Infant of Diabetic Mother: Medication Controlled
advertisement

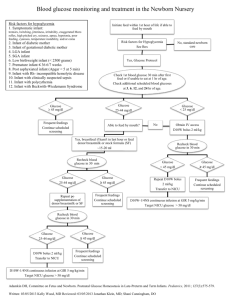
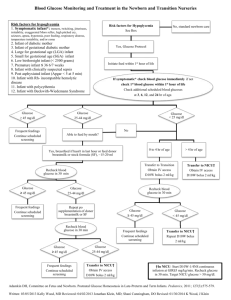
POLICY/PROCEDURE TITLE: INFANT OF THE DIABETIC MOTHER – MEDICATION CONTROLLED Women & Infant Services RELATED TO: [ ] Medical Center Policy (MCP) [ ] Nursing Practice Stds. [ x ] TJC [ ] Patient Care Stds. [ ] QA [ ] Other [ ] ADMINISTRATIVE [ x] CLINICAL Effective date: 03/04 Revision date: 01/04, 03/04, 04/04, 05/04, 06/05, 5/10, 7/10 Reviewed: 04/08, 5/09 Unit/Department of Origin: ISCC [ ] Title 22 Other Approval: L&D, FMCC, Birth Center POLICY STATEMENT: I. PAGE 1 OF4 To provide guidelines for early identification and appropriate management of the term infant of a medication controlled diabetic mother. A. Infants of Diabetic mothers have increased incidence of: Stillbirth Congenital malformations Premature delivery Perinatal mortality Neonatal mortality Infant mortality Cerebral palsy B. Possible effects on the baby of maternal hyperglycemia: Fetal hyperinsulinism Macrosomia and subsequent birth injury Respiratory distress Hypoglycemia Hypocalcemia Hypomagnesemia Polycythemia Hyperbilirubinemia Thrombotic events C. Care of the IDM infant: Review Maternal History Type of diabetes Degree of maternal control Prior OB history Other pregnancy complications Maternal medications, especially insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents. Intrapartum meds, glucose drip, insulin, etc. Fetal assessment UCSD Medical Center IDM – MEDICATION CONTROLLED Page 2 In the DR, assess for: ABC’s Macrosomia Birth injury Anomalies (cardiac, musculosketetal, CNS) Respiratory distress D. Who Goes to the ISCC? Any symptomatic hypoglycemic infant Any asymptomatic infant unable to maintain adequate glucose on oral feeds (see Hypoglycemia Policy & Procedure) Any infant with significant malformation Any birth injury causing compromise E. All Infants in the ISCC need: A physical exam by provider Glucose monitoring Ca, Mg, after 24 hrs if still in ISCC Bilirubin testing if indicated Cardiac echo if indicated (most of the Type 1 mothers have a prenatal fetal cardiac echo) CR Monitor & oximeter until glucose testing complete Begin feeds by 1 hour of birth, and feed q 3 hours (see attached IDM feeding guidelines – Appendix A). F. Glucose/Blood Sugar (BS) monitoring protocol: Testing: Check BS within 30 min of delivery, at 1 hour of life, at 2 hours of life, and thereafter ac. Infant will need 4 stable blood sugars prior to discontinuing BS checks. Treatment: BS > 45 If BS normal x4 (consecutively), no further testing required. BS 30-45 and baby is asymptomatic Initiate appropriate feeding: Breastfeeding: Put baby to breast, if breast feeds well repeat BS in 30 min o If > 45, continue BS testing and age appropriate feeding o If < 45 or baby not breastfeeding well give 10-15 ml standard term formula by SNS or finger feed(may bottle feed if not able to SNS/FF) and repeat BS in 30 min o If < 45 after formula, transfer infant to ISCC, begin IV glucose infusion of D10W at 4ml/kg/hr (7mg/kg/min of glucose), notify MD, and repeat BS in 30 min o If Not Breastfeeding: give 10-15 ml standard term formula by bottle and repeat BS in 30 min:If > 45, continue BS testing and age appropriate feeding o If < 45, transfer infant to ISCC, begin IV glucose infusion of D10W at 4ml/kg/hr (7mg/kg/min of glucose), notify MD, and repeat BS in 30 min 2/13/2016 UCSD Medical Center IDM – MEDICATION CONTROLLED Page 3 BS < 30, or < 45 and baby is symptomatic Transfer infant to ISCC Administer IV glucose bolus of 2 ml/kg of D10W, and begin IV glucose infusion of D10W at 4ml/kg/hr (7mg/kg/min of glucose), notify MD for increased glucose requirement & schedule of glucose monitoring. Recheck BS in 30 min (after bolus) o If BS > 45, re-check in 1 hr & resume q 3 hour testing o If BS < 45, repeat 2ml/kg D10W bolus and increase D10W IV rate by 1ml/kg/hour, repeat BS in 30 min and continue bolus/IV increase with q 30 min BS checks until BS remains > 45. When giving > 6 ml/kg/hr consider switching to D12.5 or the placement of a central catheter (to allow for the infusion of an elevated concentration of