Review for ch 16 and 17
advertisement

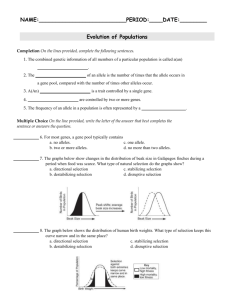
Name: ________________________________________________________ Period ________ Completion: Fill in the missing word to make the sentence complete and correct. 1. The combined genetic information of all members of a particular population is called a ___________. 2. The ___________ of an allele is the number of times that the allele occurs in the gene pool, compared with the number of times other alleles appear. 3. A(n) _____________________ is a trait controlled by a single gene. 4. _____________________________ are controlled by two or more genes. 5. The _____________________ of an allele in a population is often represented by a percentage. 6. Paleontologists use a technique called _______________________ 7. A(n) ________________ is a length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay. 8. The use of half-lives to determine the age of a sample is a process called ________________ 9. Microscopic fossils may also be called _____________________ 10. Large scale evolutionary changes that take place over long periods of time are called ______________ 11. The process by which unrelated organisms come to resemble each other is called _______________ 12. A species or small group of species evolves into many new species during __________________ 13. The pattern of long stable periods interrupted by brief periods of more rapid change is known as ________________________ Evidence of evolution: Five evidences of evolution are A (fossil evidence), B (homologous structures, C (embryology), D (vestigial organs) and E (biochemical). Write the LETTER of the type of evidence. 14. Bones in a bird’s wing and a human’s arm are similar in structure 15. All organisms use ATP in energy transfers. 16. There are similarities in structure among the early stages of fish, birds, and humans. 17. Humans, unlike rabbits, have no known use for the appendix. 18. Horses have increased in size and decreased in number of toes since the Eocene. Match the terms in the column I with the correct definition or name in column II 19. genetic drift a. all genes in a population 20. gradualism b brief periods of change interrupt long stable periods 21. natural selection c. changes in gene frequency in small populations 22. divergent evolution d. changes occur gradually over time 23. punctuated equilibrium e. Darwin 24. mass extinction f. determining age of fossils 25. mutations g. gene or chromosome changes 26. gene pool h. Lamark 27. convergent evolution i. many species vanish at one time 28. radioactive dating j. Mendel 29. use and disuse unrelated species become more alike Multiple choice. List the letter that best fits each question 30. When a paleontologist measures the amount of isotope present in a fossil, what dating technique is he using? A. fossil dating B. radioactive dating C. relative dating D. geologic dating 31. What is the formation of a new species called? A. directional selection B. Speciation C. Founder effect D. Temporal isolation 32. What situation occurs when members of two different species cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring? A. reproductive isolation B. Genetic equilibrium C. genetic drift D. natural selection 33. What kind of isolation occurs when two populations are capable of interbreeding but have differences in courtship rituals or other types of behavior? A. courtship isolation B. behavioral isolation C. geographic isolation D. temporal isolation 34. Two population kept separate by a river are characterized by A. genetic drift B. disruptive selection C. geographic isolation D. temporal isolation 35. What situation occurs when two or more species reproduce at different times? A. stabilizing selection B. behavioral isolation C. geographic isolation D. temporal isolation 36. We are currently living in the Cenozoic A. era B. period C. year D. century 37. What is(are) measured in eras and periods? A. relative dates B. fossil records C. Precambrian Time 38. Huge numbers of species disappear at once during A. punctuated equilibrium B. mass extinction C. coevolution D. geologic time D. adaptive radiation 39. A species that is easily recognizable existed for a relatively short period of time and covered a wide geographic area may be used as a(an) A. index fossil B. fossil record C. microfossil D. macrofossil 40 What type of natural selection takes place when individuals at the upper and lower ends of the curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle? A. directional selection B. destabilizing selection C. stabilizing selection D. disruptive selection 41. A random change in the allele frequency is called A. fitness B. genetic drift C. speciation 42. Genetic drift is more likely to occur in A. large populations B. medium-sized populations D. the founder effect C. small populations D. genetic equilibrium 43. What occurs when allele frequencies change as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population? A. directional selection B. the founder effect C. speciation D. genetic equilibrium 44. What principle states that the frequency of an allele in a population will remain constant unless one or more factors cause that frequency to change? A. speciation principle B. genetic equilibrium C. Hardy-Weinberg principle D. genetic-drift principle 45. The situation in which allele frequencies do not change is called A. genetic equilibrium B. stabilizing equilibrium C. behavioral equilibrium D. directional selection