RNA extraction and RT-PCR

Supplementary Methods
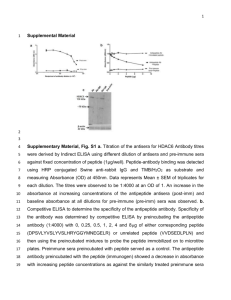
Peptide Neutralization . Cos7 cells were transfected with G72 or mock transfected, and mitochondria were isolated as described in Materials and Methods. Two lanes of each sample (5 µg of protein/lane) were loaded on a gel and Western blotting was performed.
Following transfer and blocking, the blot was split in half and each part was incubated either with the primary antibody or the peptide-neutralized antibody. For peptide neutralization, purified primary antibody (20 µl ) was combined with its blocking peptide
(250 µg/ml) in a small volume of PBS (total 500 µl) and incubated for 2 hrs at RT. The antibody was further diluted with 2 ml of the blocking buffer to a final concentration of
1:100 and the blots were incubated o/n at 4°.
RNA extraction and RT-PCR . Total RNA from HeLa cells was prepared using the
RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacture’s instruction. 5 μg of total RNA was used to synthesize the first strand cDNA with the superscript II− reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen) and oligo dT under the conditions recommended by the manufacturer. 10% of the first strand cDNA was used as template for the PCR. Following pairs of primers (5’-3’) were used:
LG72 : TGGAAAAGCTGATGGGTGCTGATT and GGTCTTTTTGCTGG TTGTAGTTGC;
Variant 4 : TGGAAAAGCTGATGGGTGCTGATT and AGTGTCTCCTTCCATAAAGTGCC;
Variant 3 :
TTTAATCCCCTAGAAGCAAAGGAG and AGTGTCTCCTTCCATAAAGTGCC,
Variant 2 : GCACAGAGGCATTTACAGAGATCA and AGTGTCTCCTTCCATAAAGTGCC.
Supplementary Figures.
Supplementary Figure 1.
Specificity of cellular localization of G72: Cos7 cells transfected with the G72-myc transfection construct and stained for the myc-tag and markers of cellular organelles.
Note that G72 does not co-localize with the Golgi (a–c), the early endosome (d–f), the endoplasmic reticulum (g–i), or the lysosomes (j–l). Scale bar: 10 µm.
Supplementary Figure 2.
Peptide neutralization: Western blot analysis using the anti-G72 antibody (bottom left) and the same antibody treated with an inhibitory peptide (bottom right). The peptide sequence against which the anti-G72 antibody was raised is also shown in bold (top).
Supplementary Figure 3.
Expression of G72 splicing variants in Hela cells: (A) Amino-acid sequences of G72 splice variants. NCBI accession numbers are given in brackets. The peptide sequence against which the anti-G72 antibody was raised is depicted in bold. Note that in addition to LG72 , Variants 3 and 4 could also be detected by the G72 antibody used in this study.
(B) Analysis of G72 splicing variants expression in HeLa cells. RT-PCR was performed using splicing variant-specific combinations of primers, as described in Supplementary
Materials and Methods.
The sequence of Variant 1 is identical to the sequence of LG72, but lacking the 71 N-terminal amino acids. Thus, it could not be discriminated from
LG72 . The identity of the LG72 PCR product was confirmed by sequencing.