Evidence for Evolution
advertisement
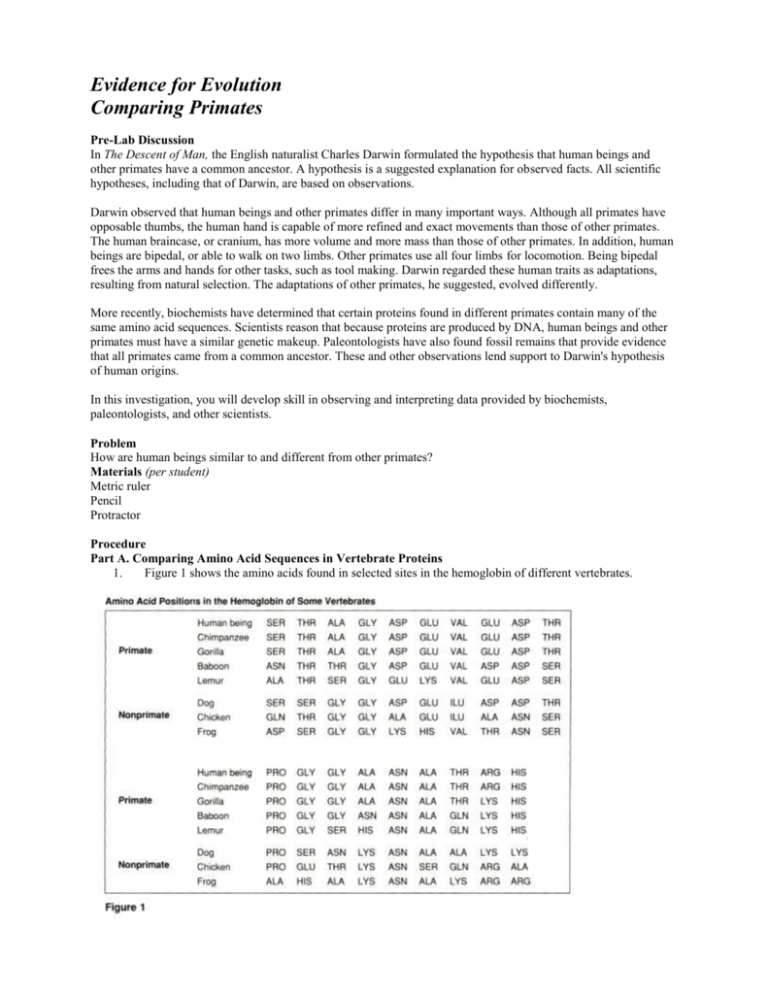
Evidence for Evolution Comparing Primates Pre-Lab Discussion In The Descent of Man, the English naturalist Charles Darwin formulated the hypothesis that human beings and other primates have a common ancestor. A hypothesis is a suggested explanation for observed facts. All scientific hypotheses, including that of Darwin, are based on observations. Darwin observed that human beings and other primates differ in many important ways. Although all primates have opposable thumbs, the human hand is capable of more refined and exact movements than those of other primates. The human braincase, or cranium, has more volume and more mass than those of other primates. In addition, human beings are bipedal, or able to walk on two limbs. Other primates use all four limbs for locomotion. Being bipedal frees the arms and hands for other tasks, such as tool making. Darwin regarded these human traits as adaptations, resulting from natural selection. The adaptations of other primates, he suggested, evolved differently. More recently, biochemists have determined that certain proteins found in different primates contain many of the same amino acid sequences. Scientists reason that because proteins are produced by DNA, human beings and other primates must have a similar genetic makeup. Paleontologists have also found fossil remains that provide evidence that all primates came from a common ancestor. These and other observations lend support to Darwin's hypothesis of human origins. In this investigation, you will develop skill in observing and interpreting data provided by biochemists, paleontologists, and other scientists. Problem How are human beings similar to and different from other primates? Materials (per student) Metric ruler Pencil Protractor Procedure Part A. Comparing Amino Acid Sequences in Vertebrate Proteins 1. Figure 1 shows the amino acids found in selected sites in the hemoglobin of different vertebrates. 2. Count the number of molecules of each amino acid in human hemoglobin. Note: Be sure to count the molecules of amino acid in human hemoglobin in the second section titled Primate as well as in the first section. Record these totals in the appropriate column in Data Table 1. 3. Count the number of molecules of each amino acid in the hemoglobin of other vertebrates in Figure 1. (Remember to count both sections.) Record these totals in the appropriate columns in Data Table 1. 4. Going from left to right, note the position of each amino acid. Count the number of similarities in the amino acid positions in human hemoglobin as compared with the hemoglobin of each of the other vertebrates in Figure 1. Record your observations in Data Table 2. 5. Reexamine Figure 1 and count the number of differences in the amino acid positions in human hemoglobin as compared with the hemoglobin of each of the other vertebrates in Figure 1. Record your observations in Data Table 2. Part B. Comparing Primate Features 1. Determine the relative size of the lower jaw of each primate by measuring the length in millimeters of lines ab and bc in Figure 2. Record these lengths in Data Table 3. Record the product of these lengths in Data Table 3. 2. Determine the angle of the jaw by using a protractor to measure the angle xy in each primate skull in Figure 2. Record your observations in Data Table 3. 