glucose) so as to avoid fluid overload. IV glucose weaning ac BS q 3 hours Continue or initiate q 3 hour feeds until infant is in couplet care and feeding well If ac BS is > 45, decrease IV rate by 1ml/kg/hr and continue to decrease IV rate 1ml/kg/hr thereafter for each ac BS > 45. Some very severe hypoglycemic infants may need to be weaned more slowly. Once IV glucose is discontinued, continue ac testing until 3 BS values >45 indicate infant is ready to come off treatment protocol. Readiness for transfer to Couplet Care Infant stable in regard to temp, cardiovascular, bili, etc. Infant feeding well orally and off IV glucose. Infants who have not required IV glucose may be transferred to FMCC for the final ac BS check if 2 consecutive ac BS checks are >45. Infants who have needed IV glucose and have had 1 normal ac BS off IV may be transferred to FMCC to complete 2 more ac BS check. If the baby requires supplementation of breastfeeds, please be sure that the FMCC staff is aware of the feeding plan. Documented feeding plan by provider prior to transfer. FMCC Care Feeding plan established in the ISCC will be continued until the medical team or lactation specialist re-evaluates the baby’s feeding needs. FMCC RN to notify HO if ac BS < 45 RESPONSIBLE PARTY: ISCC, L&D, FMCC Staff EQUIPMENT: 2/13/2016 Bedside glucose meter Chlorhexidine Gauze with tape or bandaid Safety flow lancet Nipple and bottle Formula 5 French gavage tube (for finger feeding) 10 syringe (if syringe feeding) UCSD Medical Center IDM – MEDICATION CONTROLLED Page 4 PROCEDURE: Perform bedside glucose test according to Blood Glucose Test for Point of Care Policy and Procedure and Blood Collection Heelstick / Fingerstick Policy and Procedure. REFERENCES: American Academy of Pediatrics; Policy Statement: Routine Evaluation of Blood Pressure, Hematocrit, and Glucose in Newborns (RE9322). Pediatrics. 1993; 92: 474-476. Deacon, J. and O’Neill, P. (1999). Core Curriculum for Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing (6th ed.) Philadelphia. WB Saunders Co. Cornblath, M., Hawdon, J., et al. Controversies Regarding Definition of Neonatal Hypoglycemia: Suggested Operational Thresholds. Pediatrics. 2000; 105: 1141-1145. Cowett, R. (2002). The Infant of the Diabetic Mother. NeoReviews; 3(9), p 173-189. Korones, S. B.; Bada-Elizey, H. (1993). Neonatal Decision Making (1st ed.) U.S., Mosby Year Book, Inc. Massachusetts General Hospital (1997). Infant of Diabetic Mother (Gest. Age > 37 wks) Clinical Pathway. Merenstein, G.B., & Gardner, S.L. (2010). Handbook of Neonatal Intensive Care. (7th ed.) St. Louis. Mosby. Polin, R. & Yoder, M.C. (2007). Workbook in practical neonatology (4th ed.) Philadelphia. Saunders. 2/13/2016 UCSD Medical Center IDM – MEDICATION CONTROLLED Page 5 APPENDIX A IDM in the ISCC/FMCC Feeding Guideline First 4 Days of Life To be used in conjunction with IDM – Medication Controlled Policy & Procedure I. Method Direct Breastfeeding q 1-3 hrs. whenever possible (MOB to be called whenever baby is showing signs of feeding cues) Cup/finger/supplemental nursing system (SNS) if supplement needed May bottle feed if SNS unsuccessful Formula babies will be bottle fed If breastfed infant requires supplement for: If asymptomatic hypoglycemia (blood sugar <45) have infant breastfeed, and re-check blood sugar in 30 minutes. If BS<30 or if <45 and the infant is symptomatic, give formula. **See Hypoglycemia Policy & Procedure and/or IDM – Medication Controlled policy & Procedure. II. Nutrient Breastmilk Formula babies will receive 20 calorie term formula Breastfed babies needing supplementation should receive 20 calorie term formula Mother should be pumping minimally q 3 hrs (6-8x/24 hrs) if unable to breast feed. III. Frequency of Feedings 0-24 hrs of life -- 6 - 8x 25-48 hrs -- 8-12x 49-96 hrs -- 8-12x IV. Quantity 0-24 hrs of life -- 5-15 ml 25-48 hrs of life -- 10-30 ml ad lib 49-96 hrs of life -- 30-60 ml ad lib V. Evidence of Successful Feeding Normal blood sugar (BS) testing Voiding/Stooling -DOL 1 -- min. 1 void/1 stool DOL 2 -- 2/2 DOL 3 -- 3/3 DOL 4 -- 6-8x/d <9%/day weight loss Baby content for 1-3 hrs after feeding 2/13/2016