checkpoint
advertisement

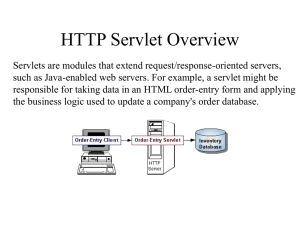
CS-603 Network Security Dr. Lilien Leszek Checkpoint Project Motive – To review and implement the Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol and study its applications especially for the internet key exchange. Members 1) Sahil Behl 2) Muhammad Rehan Fayyaz E-mail- s4behl@wmich.edu E-mail- m1fayyaz@wmich.edu Progress – 1. Understanding key terms and concepts: Application Server: We will be using Tomcat as our servlet container. We would be running the servlet on the application server provided by Tomcat. Client: We used a Java applet as our client. Server: We will use servlet as the server. 2. Creation of the Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol algorithm The Diffie- Hellman key exchange protocol algorithm was coded and implemented independently. 3. Creation of the client side program (Applet) The applet program was created on the client side. The function of the applet is to encrypt the message to be sent to the server( using the D-H algorithm). It is also able to accept a response from the server (in an encrypted form) and decode it. URL programming was used to send the encrypted message from the client to the server. The applet was coded and implemented independently. 4. Creation of a the server side program (Servlet). We then created a servlet that receives encrypted messages from the applet program. The function of the servlet is receive these encrypted messages anddecrypt them (using the D-H algorithm). It then responds to the client with an encrypted message (using D-H algorithm). The servlet itself is stateless. A test servlet was created and deployed successfully. Working : The client and the server would first establish a connection and would agree on a shared key through which they would communicate over an unsecured network using the Diffie - Hellman algorithm. After this, the client and the server would freely exchange messages between themselves. Our high level design is as follows: Establish initial connection : Using the Diffie – Hellman algorithm Client. Server <KPUBLIC-C, KPRIVATE-C > <KPUBLIC-s, KPRIVATE-s > KSHARED FIGURE 01 Exchange messages using the shared key over the insecure network. Client – encrypt P using KSHARED (Applet). Decrypt the message received from the server using C = E (P, KSHARED) Servlet – decrypt C using KPRIVATE-S . Send an encrypted reply using KSHARED. KPRIVATE-C C1 = E(P, KSHARED) Plain Text message To Do List Sr. No. Tasks Description Date 1 Integration of the modules. Implement the Diffie- Hellman algorithm within the client server model we have created. 10-Nov 2 Testing the modules Test each module individually and collectively. 18-Nov 3 Use a network sniffer 4 Project Documentation We will use Ethereal, to sniff the messages being exchanged between the client and the server. Project manuals created at each phase of software development. 21-Nov 25-Nov 5 (OPTIONAL) Implement a database Connect a database to the servlet to store the messages received from the client. The servlet itself is stateless 25-Nov Reference – Websites: 1. http://www.cc.gatech.edu/classes/cs8113e_96_winter/ - Visited on 09/16/2005 – college website 2. http://www.cryptography.com/- Visited on 09/18/2005 3. http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/jiangx/02spring/- Visited on 09/18/2005 4. http://www.securitydocs.com - Visited on 09/14/2005 – Network Security White papers 5. http://www.sans.org/rr/whitepapers/vpns/751.php - Visited on 09/17/2005 – SANS Institute 2001, a paper on the Diffie – Hellman Algorithm and its use in secure Internet protocols. 6. http://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/tip/1,289483,sid14_gci876048,00.html – Network Security Webpage. Books: 1. Java Network Programming and Distributed Computing- Davis Reilly – Michael Really. 2. Core Servlets and JSP- Marty Hall. 3. How to program Java – Deteil and Deteil.