If you were to align and analyze amino acid sequences of

1. If you were to align and analyze amino acid sequences of ion channels selectively permeable to potassium ions, the regions most likely to be highly conserved are: a) extracellular domains b) intracellular domains c) P-loop d) transmembrane regions
2. You have generated a mutant form of the Shaker potassium channel in which five of the basic residues of the transmembrane segment S4 have been replaced with neutral amino acid residues. How would you expect this mutant ion channel’s gating to be altered?
a) The channel would be more sensitive to depolarizing stimuli. b) The channel would be less sensitive to depolarizing stimuli. c) The channel would function normally. d) The channel would now open in response to hyperpolarizing stimuli.
3. In the presence of a prolonged depolarizing stimulus most voltage-gated ion channels will inactivate, blocking conductance even if depolarization continues. All of the following are forms of inactivation EXCEPT: a) P-type b) N-type c) Q-type d) C-Type
4. In this chapter, all of the following were discussed as mechanisms used to modulate the conductance of ions through membrane channels EXCEPT: a) direct interactions with calcium ions b) interaction with the calcium binding protein calmodulin c) interaction with the G
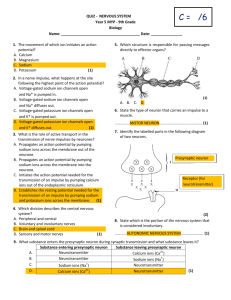
βγ subunit of activated G-protein coupled receptors d) intracellular concentrations of ATP e) regulation of membrane lipid composition
5. All of the following are models of voltage-sensor movement EXCEPT: a) Helical twist b) Paddle c) Helical shift d) Helical screw
6. If a channel is permeable to both ions A and B, but the channel opening contains a binding site with high affinity for ion B, the presence of an external mixture of ions with a large concentration of ion A and only a small amount of B would result in: a) a large influx of ion A b) a small influx of ion A c) a large influx of ion B d) an equal influx of ions A and B
7. Voltage-gated sodium channels select for sodium over potassium ions by: a) size exclusion b) charge preference c) differential in dehydration energy d) repulsion of potassium ions
Answer: c
8. The ion selectivity of voltage-gated calcium channels is dependent on which of the following?
a) the concentration of calcium in the extracellular space b) a conserved glutamine residue in the pore region of the channel c) a basic amino acid residues in the fourth transmembrane domain d) interaction between calmodulin and the intracellular domain
9. Whereas L-type calcium channels are primarily located at the soma, N- and P/Qtype calcium channels are mostly restricted to the: a) distal dendrites b) proximal dendrites c) nodes of ranvier d) axon terminal
10. The rapid decline of dendritic action potentials during repetitive firing is due to: a) inwardly rectifying potassium channels b) phosphorylation of ion channels by protein kinases c) cumulative inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels d) redistribution of ion channels in the cell membrane