3. Examine the teeth of each of the three primates in Figure 3. 4. Count the number of incisors, canines, premolars, and molars of each primate in Figure 3. Record your observations in the appropriate columns in Data Table 4. 5. Examine the two skeletons in Figure 4. 6. Compare both views of skeleton A with those of skeleton B. Answer questions 1 and 2 in Observations. Observations Data Table 1 Number of Molecules of Different Amino Acids in Some Vertebrates Amino Acid Abbreviation Alanine ALA Arginine ARG Asparagine ASN Aspartic acid ASP Glutamine GLN Glutamic acid GLU Glycine GLY Histidine HIS Isoleucine ILU Leucine LEU Lysine LYS Proline PRO Serine SER Three-nine THR Valine VAL Human Chimpanzee Gorilla Baboon Lemur Dog Chicken Data Table 2 Similarities and Differences in Amino Acid Positions in Hemoglobin Organisms Human and chimpanzee Human and gorilla Human and baboon Human and lemur Human and dog Human and chicken Human and frog Number of Amino Acid Position Similarities Number of Amino Acid Position Differences Frog Data Table 3 Comparison of Three Primate Skulls Length of Lower Jaw (mm) (ab) Skull Depth of Lower Jaw (mm) (bc) Area of Lower Jaw (mm2) (ab x bc) Angle of Jaw A B C Data Table 4 Comparison of Primate Teeth Type of Teeth Number of Teeth A B C Incisors Canines Premolars Molars 1. Describe three differences between skeleton A and skeleton B 2. Which type of primate skeleton is considered bipedal Analysis and Conclusions 1. a. From your observations in Data Table 2, which primate is most closely related to the human being? b. Which primate is least closely related? 2. a. Which nonprimate vertebrate listed in Data Table 2 is most closely related to the human being? b. Which nonprimate is least closely related? 3. a. Which of the three primates shown in Figure 2 has the largest brain? What do you think is the name of this primate? b. Which of the three primates shown in Figure 2 has the smallest brain? What do you think is the name of this primate? 4. What is the relationship between jaw size and brain size in these three primates? 5. From your observations in Data Table 4, what dental characteristics do the primates have in common? 6. Reexamine Figure 3. How would the diet of primate A differ from the diet of primate C? 7. What is an advantage of being bipedal? Critical Thinking and Application 1. Many primates use tools. For example, chimpanzees often use sticks to probe ant hills when searching for food. They also use leaves as sponges to collect drinking water. How is the use of tools by humans different from that of other primates? 2. The brain of the human being is larger than that of other primates. How would this relate to the different methods of communication displayed by humans and other primates? 3. Certain fossil evidence indicates that the primate ancestors of humans lived in areas where trees were scattered instead of clustered together. How might this type of environment have affected the development of bipedalism in humans? 4. Describe three physical characteristics that are unique to human beings. Going Further / Extra Credit Visit a local zoo to observe the behavior of gorillas, chimpanzees, baboons, and other primates. Observe the ways in which the animals communicate and interact with one another. What similarities and differences do you observe between the behaviors of the primates you studied and those of human beings? Use a notebook to record your observations.