BondTypes&PhysProperties
advertisement

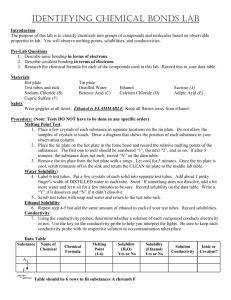
BOND TYPES AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Introduction: The type of bond present in a compound will determine the general physical properties of that compound. In this experiment the properties of solubility and melting point will be compared for typical ionic and covalent compounds. Purpose: To compare the properties of solubility, conductivity, and melting point for ionic and covalent compounds. Equipment/Materials: Small test tubes (10 per group) Test tube rack or 24-well plate Mel-temp/thermometer (set at 200oC) Capillary tubes Water (polar solvent) Iso-butanol (nonpolar solvent) Conductivity testers Safety: sodium chloride magnesium sulfate stearic acid vanillin cooking oil parafilm Always wear safety glasses in the lab. The Mel-temp can become very hot. Avoid touching the metal surfaces. Procedure: 1. Obtain ten (10) small test tubes and label two each with the identity of each solid to be tested and the cooking oil. Next to the name of each compound on one set of tubes, place a “W”. 2. Fill the set of 5 tubes that are marked with the “W” 1/3 to 1/2 full of deionized water (very polar solvent). 3. Fill the other set of 5 test tubes 1/3 to 1/2 full of iso-butanol (nonpolar or very slightly polar). 4. Place a very small sample of each solid (enough to fill up this circle O) into each tube labeled for that solid (2 test tubes each). (NOTE: Do NOT use much of the solid. If too much solid is used, even those that are soluble will be present in too high a concentration to go completely into solution. This will yield erroneous results.) Place a few drops of cooking oil into those two properly labeled test tubes. 5. Mix the contents of the test tubes well by placing a small piece of parafilm over the top of each tube and shaking. Record your observations regarding the solubility of each of the substances in each solvent. 6. For each compound that was soluble in water, pour some of that mixture from the test tube into a well on a 24-well plate. Test the wells with a conductivity tester by placing both prongs of the testers into the mixture and pressing the button on the side of the tester. Record the number displayed in the data table. 7. Place a sample of each of the solid substances in a melting point capillary tube. Mel-temps will be preset to 200oC. 8. Only three capillary tubes can be placed into a Mel-temp at one time. Pay attention to which sample is placed into which well of the Mel-temp so that you will know how to record your results. Allow the capillaries to stay in the Mel-temp for 3 minutes. At the end of the 3 minutes, observe the tubes to see if any have melted. 9. Record the melting point as “low” (below 200oC) if the solid has melted. Record the melting point as “high” (above 200oC) if the solid has not melted. 10. Identify the types of bonds present in each of the solids based upon its solubility and melting point. BOND TYPES AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Data Table Name(s): Date: Period/Lab Group: Data Table: Substance Solubility in Solubility in Water Iso-butanol (“S” or “N”) (“S” or “N”) If soluble in water, check conductivity (record number) Sodium chloride Magnesium sulfate Stearic acid Vanillin Cooking oil Questions: 1. What are two general properties of ionic compounds? 2. What are two general properties of covalent compounds? Melting Point (low or high) Type of Compound (ionic, polar covalent, or nonpolar covalent)