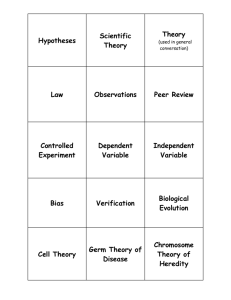
Sample questions

GENETICS (BIO S325) SUMMER 2006
Sample questions - I Exam
________________________________________________________________________
1. Which of the following choices describes the most likely pattern of inheritance of a trait shown in the given pedigree?
(a) Autosomal dominant
(b) Autosomal recessive
(c) Cytoplasmic inheritance
(d) X-linked recessive
(e) Y-linked
(f) X-linked dominant
2. The mouse autosomal genes B and S are linked and 38 map units apart. Mice with genotypes B S/B S and b s/b s are crossed and the F
1
is testcrossed to b s/b s . The proportion of mice with the genotype B-S in the testcross progeny will be
3. A dihybrid plant in trans conformation is testcrossed to a plant with the genotype ab/ab . In 28% of the cells undergoing meiosis, no chiasmata is observed between the linked genes A and B ; in 72% of the cells, there is one chiasma between the two genes. What proportion of the progeny from the cross will be ab/ab ?
1
5.
4. In a testcross of an individual, heterozygous for each of three linked genes, the most frequent classes of progeny were A B c / a b c and a b C / a b c, and the least frequent classes were A B C / a b c and a b c / a b c .
(a) What is the genotype of the trihybrid?
(b) What is the order of the genes?
Imagine a diploid sexually reproducing organism, Diploidus sexualis , that contains three pairs of chromosomes. This organism is unusual in that no recombination between homologous chromosomes occurs during meiosis.
(a) Assuming that the chromosomes are distributed independently during meiosis, how many different types of sperm or egg cells can a single individual of this species produce?
(b) What is the likelihood that two siblings of this species will be genetically identical?
6. Indicate whether the following is TRUE for meiosis, mitosis, both, or neither.
(a) Formation of a bivalent
(b) Products are genetically identical
(c) Chromosomes condense
(d) All paternal chromosomes segregate to one cell
(e) Involves DNA replication
7. For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below. Not all words or phrases will be used; each word or phrase should be used only once.
In eucaryotic __________________, DNA is complexed with proteins to form __________________. The paternal and maternal copies of human
Chromosome 1 are __________________, whereas the paternal copy of
Chromosome 1 and the maternal copy of Chromosome 3 are
__________________. Cytogeneticists can determine large-scale chromosomal abnormalities by looking at a patient’s karyotype. Fluorescent molecules can be used to paint a chromosome by virtue of DNA
__________________, and thereby to identify each chromosome using microscopy. chromosomes hybridization extended condensation kinetochore homologous nonhomologous bands chromatin
2
8. A tall pea plant with axial flowers was crossed to a dwarf plant with terminal flowers and the following offspring were obtained: 27 tall plants with axial flowers; 23 tall plants with terminal flowers; 28 dwarf plants with axial flowers; and 25 dwarf plants with terminal flowers. Tall plants and axial flowers are dominant phenotypes. Using the symbols T and t for plant height, and A and a for flower position, give the genotypes of the two parents in this cross.
9. A sex-linked recessive allele c produces a red-green colorblindness in humans. A normal woman whose father was colorblind marries a colorblind man.
(a) What genotypes are possible for the mother of the colorblind man?
(b) What are the chances that the first child from this marriage will be a colorblind boy?
10. A couple discovers that they both had an uncle who died of Tay-Sachs disease.
What is the probability of their producing a child with Tay-Sachs disease?
3
11. In corn ( Zea mays ), the genetic map of part of chromosome 4 is as follows, where w, s, and e represent recessive mutant alleles affecting the color and shape of the pollen:
w
10 m.u
s
20 m.u.
e
If the following cross is made w
+ s
+ e
+
/w
+ s
+ e
+ x wse/wse and the F
1
is testcrossed to wse/wse, and if it is assumed that there is no interference in this region of the chromosome, the proportion of progeny with the following genotypes will be:
(a) w
+ s
+ e
+
/ wse
(b) w
+ s e / wse
(c) w
+ s
+ e/ wse
(d) w
+ s e
+
/ wse
12. (a) Explain why large recombination frequency values are less accurate measures of map distance than smaller ones.
(b) During an experiment involving two genes you determine that the recombination frequency (RF) between the two genes is close to 50%.
What can you conclude about the linkage relationship of the two genes that you are studying?
13. Genes a, b, and c are present on a single chromosome in the order given and the distances between genes a and b are 20 map units and between b and c are 16 map units. In a trihybird testcross, 16 double recombinants were obtained in a total of
1000 progeny. Calculate the interference observed in this cross.
4
14. A diploid plant has a chromosome content of 2n = 8. Diagrammed below are individaul cells of a tetrahybrid plant (A/a; B/b; C/c; D/d). In each case mention if the diagram represents a cell in mitosis, meiosis I, meiosis II, or not possible.
Each line represents a chromatid.
(a)
B C D a b c a b c d A B C d
D
(b) A a a
A
B b
B b
C c
C c
D d d
D
(c)
A b C d
(d)
(e)
A
A
A
A
B b a a a b
C d c
D
B
B
C b b d
C
C c c
D
D d d
15. In humans, males are the heterogametic sex with an X and Y chromosome in each somatic cell. During the formation of gametes, each daughter cell receives either an X or a Y chromosome. Considering that the X and Y chromosomes are different in size and the genes that they carry, how do they pair during meiosis to be segregated equally among daughter cells?
5
16. What are the progressive levels of packing of DNA in eukaryotic chromosomes?
Mention the major structure observed at each stage of packaging and where known, the dimensions of the structure and the proteins involved in packing.
17. Which ONE of the following statements is true with respect to haploid and diploid life cycles?
(a) Meiosis is simpler in haploid organisms, owing to unpaired chromosomes.
(b) Zygotes differentiate directly into meiotic products in haploids without intervening meiotic divisions.
(c) Somatic nuclei of haploids have the gametic chromosome number.
(d) Somatic nuclei of diploids have the gametic chromosome number.
(e) Somatic nuclei of haploids have the zygotic chromosome number.
18. The human genome is comprised of 23 pairs of chromosomes found in nearly every cell in the body. Answer the quantitative questions below by choosing one of the numbers in the following list:
23
46
69
92
>200
>10
9
(a) How many centromeres are in each cell?
(b) How many telomeres per cell?
(c) How many replication origins per cell?
19. Evidence suggests that the replication of DNA packaged into heterochromatin occurs later than the replication of other chromosomal DNA. What is the simplest possible explanation for this phenomenon?
6
20.
In humans, the ability to taste the chemical phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) is attributed to the dominant allele of a gene, denoted T, located on chromosome 7.
The recessive allele of this gene is designated t. Individuals with the genotypes
T/T and T/t are tasters of PTC, and those with the genotype t/t are nontasters.
From 204 matings of heterozygous tasters with nontasters, 258 taster and 278 nontaster progeny were observed. Perform a chi-square test to determine if the observed results fit the Mendelian expectation of equal segregation (1:1) of alleles during the formation of gametes.
(a) Determine the chi-square value from the given data.
(b) What are the degrees of freedom in this example?
(c) Determine the approximate probability (P value) from the given table.
(d) Based on the P value, is the hypothesis accepted or rejected?
7