Y8-Unit-3-Student-2015
advertisement

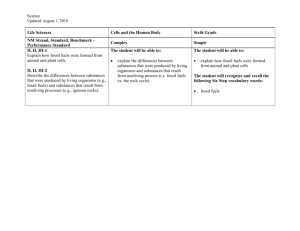
Year 8 Unit 3: Energy: A key resource Year 8 Unit 3: Energy: A key resource Year 8 Unit 3: Energy: A key resource This unit finishes at half term – Tick the bullet points when you can explain or do them This unit finishes at half term – Tick the bullet points when you can explain or do them This unit finishes at half term – Tick the bullet points when you can explain or do them At the end of this unit you will understand many of the following: At the end of this unit you will understand many of the following: At the end of this unit you will understand many of the following: That energy is a key resource What global warming is, and its predicted consequences That the fossil fuels are our main sources of energy How electricity is made, that different sources of energy can be used to make it That there are renewable and non-renewable sources of energy That use of a resource has to be planned and managed That having a resource that’s in demand (such as oil) can change a country That our intensive use of fossil fuels is harming the environment At the end of the unit you should also be able to do many of the following: Explain that we convert energy from fuels into other forms of energy (electricity, heat, light, movement) Explain what global warming is, and its link to fossil fuels; describe some predicted consequences Name the fossil fuels; explain that they are stores of energy and we can burn them directly, or use them to make electricity; say why oil is especially important Explain how electricity is generated, and describe different ways to make the turbine spin (from jets of steam to wind and waves) Give examples of renewable and non-renewable sources of energy Give the National Grid as an example of resource planning and management Describe how the discovery of oil has changed Dubai, and how it’s planning ahead for when the oil runs out Give at least five examples of how our use of fossil fuels can harm the environment That energy is a key resource What global warming is, and its predicted consequences That the fossil fuels are our main sources of energy How electricity is made, that different sources of energy can be used to make it That there are renewable and non-renewable sources of energy That use of a resource has to be planned and managed That having a resource that’s in demand (such as oil) can change a country That our intensive use of fossil fuels is harming the environment At the end of the unit you should also be able to do many of the following: Explain that we convert energy from fuels into other forms of energy (electricity, heat, light, movement) Explain what global warming is, and its link to fossil fuels; describe some predicted consequences Name the fossil fuels; explain that they are stores of energy and we can burn them directly, or use them to make electricity; say why oil is especially important Explain how electricity is generated, and describe different ways to make the turbine spin (from jets of steam to wind and waves) Give examples of renewable and non-renewable sources of energy Give the National Grid as an example of resource planning and management Describe how the discovery of oil has changed Dubai, and how it’s planning ahead for when the oil runs out Give at least five examples of how our use of fossil fuels can harm the environment That energy is a key resource What global warming is, and its predicted consequences That the fossil fuels are our main sources of energy How electricity is made, that different sources of energy can be used to make it That there are renewable and non-renewable sources of energy That use of a resource has to be planned and managed That having a resource that’s in demand (such as oil) can change a country That our intensive use of fossil fuels is harming the environment At the end of the unit you should also be able to do many of the following: Explain that we convert energy from fuels into other forms of energy (electricity, heat, light, movement) Explain what global warming is, and its link to fossil fuels; describe some predicted consequences Name the fossil fuels; explain that they are stores of energy and we can burn them directly, or use them to make electricity; say why oil is especially important Explain how electricity is generated, and describe different ways to make the turbine spin (from jets of steam to wind and waves) Give examples of renewable and non-renewable sources of energy Give the National Grid as an example of resource planning and management Describe how the discovery of oil has changed Dubai, and how it’s planning ahead for when the oil runs out Give at least five examples of how our use of fossil fuels can harm the environment Key words to learn: Key words to learn: Key words to learn: Global warming, power stations, non-renewable, renewable, fossil fuel; generate, electromagnet, turbine, hydroelectric, windfarm, National Grid, fossil fuels, developed, firewood, Middle East; tourism, information technology, trade, groundwater, desalinates; pipeline, tankers, acid rain, carbon dioxide, pollutant, particulates; greenhouse gas, climate change; onshore windfarm, offshore windfarm; solar power, kerosene. [R1 = Readiness / R2 = Relationships / R3 = Resourcefulness R4 = Resilience / R5 = Remembering / R6 = Reflective] Global warming, power stations, non-renewable, renewable, fossil fuel; generate, electromagnet, turbine, hydroelectric, windfarm, National Grid; fossil fuels, developed, firewood, Middle East; tourism, information technology, trade, groundwater, desalinates; pipeline, tankers, global warming, acid rain, carbon dioxide, pollutant, particulates; global warming, greenhouse gas, climate change; onshore windfarm, offshore windfarm; solar power, kerosene. [R1 = Readiness / R2 = Relationships / R3 = Resourcefulness R4 = Resilience / R5 = Remembering / R6 = Reflective] Global warming, power stations, non-renewable, renewable, fossil fuel; generate, electromagnet, turbine, hydroelectric, windfarm, National Grid; fossil fuels, developed, firewood, Middle East; tourism, information technology, trade, groundwater, desalinates; pipeline, tankers, global warming, acid rain, carbon dioxide, pollutant, particulates; global warming, greenhouse gas, climate change; onshore windfarm, offshore windfarm; solar power, kerosene. [R1 = Readiness / R2 = Relationships / R3 = Resourcefulness R4 = Resilience / R5 = Remembering / R6 = Reflective]