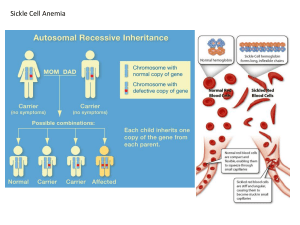
CHAPTER 20
advertisement

CHAPTER 20 EXTENDING YOUR IDEAS 1. A–B = 20% A–C = 8% Thus _____________________________________________ B 20 A 8 C C = 28% or A 2. _______________________________ 8 C 12 B Tall dominant Yellow dominant Smooth dominant a. T Y S TtYySs tys x i.e. recombination B–C = 12% dwarf green wrinkled t y s ttyyss TYS TYs TyS tYS Tys tYs tyS tys TtYySs TtYyss TtyySs ttYySs Ttyyss ttYyss ttyySs ttyyss tall yellow smooth (TtYySs) tall yellow wrinkled (TtYyss) tall green smooth (TtyySs) tall green wrinkled (Ttyyss) dwarf yellow smooth (ttYySs) dwarf yellow wrinkled (ttYyss) dwarf green smooth (ttyySs) dwarf green wrinkled (ttyyss) b. i.e. recombination B– TtyySs x 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ttYySs TyS Tys tyS tys tYS TtYySS TtYySs ttYySS ttYySs tYs TtYySs TtYyss ttYySs ttYyss tyS TtyySS TtyySs ttyySS ttyySs tys TtyySs Ttyyss ttyySs ttyyss tall yellow smooth tall yellow wrinkled tall green smooth tall green wrinkled dwarf yellow smooth dwarf yellow wrinkled dwarf green smooth dwarf green wrinkled 3 1 3 1 3 1 3 1 TtYySs; TtYySS TtYyss TtyySS; TtyySs TtYyss ttYySS; ttYySs ttYyss ttyySS; ttyySs ttyyss 3. Red (R) dominant to yellow (r). Round (P) dominant to pear-shaped (p). Tall (T) dominant to dwarf (t). a. TTPPRR x F1 all TtPpRr b. ttpprr i.e. tall, round and red F2 TPR TPr TpR Tpr tPR tPr tpR tpr TPR TTPPRR TTPPRr TTPpRR TTPpRr TtPPRR TtPPRr TtPpRR TtPpRr TPr TTPPRr TTPPrr TTPpRr TTPprr TtPPRr TtPPrr TtPpRr TtPprr TpR TTPpRR TTPpRr TTppRR TTppRr TtPpRR TtPpRr TtppRR TtppRr Tpr TTPpRr TTPprr TTppRr TTpprr TtPpRr TtPprr TtppRr Ttpprr tPR TtPPRR TtPPRr TtPpRR TtPpRr ttPPRR ttPPRr ttPpRR ttPpRr tPr TtPPRr TtPPrr TtPpRr TtPprr ttPPRr ttPPrr ttPpRr ttPprr tpR TtPpRR TtPpRr TtppRR TtppRr ttPpRR ttPpRr ttppRR ttppRr tpr TtPpRr TtPprr TtppRr Ttpprr ttPpRr ttPprr ttppRr ttpprr Thus 4. tall round red (TPR) tall round yellow (TPr) tall pear red (TpR) tall pear yellow (Tpr) dwarf round red (tPR) dwarf round yellow (tPr) dwarf pear red (tpR) dwarf pear yellow (tpr) a. Presence of 27 9 9 3 9 3 3 1 three dominant alleles (WWW) two dominant alleles (WW) one dominant allele (W) no dominant allele 22% amylase 20.4% 18.4% 0.0% Thus for wax to be present at least one dominant allele must be present. Further, approximately 1.6% was deposited for each extra dominant allele. E.g. predict: WxWxWxWx would have approximately 23.6% amylase WxWxWxWxWx would have approximately 25.2% Case of continuous variation rather than simple dominance. Each dominant allele causes production of an amount of the specific enzyme, amylase. 5. b. A gene determines, through protein synthesis, the presence or absence of specific characteristics. a. i. 0.1 x 0.1 = 0.001 per thousand. ii. 0.04 x 5 (average) x 0.4 = 0.08 per thousand. Individuals that are heterozygous for a recessively inherited disease do not exhibit the symptoms and thus may be unaware that they carry the disease (e.g. cystic fibrosis), whereas diseases that are inherited through the dominant allele are expressed and the individual is unlikely to reach adulthood (e.g. neurofibromatosis), or may elect not to have children (e.g. myotonic dystrophy). b. c. d. In both myotonic and muscular dystrophy there is progressive muscular weakness. This affects not only the skeletal muscles but also the cardiac and smooth muscles. Thus whilst there will be a decrease in locomotion and