Health_7.4.3_tutoria..
advertisement

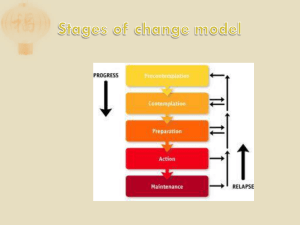
Course: Health Unit: Physical Health – Drug and Alcohol Awareness Section: Tobacco Awareness Tutorial: Tobacco SLIDE 1 Although classified as a stimulant, nicotine acts as both a stimulant and a depressant. At the first puff over 3000 chemicals enter the system, (one of them nicotine). The oxygen exchange is replaced by carbon monoxide, which remains in the system for over an hour. The nicotine stimulates the release of glucose (sugars) and adrenalin into the system. As a result, the heart beats faster, the blood vessels constrict, the blood pressure rises and the user feels lightheaded or dizzy. At the same time, dopamine is released and remains in the brain, relieving tension, and giving a sense of well being. Tiredness is relieved by the adrenalin, and tension by the dopamine. The first time user may also feel nauseas as the stomach reacts to Nicotine, the poison and to the high levels of adrenalin in the system. At the same time, the increased energy and the “reward” system (dopamine) are remembered by the brain, beginning the physical and psychological addiction. SLIDE 2 Friends and family as well as physicians can see the effects of smoking. Although the smoker has become desensitized to it, the odor of tobacco clings to the hair and clothing and on the breath. Dermatologists can tell you immediately if a person is a smoker, by seeing the fine lines and leathery appearance of the skin. This because the substances in cigarettes cause the loss of collagen, the substance that provides elasticity to the skin. The constricted blood vessels reduce the flow of oxygen to the skin, also contributing to the premature aging of the smoker. Smokers often report that their sense of smell and taste are reduced, which is seen as a possible reason for reduced weight among smokers (smokers tend to be 4 to 10 pounds below normal body weight). Unfortunately, this is why some teenagers take up smoking, regardless of the risks and the risks are many. The tobacco stains on the teeth give you a clue about what is happening inside of the body. SLIDE 3 Over time, smoking causes damage to the respiratory system, the circulatory system, to the digestive system and to the skeletal system of the body. The most significant long-term effect of smoking is the very high risk of lung cancer. The tar (a chemical found in tobacco) deposited in the throat, mouth, and lungs is a known © KC Distance Learning carcinogen, and causes cancer of the mouth and throat as well as the lungs. About 90 percent of all lung cancer cases are linked to smoking. Smoking narrows the airway, paralyzes the cilia, and destroys the air sacs required for the lungs to hold air. The cilia are hair-like bodies that remove microbes and bacteria from the lungs. The cilia is the first line of defense for the lungs, so bronchitis, and other airborne diseases are more common among smokers. As the lungs become inflamed they release harmful substances that destroy lung tissue. Weaker lungs cannot take in the oxygen they need, nor recover as quickly. The smoker develops COPD, and other lung diseases leading to breathlessness and the lung turns black from the deposits of tar in it. Smoking also increases the presence of HDL cholesterol, responsible for coronary and peripheral artery disease, and reduces the presence of LDL (the good cholesterol), increasing the risks of high blood pressure, heart attack, blood clots and strokes. Smoking is also associated with causing stomach ulcers, delaying their healing, and causing their recurrence, and several studies have linked it to osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a loss of bone density, creating weakened bones and resulting in broken bones, and difficulty in healing broken bones. Research has shown a link between smoking, bone loss and fractures. The incidents are even higher when combined with abuse of alcohol as well. SLIDE 4 Many smokers attempt to quit smoking. It is not an easy task. Because smoking is both physically and psychologically addicting the withdrawals can be uncomfortable. Some of the physical withdrawals last only 3 or 4 days and others may last a few weeks. Smokers will feel a variety of symptoms in addition to intense cravings for a cigarette. He/she may experience flu like symptoms for a few days and an increase in appetite (once taste is restored). Since the body is not producing it’s own epinephrine or dopamine, the smoker may be irritable and depressed and unable to sleep. These symptoms may last for several weeks but once the smoker has quit, he/she immediately reduces the risks faced. Former smokers live longer than smokers, and their risks of cancer and lung disease drop. For the person who is pregnant, the risks are greater. They affect the baby as well as the mother. © KC Distance Learning SLIDE 5 Why quit smoking? According to the American Cancer Society, all of the risks associated with smoking decrease when you quit smoking. And the longer you have not smoked, the greater the risk improvement. Notice that some of the health problems are improved within months, and some long-term risks improve as soon as a year after quitting. It is not too late to quit smoking. © KC Distance Learning