cells tissues and organs “school reach” review
advertisement

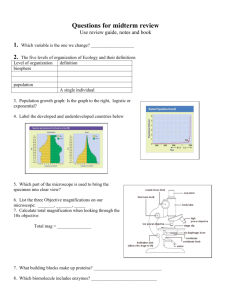
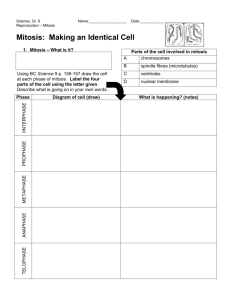
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. CELLS TISSUES AND ORGANS REVIEW Name: ____________________ Which organelle moves materials such as proteins throughout the cell? What does DNA stand for? Name two parts of the cell theory. Name two rules when DRAWING formal diagrams. Name two rules when LABELLING formal diagrams. A cell contains numerous mitochondria. What might be its function? Which organelle places molecules inside special vacuoles so that they may be moved out of the cell? What is the name of these “special vacuoles”? What is DNA called when it is stretched out in the nucleus during interphase? Name an organelle that plant cells have that are not in animal cells. If a cell takes 20 hours to reproduce but it spends 10% of the time in anaphase, how many hours does it spend in this phase? If a cell makes a lot of protein which organelle would it have in high numbers? Name the formula for determining the size of a cell using a microscope. Name the subunits of DNA. What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide? Given that A goes with T and G goes with C. A DNA strand has the base sequence TACA, what would be the sequence on its complementary strand? What is a use for DNA screening? Name the phases of mitosis in order. Which organelle holds onto the spindle fibres during mitosis. When does a chromosome move from being single stranded (chromatid) to double stranded? Name the phase of mitosis when the nuclear membrane breaks down and the chromosomes become visible. What happens to the chromosomes during anaphase? If there are 46 chromosomes at the beginning of mitosis, how many are at the end of mitosis? How do the chromosomes differ between the beginning of mitosis and the end of mitosis? What is the purpose of mitosis? Which phase of the cell cycle does a cell spend the longest time in this stage? Name the type of cancer that does not spread, that it is contained in a tumour? What is a tissue? Name the type of tissue that protects and covers the body, acting as a barrier? Which type of tissue results in cells of one type to be ‘joined’ to cells of another type? Name an example of connective tissue? Which type of tissue is allows digested material to move along the intestines. This type of tissue also allows the body to move. Which type of tissue contains neurons(cells that transmit signals from the brain to the spinal cord etc.) This is the scientific word for “eating”. The word that describes the movement of nutrients from the digestive system into the blood. What is the main function of the large intestine? What is the function of bile? Which organ makes bile? Where is bile stored? Which organ makes enzymes that speed up the breakdown of ‘food’ materials? What is the function of an artery? Name the blood vessel that carries blood from the lower legs to into the heart. Which side of the heart contains deoxygenated blood? What is the scientific word referring to the lungs? After the right ventricle, to which blood vessel does the blood flow next? What is the function of the valves in the heart? What is the function of the pulmonary vein? Which structure in the respiratory system prevents food from entering the lungs upon swallowing? Name the muscle that when it contracts, it moves down to provide space for the air to enter the lungs. From where does air enter the bronchioles from? What is the function of alveoli? How can you tell the difference between the trachea and the esophagus by its structure? Which level of structure would a plant’s root be considered? (ie. Cell, tissue, organ or organ system) and why? ANSWERS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. endoplasmic reticulum deoxyribonucleic acid All living things made of cells; functional unit of life; cells come from pre-existing cells. Use dark, well defined lines. Stipple, don’t shade. Labels on right hand side in a column. No crossing of lines (parallel if possible) Provide energy Golgi Vesicles Chromatin chloroplast or cell wall 2 hours Ribosomes Estimate the number of nuclei that fit across the cell and divide that number into 800. Nucleotide Phosphate, sugar and a base ATGT To detect genetic disorders Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase Centrioles interphase Prophase Split apart at the centromere and go to opposite poles. 46 Single stranded at the end. To make identical copies of the cells. Interphase Benign A group of cells working together with a common function (or similar) Epithelial Connective bone, blood, fat, ligaments, or cartilage muscle nervous ingestion absorption absorb water To break fat down (emulsify) into tiny particles—soap has a similar function Liver gall bladder Pancreas To carry blood away from the heart. Inferior vena cava right side pulmonary pulmonary artery To prevent the blood from reversing direction. Carries blood from the lungs back to the heart (left atrium) Epiglottis Diaphragm bronchus (or bronchi) gas exchange Esophagus is flexible (muscle tissue) and the trachea is hard due to the rings of cartiliage (connective tissue) 53. A root is an organ as it is made of epidermal tissue, vascular tissue (carries water and sugars)