handout from class (with answers)
advertisement
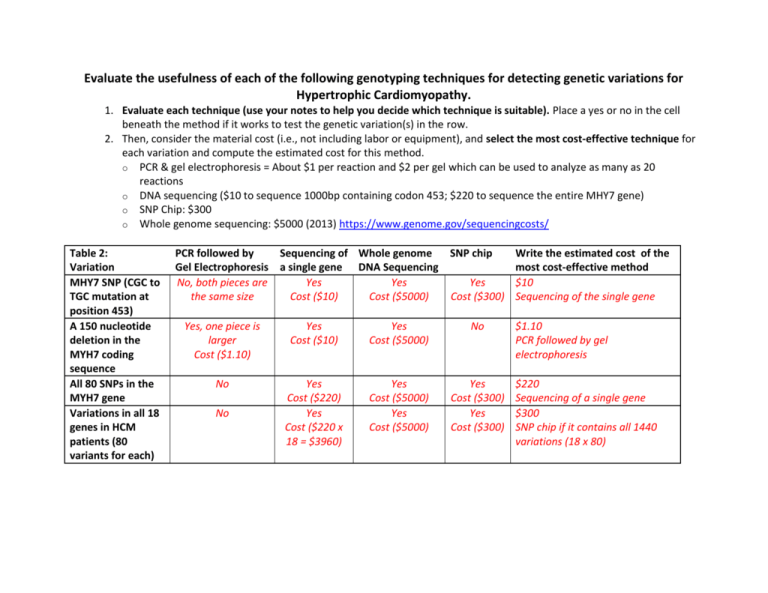
Evaluate the usefulness of each of the following genotyping techniques for detecting genetic variations for Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. 1. Evaluate each technique (use your notes to help you decide which technique is suitable). Place a yes or no in the cell beneath the method if it works to test the genetic variation(s) in the row. 2. Then, consider the material cost (i.e., not including labor or equipment), and select the most cost-effective technique for each variation and compute the estimated cost for this method. o PCR & gel electrophoresis = About $1 per reaction and $2 per gel which can be used to analyze as many as 20 reactions o DNA sequencing ($10 to sequence 1000bp containing codon 453; $220 to sequence the entire MHY7 gene) o SNP Chip: $300 o Whole genome sequencing: $5000 (2013) https://www.genome.gov/sequencingcosts/ Table 2: Variation MHY7 SNP (CGC to TGC mutation at position 453) A 150 nucleotide deletion in the MYH7 coding sequence All 80 SNPs in the MYH7 gene Variations in all 18 genes in HCM patients (80 variants for each) PCR followed by Sequencing of Whole genome SNP chip Gel Electrophoresis a single gene DNA Sequencing No, both pieces are Yes Yes Yes the same size Cost ($10) Cost ($5000) Cost ($300) Yes, one piece is larger Cost ($1.10) Yes Cost ($10) Yes Cost ($5000) No No Yes Cost ($220) Yes Cost ($220 x 18 = $3960) Yes Cost ($5000) Yes Cost ($5000) Yes Cost ($300) Yes Cost ($300) No Write the estimated cost of the most cost-effective method $10 Sequencing of the single gene $1.10 PCR followed by gel electrophoresis $220 Sequencing of a single gene $300 SNP chip if it contains all 1440 variations (18 x 80)