DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis Worksheet
advertisement

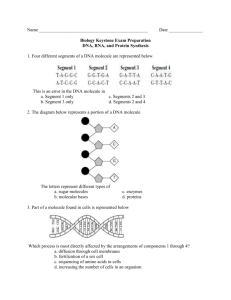
NAME ____________________________________________ DNA REPLICATION WORKSHEETS 1. What is the name given to the enzyme that unwinds the two strands of DNA when replication starts on a DNA molecule? ______________________________________________________________ 2. What does Chargaff’s Rule state? _____________________________________________________ 3. Who were the two men responsible for making the first model of DNA out of tin & wire? _________________________________________________________________________________ 5-6. Write the name of the appropriate Nitrogen base beside each letter: A: _______________________ T: _______________________ G: ___________________________ C: ___________________________ 7. Which two nitrogen bases are classified as Purines? _____________________________________ 8. Which two nitrogen bases are classified as Pyrimidines? _________________________________ 9. What 3 things make up a nucleotide in DNA? a. __________________________________________________________________________ b. __________________________________________________________________________ c. __________________________________________________________________________ 10. What 3 things make up a nucleotide in RNA? a. __________________________________________________________________________ b. __________________________________________________________________________ c. __________________________________________________________________________ 11. What is the process of making new strands of DNA called? ________________________________ 12. Using your answer to #10, where in the cell is this taking place? ____________________________ 13. Name the 2 molecules which alternate to form the upright or side portion of a DNA molecule. ___________________________________________________________ 14. If 4 guanine bases appear in a DNA model, how many cytosine bases should there be? _______________________________________________________________________ 15. Your DNA model has 4 guanine bases. Does the number of cytosine bases in your model agree with your prediction from questions #13? __________________________________ 16.The following are the bases on the left side of a DNA molecule. List the bases that would make up the right side of the DNA molecule. Thymine Adenine _____________________ _____________________ 17. Guanine _____________________ Guanine _____________________ Cytosine _____________________ Thymine _____________________ Cytosine _____________________ Adenine _____________________ How many molecules of adenine are in each DNA molecule? __________________________ 18. How many molecules of thymine? _______________________________________________ 19. Do the numbers agree? ________________________________________________________ 20. Explain how the pairing of the nitrogen bases in a DNA molecule allows the DNA to replicate itself. _______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ RNA is similar to DNA in that its molecules also form nucleotides. However, deoxyribose and thymine are not found in RNA. Ribose replaces deoxyribose and uracil replaces thymine. Phosphoric acid, guanine, adenine, and cytosine are present in RNA. 21. Knowing the shapes of purine & pyrimidine groups, what group would uracil belong in? _____________________________________________________________________________ 22. Is the sequence or order of bases in RNA different from the unused left side of the original DNA molecule above? (Do not consider uracil replacing thymine as a change in sequence) ____________________________________________________________________________ 23. Do the RNA half rung bases pair exactly as they would if this were DNA replication? (Once again, do not consider uracil replacing thymine as a change.) ___________________________ Scientists believe that RNA is only a single stranded molecule. Thus, the series of RNA nucleotides formed from DNA represents an RNA molecule. After its formation, RNA leaves the nucleus of the cell and goes to the ribosomes. It carries the DNA message of base sequences (in complementary form) to the cell’s ribosomes. Complete Table 1 by using check marks to indicate to which molecule each item applies. TABLE 1 – Similarities and Differences Between DNA & RNA DNA RNA Ribose present Deoxyribose present Phosphoric acid present Adenine present Thymine present Uracil present Guanine present Cytosine present Double stranded Single strand Remains in nucleus Moves out of nucleus tRNA & Protein Building RNA produced in the nucleus of a cell moves out of the nucleus toward the cell’s ribosomes. It carries with it a specific sequence of bases copied from the DNA. RNA carries the genetic message of the chromosomes into the cell. Thus, it is called messenger RNA, or simply mRNA. At the ribosomes, mRNA directs the building of proteins. How can mRNA secure the proper amino acids to construct protein molecules? How