4.Islam
advertisement
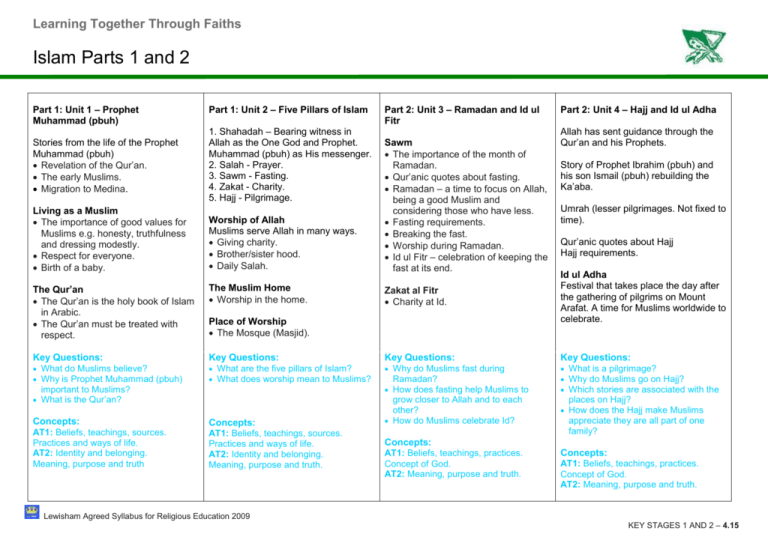
Learning Together Through Faiths Islam Parts 1 and 2 Part 1: Unit 1 – Prophet Muhammad (pbuh) Part 1: Unit 2 – Five Pillars of Islam Stories from the life of the Prophet Muhammad (pbuh) Revelation of the Qur’an. The early Muslims. Migration to Medina. 1. Shahadah – Bearing witness in Allah as the One God and Prophet. Muhammad (pbuh) as His messenger. 2. Salah - Prayer. 3. Sawm - Fasting. 4. Zakat - Charity. 5. Hajj - Pilgrimage. Living as a Muslim The importance of good values for Muslims e.g. honesty, truthfulness and dressing modestly. Respect for everyone. Birth of a baby. Worship of Allah Muslims serve Allah in many ways. Giving charity. Brother/sister hood. Daily Salah. Part 2: Unit 3 – Ramadan and Id ul Fitr Sawm The importance of the month of Ramadan. Qur’anic quotes about fasting. Ramadan – a time to focus on Allah, being a good Muslim and considering those who have less. Fasting requirements. Breaking the fast. Worship during Ramadan. Id ul Fitr – celebration of keeping the fast at its end. Part 2: Unit 4 – Hajj and Id ul Adha Allah has sent guidance through the Qur’an and his Prophets. Story of Prophet Ibrahim (pbuh) and his son Ismail (pbuh) rebuilding the Ka’aba. Umrah (lesser pilgrimages. Not fixed to time). Qur’anic quotes about Hajj Hajj requirements. Zakat al Fitr Charity at Id. Id ul Adha Festival that takes place the day after the gathering of pilgrims on Mount Arafat. A time for Muslims worldwide to celebrate. Key Questions: Key Questions: Key Questions: What are the five pillars of Islam? What does worship mean to Muslims? Why do Muslims fast during What is a pilgrimage? Why do Muslims go on Hajj? Which stories are associated with the The Qur’an The Qur’an is the holy book of Islam in Arabic. The Qur’an must be treated with respect. The Muslim Home Worship in the home. Key Questions: What do Muslims believe? Why is Prophet Muhammad (pbuh) Place of Worship The Mosque (Masjid). important to Muslims? What is the Qur’an? Concepts: Concepts: AT1: Beliefs, teachings, sources. Practices and ways of life. AT2: Identity and belonging. Meaning, purpose and truth AT1: Beliefs, teachings, sources. Practices and ways of life. AT2: Identity and belonging. Meaning, purpose and truth. Ramadan? How does fasting help Muslims to grow closer to Allah and to each other? How do Muslims celebrate Id? places on Hajj? How does the Hajj make Muslims appreciate they are all part of one family? Concepts: AT1: Beliefs, teachings, practices. Concept of God. AT2: Meaning, purpose and truth. Concepts: AT1: Beliefs, teachings, practices. Concept of God. AT2: Meaning, purpose and truth. Lewisham Agreed Syllabus for Religious Education 2009 KEY STAGES 1 AND 2 – 4.15 Learning Together Through Faiths Islam in the Thematic Units The Natural World Belonging Right and Wrong Muslims believe in one God Allah is the Arabic and Islamic name for God. He is the Creator, who provides all things. He has no partners. Know what is involved for a child in belonging to the Muslim faith at home. Muslims learn how to behave from the Qur’an and stories about Prophet Muhammad (pbuh). Key Questions: Key Question: Key Questions: How do Muslims believe the How does Muslim life show faith in How does Islam teach how you world began? What do Muslims believe about Allah? The story of Prophet Muhammad (pbuh) and the Old Woman. Allah? Concepts: Concepts: AT1: Beliefs, teachings. Concept of God. AT2: Values and commitments should treat others? What message did Muhammad AT1: Beliefs, teachings, practices. Concept of God. AT2: Meaning, purpose and truth. (pbuh) give to the old woman about how Allah expected people to behave? Concepts: AT1: Beliefs, teachings practices. AT2: Meaning, purpose and truth. Lewisham Agreed Syllabus for Religious Education 2009 KEY STAGES 1 AND 2 – 4.16 Learning Together Through Faiths Islam in the Thematic Units Peace The Journey of Life and Death Bridging Unit ‘As-salaam’ is one of the beautiful names of Allah meaning the ‘Source of Peace’. The ways in which human experiences associated with death, loss, hope, and meaning in life are understood in Islam. Guidelines for living – Qur’an and Hadith (statements and actions of the Prophet Muhammad (pbuh) a second source of Islamic law after the Qur’an). The Story of the Crying Camel. Key Question: Key Questions: Key Questions: How does the Muslim greeting What do Muslims believe happens Why is this story important to Muslims? What values does it teach? How do Muslims put these beliefs/ values ‘Assalaamu alaykum’ (Peace be upon you) reflect Muslim beliefs about Allah? after death? How do Muslims support people during times of loss? into practice in their daily lives? Concepts: Concepts: Concepts: AT1: Beliefs, teachings, practices. Concept of God. AT2: Meaning, purpose and truth AT1: Beliefs, teachings, practices. AT2: Meaning, purpose and truth AT1: Beliefs, teachings and sources. Practices and ways of life. AT2: Values and commitments. Lewisham Agreed Syllabus for Religious Education 2009 KEY STAGES 1 AND 2 – 4.17





