Unit Planner
advertisement

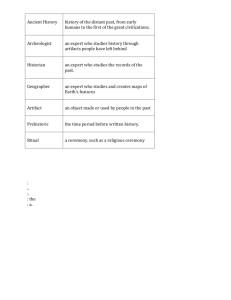
1 Critical Content/Concept Web Unit Topic: This unit of study will begin with the existence of humans and will end around 4000 BCE. Students will focus on the transition from prehistoric living to civilizations. Teachers could identify climatic changes which lead to migration. Teachers could identify the river valleys where the first civilizations developed. Teachers could reference the “Iceman Saga”. Beginnings of Human Conceptual Lens: Grade: Unit Overview Survival/Adaptation 6th social and political order Vocabulary People Duration: Unit Topic: Beginnings of Human Society ECONOMICS • • • • Hunter-Gatherers Shepherd/Nomadic Life Division of labor Development of small Farms GEOGRAPHY Physical Features Climatic Change Migration Civilization Region CULTURE Artifacts Agricultural inventions Complex society Religion Written language (pictographs to cuneiform) Migration Fertile Crescent HumanEnvironmental Interaction Mesopotamia City-state Civilization Social structure Merchant Artisan Scribe Ziggurat Cuneiform Pictograph technology “Lucy” “Iceman” Sumerians Hammurabi Assessments Formative: 1. Map 2. Responses to map activity 3. Cave man comic strip 4. Foldable – vocab 5. Compare/cont rast foldable – neo and paleo Summative: 1. Chapter tests – History alive 2. Era 1 Exam 2 Grade: 6th Subject: Social Studies Unit: “We’ve Only Just Begun” Lens: Survival/Adaptation Enduring Understandings Guiding Questions Global Perspectives 1. The needs of mankind result in the development of technology. 2. Artifacts are evidence of cultural change over time. 3. Change affects cultures. State Standards 6-9 WHC 1.6.1 Describe types of evidence used by anthropologists, archaeologists, and other scholars to reconstruct early human and cultural development. 1.6.2 Using archaeological evidence, describe the characteristics of early hunter-gatherer communities. 1. a. How is culture defined? b. What tools/artifacts were used by Paleolithic man? c. What tool/artifacts were used by Neolithic man? 2. a. How do artifacts reflect time, place, and human condition? b. What is the difference between a fossil and an artifact? 3. a. How is change beneficial/detrimental? b. What kinds of change affect cultures? What defines the change from the Paleolithic to Neolithic periods? Economics 4. Revolution of agriculture leads to division of labor. 5. Competition for economic resources and land result in movement and social conflict. State Standards WHC 1.7.2 Identify the technological advances developed by Ancient, Greco Roman, Medieval, Early-Modern, and Modern European societies and civilizations. 2.3.1 Identify main reasons for major migrations of people. 2.5.1 Explain how the resources of an area can be the source of conflict between competing groups. 3.1.1 Explain how historically people have relied on their natural resources to meet their needs. State Standards GEH 2.5.2 Analyze and give examples of the consequences of human impact on the physical environment and evaluate ways in which technology influences human capacity to modify the physical environment. 4. a. How did farming impact prehistoric peoples? b. How did domestication of animals impact prehistoric people? c. How did division of labor lead to specialization? 5. a. How does conflict alter land boundaries? b. How does the need for resources affect the location of the people? 3 Geography 6. Resources of a region determine types of food, clothing, shelter, and tools. 6. a. How do groups organize to meet their basic needs? b. What resources were available to prehistoric mankind? 7. The search for resources to meet basic needs determines migration patterns. State Standards WHC 2.1.1 Locate places on maps using latitude and longitude systems and compass directions 2.1.2 Locate and label on map or globe major rivers, mountain ranges, gulfs, and seas of the continents and their countries. 2.3.1 Identify main reasons for major migrations of people. 2.3.2 Explain how climate affects human migration and settlement. 2.4.1 Compare and contrast physical features on the planet 2.4.2 Explain the impact of waterways on civilizations. 2.5.1 Explain how the resources of an area can be the source of conflict between competing groups. .3.1.1 Explain how historically people have relied on their natural resources to meet their needs. 7. a. Why do groups move? b. How does geography impact people? c. What determines areas of settlement? Civics & Government 8. Governing systems organize citizenry to maintain order and achieve societal goals. a. Why do societies create systems to govern society and how do these systems differ across cultures and through time? History 9. Civilizations progress socially, economically and politically. State Standards WHC 1.6.3 Analyze the characteristics of early civilizations. 2.4.3 Identify the characteristics of significant early civilization. 