INTERPRETING INFORMATION IN A PEDIGREE
advertisement

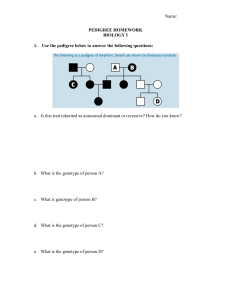
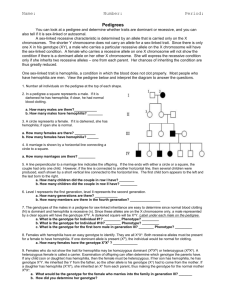
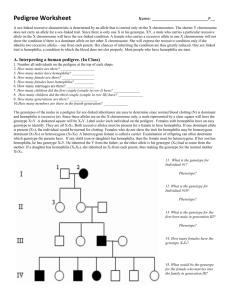
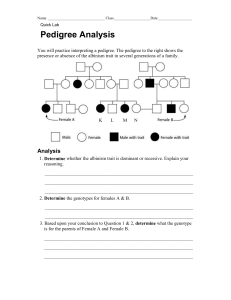
INTERPRETING INFORMATION IN A PEDIGREE Name ___________________ Date _________ Period _____ Organizing information is often the key to solving a problem. Tracing the hereditary characteristics over many generations can be especially confusing unless the information is well organized. In this activity, you will learn how to organize hereditary information, making it much easier to analyze. In this activity you will construct and analyze a pedigree. 1. Pedigree 1 traces the dimples trait through three generations of a family. Blackened symbols represent people with dimples. Dimples are inherited as a dominant trait. Circles represent females and square represent males. I I I 1 3 2 1 2 4 3 II I 4 5 1 Pedigree 1 2. The following passage describes the family shown in Pedigree 1. Although Jane and Joe Smith have dimples, their daughter, Clarissa does not. Joe’s dad has dimples, but his mother, and his sister, Grace do not. Jane’s dad, Mr. Renaldo, her brother, Jorge, and her sister, Emily, do not have dimples, but her mother does. 3. Write the name of each person below the correct symbol in Pedigree 1. How are marriage and offspring symbolized? ______________________________________________ What do the Roman numerals symbolize? ___________________________________ 4. Make a pedigree based on the following passage about freckles. Freckles are inherited as a dominant trait. Write the name and genotype of each individual under the appropriate symbol. Remember to include all of the parts of a pedigree. Andy, Penny, and Delbert have freckles, but their mother, Mrs. Cummins, does not. Mrs. Giordano, Mrs. Cummins sister, has freckles like her father, Mr. Lutz, but her mother, Mrs. Lutz does not have freckles. Deidra and Darlene Giordano are freckled, but their sister, Dixie, like her father, is not freckled. 5. What advantages does a pedigree have over a written passage? _____________________ ________________________________________________________________ 6. How does a pedigree organize hereditary information, making it easier to understand? _____________________________________________________________________ A HUMAN PEDIGREE Name ________________________ Date ___________ Period ________ A sex-linked characteristic is determined by an allele that is carried only on the X chromosome. The shorter Y chromosome does not carry an allele for a X-linked trait. Most sex-linked traits are recessive. Since there is only one X in his genotype, XY, a male who carries a particular recessive allele on the X chromosome will have the sex-linked condition. A female who carries a recessive allele on one X chromosome will not show the condition if there is a dominant allele on her other X chromosome. She will express the recessive condition only if she inherits two recessive alleles --- one from each parent. Her chances of inheriting the condition are thus greatly reduced. One sex-linked trait is hemophilia, a condition in which the blood does not clot properly. Most people who have hemophilia are men. In this investigation, you will determine why this is occurs. Procedure: 1. Study the pedigree for hemophilia shown in Figure A. In a pedigree, a square represents a male. If it is darkened, he has hemophilia; if clear, he has normal blood clotting. How many males represented by this pedigree have hemophilia? How many males are normal? # if males with hemophilia: __________ # of normal males: __________ 2. A circle represents a female. if clear, she is normal. If it is darkened, she has hemophilia; How many females in this pedigree have hemophilia? How many are normal? # if females with hemophilia: __________ # of normal females: __________ 3. A marriage is indicated by a horizontal line connecting a circle to a square. How many marriages are indicated in the pedigree? __________ 4. A line perpendicular to a marriage line indicates the offspring. If the line ends with either a circle or square, the couple had only one child. However, if the line is connected to another horizontal line, then several children were produced, each indicated by a short vertical line connected to the horizontal line. The oldest child appears to the left and the youngest child to the right. How many children did the first couple have? 5. II represents the second generation. generation, and so on. __________ III represents the third How many generations are represented in this pedigree? __________ Figure A I 1 2 1 3 2 1 2 3 4 4 5 6 5 6 7 7 8 I I 8 II I IV 1 2 3 4 5 6 Pedigree of Heredity 6. The genotypes of the males in a pedigree for sex-linked inheritance are easy to determine since normal blood clotting (XN) is dominant and hemophilia (Xn) is recessive. Since these alleles are on the X chromosome only, a male represented by a clear square will have the genotype XNY. One represented by a darkened square will be XnY. Label the genotypes of all the squares. How many males have the genotype XNY? _________________ 7. Females who have hemophilia have an easy genotype to identify. They are all XnXn. Both recessive alleles must be present for a female to have hemophilia. If one dominant allele is present (XN) the individual would be normal for clotting. Label all the females with hemophilia as genotype XnXn on the pedigree. How many women have genotype XnXn in this pedigree? _________________ 8. Females who do not show the trait for hemophilia may be homozygous dominant (XNXN) or heterozygous (XNXn). A heterozygous female is called a carrier. Examination of offspring can often determine which genotype the parents have. If any child (son or daughter) has hemophilia, then the female must be heterozygous (XNXn). If her son has hemophilia, he has genotype XnY. He inherited the Y from the father, so the other allele in his genotype (Xn) had to come from the n n mother. If a daughter has hemophilia (X X ), she inherited an Xn from each parent, thus making the genotype of the normal mother XnXn. Label all female XNXn that have children with hemophilia. What is the genotype of the female in the first generation? _____________ 9. Females who have more than four sons, with none exhibiting hemophilia, are likely to be genotype XNXN. If she has had four or fewer sons, her genotype is less certain. In such cases her genotype is labeled N ? as X X . Label the rest of the females in the pedigree as XNX? or XNXN. How many females in the pedigree have the genotype XNXN? __________ 10. The genotype of all people represented in the pedigree should now be labeled. Complete the following chart using the pedigree in figure B. Figure B I 1 1 2 3 2 4 5 6 7 8 I I II 2 3 9 1 4 7 10 I 8 5 6 11. Label the genotypes of the individuals in the pedigree of Figure B. Table B Pedigree Analysis 12. Fill in Table B based on the pedigree in Figure B. Questions about the pedigree in Figure B Number of generations Number of men with hemophilia Number of women with normal blood clotting Number of marriages Number of men with genotype XNY Number of women with genotype XnXn Number of single women Number of people that never married Number of women with genotype XNX? Number of couples with only one child Answer Analysis and Conclusions 1. Which sex usually inherits a sex-linked condition? Explain why. ___________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 2. How can you tell whether a female has a genotype XNXN, XNXn, or XNX?? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 3. How many genotypes are possible in a pedigree of sex-linked traits? _____ What are they? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________