does mRNA decode the base sequence of the DNA? The answer to the first question involves another molecule. The molecule is transfer RNA or tRNA. This molecule brings amino acids to the mRNA 1. To join tRNA molecules to the mRNA pattern, which sequence of tRNA molecules will match base pairs of the U, U, A sequence in mRNA? _______________________________________ Which tRNA sequence of bases can join the U, C, A sequence of bases in mRNA? __________ 2. How does the sequence of bases on mRNA control the type of mRNA joining with it? _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 3. A base sequence of A, A, A in mRNA could only join with what sequence of bases in tRNA? _____________________________________________________________________________ 4. What specific amino acid is brought to the mRNA by a tRNA molecule with a terminal sequence of A, A, U? (Look at the genetic code for the answer) ___________________________________ 5. What amino acid is brought to the mRNA by a tRNA terminal sequence of A, G, U? (Look at the genetic code for the answer) ________________________________________________________ 6. How many base of mRNA are responsible for the coding of one amino acid? ___________ When many amino acid molecules are brought to the mRNA by tRNA, the amino acids join together to form a protein molecule. Thus, joining tRNA molecules with their attached amino acids to the bases of the mRNA simulates the beginning of a protein molecule. Depending on the type and order of amino acids, an almost endless variety of proteins can be produced. Because of the repeated matching of base sequence, the sequence of bases in the DNA of chromosomes codes and controls the formation of protein molecules at ribosomes. 7. A protein molecule consists of the following amino acid sequence: leucine, glutamine, tyrosine, leucine, serine, serine. What would be the sequence of tRNA molecules responsible for forming this protein? (Use Table 2 below) __________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 8. A ribosome receives the following mRNA message: AAA, CGA, GAA, GUU. What will be the sequence of tRNA bases joining the mRNA molecule? (Use Table 2 below) ______________________________________________________________________________ 9. What will be the sequence of amino acids formed from this code? (Use Table 2 below)_______ ________________________________________________________________________ TABLE 2 – TRNA TRIPLET CODES OF SOME AMINO ACIDS AMINO ACIDS tRNA Code Serine AGU Proline GGG Leucine AAU Glutamin Acid CUU Tyrosine AUA Arginine GCU Glutamine GUU Phenylalanine AAA Valine CAA Lysine UUU A portion of DNA on a chromosome has the sequence of bases along one strand of DNA as indicated in Table 3. Complete the 2nd column with the sequence of bases of an mRNA molecule formed from the DNA strand. Complete the 3rd column with the sequence of bases of the tRNA molecules that would join the mRNA strand. Complete the 4th column with the sequence of amino acids that results from the mRNA strand. TABLE 3 – BASE SEQUENCE CHANGES DURING AMINO ACID FORMATION Chromosome (DNA) mRNA tRNA Amino Acid A A T G G G A T A A A A G T T Mutations and Base Sequence Rarely does the DNA code of instructions make an error in directing cells to form a protein. When it does, however, the error is called a mutation and will result in formation of a different type of protein. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells. Hemoglobin results from the proper arrangement of almost 600 amino acids. Most humans have the correct type of hemoglobin. However, in some people the arrangement is incorrect. These people have a disease called sickle-cell anemia. Their red blood cells are sickle-shaped rather than round. As a result, the red blood cells cannot transport oxygen efficiently. The following amino acid sequence represents a portion of the normal hemoglobin molecule: proline, glutamic acid, glatamic acid, lysine. In sicle-cell anemia, the first glutamic acid is replaced by the amino acid valine. 9. List the sequence of amino acids that represent the same area of a sickle-shaped hemoglobin molecule. 10. Using the list of tRNA bases in Table 2, what is the sequence of bases of the segment of normal hemoglobin? ______________________________________________________ sickled hemoglobin? ______________________________________________________ 11. What is the sequence of mRNA bases that determine the amino acid sequence of the segment of normal hemoglobin? _____________________________________________ sickled hemoglobin? ______________________________________________________ 12. What is the sequence of bases in this segment of DNA of a person who has normal hemoglobin? ______________________________________________________ sickled hemoglobin? ______________________________________________________ 13. Why do persons having a mutation pass this condition on to their offspring? __________ _______________________________________________________________________