3.2.2 Trace the evolution of hunting-gathering, agrarian, industrial and technological economic systems. State Standards GEH 1.8.4 Recognize historical perspective by identifying the context in which events occurred. a. What is the difference between Paleolithic man and Neolithic man? b. How did Neolithic society develop from Paleolithic people? c. What is the timeline for prehistoric man? 4 Grade: Subject: Unit: Lens: Survival/Adaptation Critical Content and Skills AC = Assessment Code: Students will Know… 1. Elements of physical geography such as water, topography, climate and natural resources affect the location and growth of ancient civilizations. 2. The history of ancient people is understood through tools, petroglyphs and other artifacts. 3. The development of agriculture and trade changed the way ancient people lived. 4. The worlds earliest people banded together to provide for their basic needs, creating the first civilizations. AC Q – Quizzes O – Observations D – Dialogues T - Tests Students will be able to… P - Prompts WS – Work Samples SA – Student Self-Assessment 1. Read and interpret maps. 2. Examine and draw conclusions from artifacts. 3. Compare technologies using artifacts between Neolithic and Paleolithic civilizations. 4. Identify the factors leading to the change from hunter/gatherer to agricultural societies. 5. Create, read and interpret timelines. AC 5 Grade: 6th Subject: Social Studies Unit: Prehistoric Society: Survival Lens: Survival/Adaptation Instructional Plan/Activities (Correlations) 1. Students will measure and mark equal intervals for grid lines with string and tape in place. Excavate the “dig-site” carefully using the tools and record findings/locations on grid paper marked with cardinal directions to match the pan. Students examine artifacts to draw conclusions about the culture. Assign materials a monetary value and have students plan a budget for the dig. Write a creative story about the culture using the found artifacts. 2. Students construct a graphic organizer identifying factors leading to change from hunter/gatherer to agricultural societies. Text Resources: History Alive 1. “From Paleolithic to Neolithic: Identifying Changes in Daily Life” chapters 1-10 *Additional Suggestions: Motel of Mysteries by David McCauley Digging into Archaeology Ancient History Simulations by Teacher Created Materials, Inc. 1. “Grapes and Nuts” Unit 1; Ch. 1 Harcourt Brace “Ancient Civilizations” 2 2-3 3-4 3-4 6 Performance Assessment Subject: Social Studies Common Core Objectives: RH 6, 7 Unit Topic: Beginnings of Humans (Resource: History Alive Chapter One) Grade: 6th Conceptual Lens: Survival/Adaptation What: The students will analyze and answer questions for the continent of Africa. Students will label and interpret the continent of Africa, including the Fertile Crescent. Students will use a given set of questions in order to label and interpret information for Africa and the Fertile Crescent. Why: To have students gain knowledge of the beginnings of civilizations. To have students understand how archeologists, historians, and geographers interpret and study the past. How: *Label and interpret information about Africa. *Use of reading notes (preview and section notes. *Create a cave painting *Students will play the role “detective of the past” and enter a cave that was once inhabited by early hominids (teacher created cave including student cave paintings, placards of “real” found cave paintings, and answer provided questions based upon the placards). *Wrap up the activities with a whole group class discussion. *Students will make a Venn diagram comparing student interpretations of the drawings vs. the intended meaning of the artist ************************************************************************************************** 7 Performance Assessment: Task and Rubric Subject: Social Studies Grade: 6th Unit Topic: Beginnings of Humans Conceptual Lens: Survival and Adaptation Task 1: *Label and interpret information about Africa *Use of reading notes (preview and section notes *Create a cave painting *Students will play the role “detective of the past” and enter a cave that was once inhabited by early hominids (teacher created cave including student cave paintings, placards of “real” found cave paintings, and answer provided questions based upon the placards) *Wrap up the activities with a whole group class discussion *Students will make a Venn diagram comparing student interpretations of the drawings vs. the intended meaning of the artist *Chapter One assessment: Multiple choice, open-ended response questions Rubric: Exemplary Extends the concepts and enduring understanding to include modern day applications Illustrations are realistic and creative representations of pictographs Unique and creative use of materials and space Proficient Illustrated and described the required enduring understandings or guiding questions Illustrations are realistic representations of pictographs/petrographs No grammar/mechanical errors Progressing Does not illustrate and describe enduring understandings Illustrations may not be factual or realistic Grammar and mechanical errors are present 8 Performance Assessment Subject: Social Studies Common Core Objectives: RH 1, 2, 7, 10 WHST 2, 4, 9, 10 Unit Topic: Beginnings of Humans (Resource: History Alive Chapter Three) Grade: 6th Conceptual Lens: Survival/Adaptation What: Compare and Contrast