ventilation, there will also be deterioration of peristalsis and cardiovascular activity. The individual will take in less oxygen and be less able to distribute this to the organs, particularly the brain cells. There would probably also be an accumulation of wastes as the circulatory system would be slower in their removal to the appropriate organs. The overall result would be poor metabolic activities, which would cause deterioration of other organs and systems. Because these diseases are carried on the X chromosome, there is no masking effect of a dominant allele in males and thus the disease is more commonly expressed in them. 6. Barking dominant B Erect ears dominant E Want pure breeding BBee Select only dogs which bark and have drooping ears. Mate to drooping eared silent dogs – if any progeny are silent (i.e. barker was heterozygous Bb), then cull that barker from breeding. 7. Short dominant S Black dominant B Long recessive Black and tan recessive s b BBss x bbSS All offspring will be BbSs – short haired and black. Proportion F2 being long haired as well as black and tan (bbSS or bbSs) = 3/16 (Dihybrid ratio). 8. a. RRPp rP x rrPp RP Rp RrPP Rrpp Thus rp RrPp Rrpp 3 walnut (RrPP and RrPp) : 1 rose (Rrpp) b. rrPP x RrPp rP Thus c. RP RrPP walnut Rp RrPp walnut rP rrPP pea rp rrPp 1 walnut : 1 pea comb pea RrPp x Rp rp Thus Rrpp RP Rp rP rp RRPp walnut RRpp rose RrPp walnut Rrpp rose RrPp Rrpp rrPp walnut rose pea 3 walnut : 3 rose : 1 pea : 1 normal rrpp normal 9. X Sc X sc Cv V X sc x cv v cv V Y X Sc X sc cv V Y Cv V X sc cv v X Sc Cv V X sc cv V X sc X sc cv v X Sc Y X sc Y cv v Cv V cv V Thus: 1 wild type female : 1 scute crossveinless female : 1 wild type male : 1 scute crossveinless vermillion male. But the original female may have the following genotypes on her X chromosomes: Sc cv V sc Cv v sc Cv V Sc cv v sc cv V Sc Cv v Sc Cv v sc cv V Sc cv v sc CV V in which case the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring will differ. E.g. X Sc X sc cv V Y cv V X sc Cv v X Sc cv V X sc cv V X sc Cv v X sc cv V X Sc Y X sc Y cv V Cv v i.e. 1 crossveinless female : 1 scute female : 1 crossveinless male : 1 scute vermillion male 10. Text error: the cross should read: y xn lz × y+ sn+ Lz+ – y sn lz Possibilities for crossing over assuming y, sn and lz are equidistant on the chromosome: a. between y and sn b. between sn and lz c. between y and sn and between sn and lz Thus with female y+ sn+ lz+ y sn lz Male progeny: No crossing over y+ sn+ lz+ Y y sn lz Y Crossover a Crossover b wild type yellow, singed, lozenge y sn+ lz+ Y y+ sn lz Y yellow y+ sn+ lz Y y sn lz+ Y lozenge singed, lozenge yellow, singed Crossover c y sn+ lz Y + y sn lz+ Y yellow, lozenge singed 11. No. It is possible that the female was homozygous for a dominant allele whose only effect was to suppress the effect of the bar gene in males. 12. If A and B are 10 crossover units apart then you would get 10% recombination between A and B. Thus the proportion of gametes and possible combinations will be: 9 AB 9 ab 1 aB 1 Ab 9 AB 81 AB//AB 81 AB//ab 9 AB//aB 9AB//Ab 9 ab 81 AB//ab 81 ab//ab 9 aB//ab 9Ab//ab 1 aB 9 AB//aB 9 aB//ab 1 aB//aB 1 Ab//aB 1 Ab 9 AB//Ab 9 Ab//ab 1 Ab//aB 1 Ab//Ab i.e. 81 AB//AB : 162 AB//ab : 81 ab//ab : 18 AB//aB : 18 AB//Ab : 18 aB//ab: Ab//ab: 2Ab//aB : 1aB//aB : 1 Ab//Ab 13 h–c Xg–h Xg–c 12 units 46 units 34 units Thus: Xg _________________________________ 34 c 12 h