Chapter 18: Climate and Climate Change
advertisement

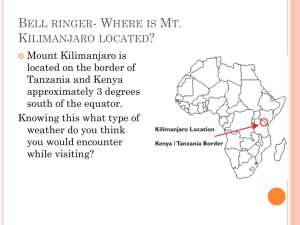
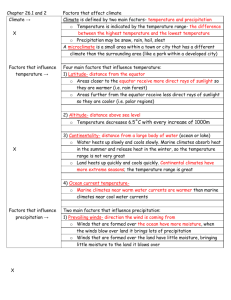
Chapter 18: Climate and Climate Change Section 1: What Causes Climate? Weather: condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time (short term) Climate: average conditions of temperature, precipitation, winds and clouds in an area (long term) What Causes Climate? 1. Temperature (cold or warm climate) 2. Precipitation (dry or humid climate) Factors Affecting Temperature 1. 2. 3. 4. Latitude Altitude Distance From Large Bodies of Water Ocean Currents 1. Latitude: The distance from the equator measured in degrees A climate zone is an area of Earth that has a certain temperature range and similar weather conditions. There are three main climate zones: The Tropical zone, The Polar zones, and the Temperate zones. Tropical Zones: warm climates Temperate Zones: ranging temperatures Polar Zones: cold climates Regions with latitude closer to the equator receive more solar radiation 2. Altitude elevation above sea level High land areas have cooler climates Higher altitudes = cooler temperatures Lower altitudes = warmer temperatures 3. Distance From Large Bodies of Water Large bodies of water affect climates by absorbing or giving off heat Large bodies of water can cause areas to be warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer. 4. Ocean Currents Why do warm currents begin near the equator? Because the equator receives the most direct sunlight. The equator is located at the midsection of the Northern and Southern hemispheres, so it receives the most direct sunlight. Factors Affecting Precipitation Prevailing Winds Mountain Ranges Prevailing Winds movement of air masses caused by directional winds in a region The amount of water vapor in an air mass influences how much rain or snow will fall The amount of water vapor in the prevailing wind depends on where the wind comes from Mountain Ranges Air forced up the mountain cools, condenses, and creates clouds Falls as precipitation on windward side Leeward side of mountain has drier conditions Why doesn't air in the mountains absorb heat as well as air found at sea level? The atmosphere and air is thinner. In the mountains, the air and the atmosphere are thinner and have fewer molecules to absorb heat. As air rises and cools it releases heat and precipitation Why are deserts are commonly found on the leeward sides of mountains? The leeward side of a mountain is the side where air descends, heats up, and dries up the land. Microclimates: small region with specific climate conditions Examples: parks, cities, areas near lakes or ponds, gardens, etc. THE REASONS FOR THE SEASONS The Earth's seasons are not caused by the differences in the distance from the Sun throughout the year (these differences are extremely small). The seasons are the result of the tilt of the Earth's axis. When the tilt of Earth increases, the change between winter and summer is greater. When the tilt of Earth decreases, the change between winter and summer lesser. Climate conditions and weather are affected by how directly the Sun’s rays strike an area. The Sun’s rays are most direct at the equator, giving it the warmest climate. The poles are the coldest places on Earth, because they get the least amount of sunlight.