the Neolithic Age and Paleolithic Age Why: Students need to understand adaptations that civilizations made in order to survive How: Students will create a comic book ************************************************************************************************** 9 Performance Assessment: Task and Rubric Subject: Social Studies Grade: 6th Unit Topic: Beginnings of Humans Conceptual Lens: Survival and Adaptation Task 1: Students will create a comic book based upon the comparison of the two ages and the following categories: Creating a stable food supply, making permanent shelters, establishing communities, developing new jobs, and beginning trade. Rubric: Exemplary Extends the concepts and enduring understanding to include modern day applications Illustrations are realistic and creative representations of pictographs Unique and creative use of materials and space Proficient Illustrated and described the required enduring understandings or guiding questions Illustrations are realistic representations of pictographs/petrographs No grammar/mechanical errors Progressing Does not illustrate and describe enduring understandings Illustrations may not be factual or realistic Grammar and mechanical errors are present 10 Performance Assessment Subject: Social Studies Common Core Objectives: RH 4, 6, 7 WHST 1 Unit Topic: Beginnings of Humans (Resource: History Alive Chapter Four) Grade: 6th Conceptual Lens: Survival/Adaptation What: Students will provide solutions to the following four problems based upon the Mesopotamians: Food shortage, uncontrolled water supply, building and maintaining complex irrigation systems, a tax by neighboring communities Why: To describe the development of agriculture and other factors that lead to the emergence of city-states in Mesopotamia. List the key features of the city-states. How: Students will be presented with a “problem” and assume the role of a person of an ancient Mesopotamian. Evaluate which solution is the best and justify. Students will present to the class, as well as read the text to find out how the actual Mesopotamians problem solved. ************************************************************************************************** 11 Performance Assessment: Task and Rubric Subject: Social Studies Grade: 6th Unit Topic: Beginnings of Humans Conceptual Lens: Survival and Adaptation Task 1: Students will be presented with a “problem” and assume the role of a person of an ancient Mesopotamian. Evaluate which solution is the best and justify. Students will present to the class, as well as read the text to find out how the actual Mesopotamians problem solved. (Repeat for each of the above mentioned problems) Rubric: Exemplary Extends the concepts and enduring understanding to include modern day applications Illustrations are realistic and creative representations of pictographs Unique and creative use of materials and space Proficient Illustrated and described the required enduring understandings or guiding questions Illustrations are realistic representations of pictographs/petrographs No grammar/mechanical errors Progressing Does not illustrate and describe enduring understandings Illustrations may not be factual or realistic Grammar and mechanical errors are present 12 Performance Assessment Subject: Social Studies Common Core Objectives: RH 4, 6, 7 WHST 1 Unit Topic: Beginnings of Humans (Resource: History Alive Chapter Five) Grade: 6th Conceptual Lens: Survival/Adaptation What: Students will decide if ancient Sumer qualifies as a civilization Why: Students need to understands the components make up what is considered to be a civilization How: Students will complete the reading notes, as well as determining whether ancient Sumer artifacts and decide if the artifacts meet the qualifications. Characteristics: A stable food supply, social structure, government, religion, art, technology, and writing. ************************************************************************************************** 13 Performance Assessment: Task and Rubric Subject: Social Studies Grade: 6th Unit Topic: Beginnings of Humans Conceptual Lens: Survival and Adaptation Task 1: Students will complete the reading notes, as well as determining whether ancient Sumer artifacts and decide if the artifacts meet the qualifications. Characteristics: A stable food supply, social structure, government, religion, art, technology, and writing With the use of placards (showing artifacts) answer guiding questions to analyze and how many characteristics does each artifact show Wrap up activity: Whole class discussion (teacher lead) Rubric: Exemplary Extends the concepts and enduring understanding to include modern day applications Illustrations are realistic and creative representations of pictographs Unique and creative use of materials and space Proficient Illustrated and described the required enduring understandings or guiding questions Illustrations are realistic representations of pictographs/petrographs No grammar/mechanical errors Progressing Does not illustrate and describe enduring understandings Illustrations may not be factual or realistic Grammar and mechanical errors are present