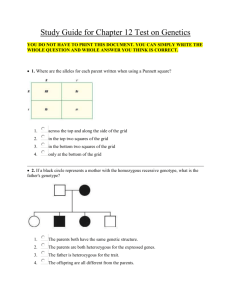
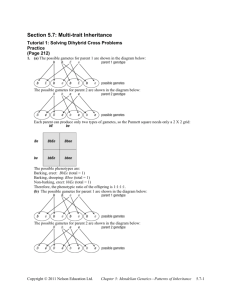
File
advertisement

1. In horses, black coat colour is influenced by the dominant allele (B) and chestnut coat colour by the recessive allele (b). Trotting gait is due to a dominant gene (T), pacing gait to the recessive allele (t). Horse trotting Horse pacing A horse trainer wanted to find the genotype of a black trotter she had just bought. (a) Give the genotype and phenotype of the horse she would use to find out the genotype of a black trotter. Explain your answer. (b) Use a Punnett square to work out the phenotypic ratio of all the possible offspring when a male black trotter that is heterozygous for both traits is mated with a female that is heterozygous for both traits. (c) Explain why, when breeding chestnuts together, she would not get any black foals, but when breeding black horses, she could get chestnut foals. 2. A rooster with grey feathers is mated with a hen with grey feathers. When their offspring are examined, there are 15 chicks with grey feathers, 6 with black, and 8 with white. a) What is the simplest explanation for the inheritance of these colours? b) What offspring would you predict from the mating of a grey rooster and a black hen? (do a punnet square cross to figure it out) 3. The genotype and phenotype of certain cat colours are shown in the table Phenotype Black Ginger Tortoise shell Genotype Male Female g XY XgXg G X Y XGXG XGXg A breeder has a number of black, ginger and tortoiseshell cats. a) If she wants all the female kittens to be tortoiseshell, what are the genotypes and phenotypes of the parents she should use? List all possible answers. b) What will be the phenotypes of the male kittens in the crosses you have suggested? 4. In tigers, a recessive gene codes for white fur, and another recessive gene codes for cross-eyes (these genes are on different chromosomes). Two tigers that appear normal (i.e. have a normal phenotype) but are heterozygous for both characteristics mate. a) What is the expected ratio of their offspring to show whit fur? b) What is the expected ratio of their offspring to show cross-eyes? c) What is the expected ratio of their offspring showing both characteristics? 5. Coat colour in an animal is controlled by two genes, each with two alleles B and b; E and e. The genes are found on different chromosomes. Their possible phenotypes and genotypes are shown here: Black BBEE BbEE BBEe BbEe Brown bbEE bbEe Golden BBee Bbee bbee a) What is the genotype of an animal heterozygous for both genes? b) What is the genotype of an animal homozygous for both genes? c) If the animal in a is mated to the animal in b, what would be the ratio of phenotypes in the offspring.? Show all your working clearly. 6. In rabbits, long fur is determined by the dominant gene R and short fur (rex) by the recessive allele r. Black fur is determined by the dominant gene B and the recessive characteristic, brown fur, by the gene b. a) A homozygous long-fur rabbit was crossed with a homozygous rex. What is the expected genotypes and phenotypes of their offspring? b) A rabbit of genotype RrBb was crossed with a rabbit which has short fur and is brown. What is the probability that the first rabbit born would be expected to be black and have short fur? c) A double heterozygous long-fur black male was crossed with many females of the same genotype. Out of 160 rabbit born, how many would be expected to be black and have short fur? d) Two long-fur black rabbits are crossed. In the first litter is one brown short-fur rabbit. What are the genotypes of the two parents? 7. The pedigree below shows the pattern of transmission of alleles from the mating of a Saddleback (a) and Danish Pied (d). Saddleback individuals are indicated by a solid upper half of the symbol: those showing Danish Pied are indicated by a shaded lower half. (c) (i) (ii) What is the genotype of I-2? Explain your answer to (i) above.