Carbon dioxide - Läkemedelsverket

Svensk läkemedelsstandard 2011.2
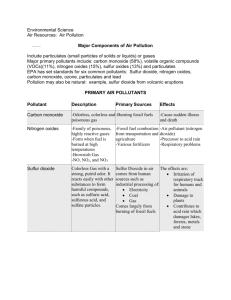
Carbon dioxide
Postadress/Postal address: P.O. Box 26, SE-751 03 Uppsala, SWEDEN
Besöksadress/Visiting address: Dag Hammarskjölds väg 42, Uppsala
Telefon/Phone: +46 (0)18 17 46 00 Fax: +46 (0)18 54 85 66
Internet: www.lakemedelsverket.se E-mail: registrator@mpa.se
Ansvarig utgivare:
Svenska farmakopékommittén
Läkemedelsverket
Box 26
S-751 03 Uppsala, Sweden
Tel. 018/17 46 00
2(6)
CARBON DIOXIDE
1
Carbonei dioxidum
CO
2
[124-38-9]
DEFINITION
M r
44.01
Content : minimum 99.5 per cent V/V of CO
2
in the gaseous phase.
This monograph applies to carbon dioxide for medicinal use.
CHARACTERS
Appearance : colourless gas.
Solubility
: at 20 °C and at a pressure of 101 kPa, 1 volume dissolves in about 1 volume of water.
PRODUCTION
Examine the gaseous phase.
If the test is performed on a cylinder of gas, keep the cylinder of the substance to be examined at room temperature for not less than 6 h before carrying out the tests. Keep the cylinder in the vertical position with the outlet valve uppermost.
Carbon monoxide . Gas chromatography (2.2.28).
Gas to be examined.
The substance to be examined.
Reference gas.
A mixture containing 5 ppm V/V of carbon monoxide R in nitrogen R1 .
Column :
material : stainless steel,
size : l = 2 m, Ø = 4 mm,
stationary phase : an appropriate molecular sieve for chromatography (0.5 nm).
Carrier gas : helium for chromatography R .
Flow rate : 60 ml/min.
Temperature :
column
: 50 °C,
injection port and detector
: 130 °C.
1
Kapitlet är hämtat från Ph Eur 7th Ed för information. I händelse av tvist gäller alltid det vid tillfället giltiga kapitlet i Ph Eur.
3(6)
Detection : flame ionisation with methaniser.
Injection : loop injector.
Adjust the injected volumes and the operating conditions so that the height of the peak due to carbon monoxide in the chromatogram obtained with the reference gas is at least 35 per cent of the full scale of the recorder.
Limit :
carbon monoxide : not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference gas (5 ppm V/V).
Nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide : maximum 2 ppm V/V in total, determined using a chemiluminescence analyser (2.5.26).
Gas to be examined. The substance to be examined.
Reference gas (a). Carbon dioxide R1 .
Reference gas (b). A mixture containing 2 ppm V/V of nitrogen monoxide R in carbon dioxide R1 or in nitrogen R1 .
Calibrate the apparatus and set the sensitivity using reference gases (a) and (b). Measure the content of nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide in the gas to be examined.
If nitrogen is used instead of carbon dioxide in reference gas (b), multiply the result obtained by the quenching correction factor in order to correct the quenching effect on the analyser response caused by the carbon dioxide matrix effect.
The quenching correction factor is determined by applying a known reference mixture of nitrogen monoxide in carbon dioxide and comparing the actual content with the content indicated by the analyser which has been calibrated with a NO/N
2
reference mixture.
Total sulphur : maximum 1 ppm V/V, determined using an ultraviolet fluorescence analyser after oxidation of the sulphur compounds by heating at 1000 °C (Figure 0375.-1).
The apparatus consists of the following:
a system generating ultraviolet radiation with a wavelength of 210 nm, made up of an ultraviolet lamp, a collimator, and a selective filter; the beam is blocked periodically by a chopper rotating at high speed,
a reaction chamber through which flows the previously filtered gas to be examined,
a system that detects radiation emitted at a wavelength of 350 nm, made up of a selective filter, a photomultiplier tube and an amplifier.
4(6)
Figure 0375.-1.— UV Fluorescence Analyser
Gas to be examined . The substance to be examined.
Reference gas (a) . Carbon dioxide R1 .
Reference gas (b) . A mixture containing between 0.5 ppm V/V and 2 ppm V/V of hydrogen sulphide R1 in carbon dioxide R1 .
Calibrate the apparatus and set the sensitivity using reference gases (a) and (b). Pass the gas to be examined through a quartz oven heated to 1000 °C. Oxygen R is circulated in the oven at a tenth of the flow rate of the gas to be examined. Measure the sulphur dioxide content in the gaseous mixture leaving the oven.
Water : maximum 67 ppm V/V, determined using an electrolytic hygrometer (2.5.28).
Assay . Infrared analyser (2.5.24).
Gas to be examined . The substance to be examined. It must be filtered to avoid stray light phenomena.
Reference gas (a) . Carbon dioxide R1 .
Reference gas (b) . A mixture containing 95.0 per cent V/V of carbon dioxide R1 and
5.0 per cent V/V of nitrogen R1 .
Calibrate the apparatus and set the sensitivity using reference gases (a) and (b). Measure the content of carbon dioxide in the gas to be examined.
5(6)
IDENTIFICATION
First identification : A.
Second identification : B, C.
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison : Ph. Eur. reference spectrum of carbon dioxide.
B. Place a glowing splinter of wood in an atmosphere of the substance to be examined. It is extinguished.
C. Pass a stream of the substance to be examined through barium hydroxide solution R . A white precipitate is formed which dissolves with effervescence in dilute acetic acid R .
TESTS
Examine the gaseous phase.
If the test is performed on a cylinder of gas, keep the cylinder of the substance to be examined at room temperature for not less than 6 h before carrying out the tests. Keep the cylinder in the vertical position with the outlet valve uppermost.
Carbon monoxide : maximum 5 ppm V/V, determined using a carbon monoxide detector tube
(2.1.6).
Hydrogen sulphide : maximum 1 ppm V/V, determined using a hydrogen sulphide detector tube
(2.1.6).
Nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide : maximum 2 ppm V/V in total, determined using a nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide detector tube (2.1.6).
Sulphur dioxide : maximum 2 ppm V/V, determined using a sulphur dioxide detector tube (2.1.6).
Water vapour : maximum 67 ppm V/V, determined using a water vapour detector tube (2.1.6).
STORAGE
Store liquefied under pressure in suitable containers complying with the legal regulations.
IMPURITIES
A. nitrogen monoxide,
B. nitrogen dioxide,
C. carbon monoxide,
D. total sulphur,
E. water.
6(6)


![oxygen (93 per cent)[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007364439_2-6ea8d9ccae06af63d51c1b7821cf5906-300x300.png)