Science_lesson_3_mountains
advertisement

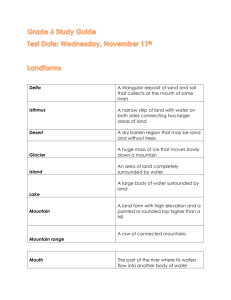
1. Descriptive Data Teacher: Laura McNeese Subject Area: Science Date: 11/18/08 Grade Level: 6th Unit Title: Pluto Planet/Not Lesson Title: Types Mountain’s on Earth Lesson #: 3 Unit Concept: Pluto Lesson Topic or Overview: Discover different mountain types on Earth. 2. Lesson Goal Students will discover different mountains on Earth. Lesson Objective Learner will distinguish between different mountains types on Earth. 3. Connection Curriculum: English Standards: ESS.8.6.6 Explain how volcanic activity relates to mountain formation. ESS.8.6.8 Compare and contrast the different land forms caused by earth’s internal forces: mountains. How does the lesson relate to previous learning and future learning of students? In the previous lesson we learned about volcanos and eruptions. Mountains can form because the magma is forced out of the volcano and turns to lava, this adding to the volcanic mountain. Learning the other types of mountains is important to know for future knowledge. 4. Procedure Grouping for lesson: Small group and Individual Set: 5 minutes Mountains make up about 1/5 of the world’s landscape. Did you know that the tallest 14 mountains are found in the Himalayas? Does anyone know the highest peak on land? (Mt. Everest) Where is the tallest mountain in the solar system? Mars I wonder if Pluto has mountains. Most mountains are formed by Earth’s internal forces. Do you think all mountains are the same? There are actually different kinds of mountains, formed in different ways. Explain the activity, after pairing the students in groups, they will each get a type of mountain and start researching to teach the class. They are instructed to use internet, books, encyclopedias, and etc any source that will help relay facts about mountains. Each student is responsible for filling out the concept map that I am giving in class. See attached types of mountains. C2 (Making the Content Comprehensible) 50 minutes for research. Jigsaw method: Each group is responsible for the material they are going to teach about their assigned mountain type. During class they will need to find as much information and fill out the content map supplied. Teacher should participate in each groups work making sure they have key terms and material to discuss in report. Also offer ideas about the report, speech, and illustrations. Day 2 45 minutes for presentations and discussion Students are informed to respect the speaker and groups presenting material. They are instructed to take notes because the information they are given is how they will be assessed. The teacher is also taking notes and adding more specific material that group did not cover on specified type of mountain. Teacher will also encourage class to ask questions and discuss material they are confused about. Independent Activity: (2 minutes) Groups are individual responsible for speech, report, and illustrator. Speaker: The will deliver the content to the class. Reporter: Will follow up on the research done in class and write a report of on pertinent material. Illustrator: Responsible for visuals. (Poster, Pictures, and etc.) Closure: (5 minutes) Let’s quickly review the types of mountain on earth we researched! Plateau, volcanic, fault-block, and fold mountains. Have class participation on naming one fact for each type of mountain discussed in class. 6. Lesson Extension: As we discussed in the last lesson some scientist believe that volcanoes exists on Pluto so are there mountains? Discuss 7. Modifications for special needs and gifted Modifications for special needs student will be followed as determined in portfolio. Gifted students will need no modifications they are to participate and be responsible for the individual activity they are assigned. 8. Material and Equipment Content map Mountain Type Pen Encyclopedia Books Internet 9. Assessment of Student Learning All students are required to participate in the speaker, illustrator, or writer’s part. Students will be assessed by class participation, answering questions, and following directions. They will be assessed on organization, neatness, and material taught. 10. Reflection and Revision Types of Mountains for Students to Research. Plateau Mountains (Erosion Mountains) These are mountains that are really plateaus that have worn down from erosion. The dictionary describes these as large areas of ‘high levels’ of flat land. Volcanic Mountains Volcanic Mountains are formed when molten rock or magma deep within the earth, erupts, and piles upon the surface. Examples of Volcanic Mountains include Mount St. Helens in North America and Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines. Fault-block Mountains These mountains form when faults or cracks in the earth's crust force some materials or blocks of rock up and others down. Instead of the earth folding over, the earth fractures and blocks are stacked. Examples include the Sierra Nevada Mountains in North America and the Harz Mountains in Germany. Fold Mountains Fold mountains are formed when two plates collided head on, and their edges crumbled, much the same way as a piece of paper folds when pushed together. Examples of fold mountains include Himalayas in Asia, the Alps in Europe and the Andes in South America Group Planning -- Research Project : Types of mountain! Jigsaw Teacher Name: Mrs. McNeese Student Name: CATEGORY ________________________________________ 4 Excellent 3 Great 2 Good 1 Fair Plan for Organizing Information Students have developed a clear plan for organizing the information as it is gathered and in the final research product. All students can independently explain the planned organization of the research findings. Students have developed a clear plan for organizing the information in the final research product. All students can independently explain this plan. Students have developed a clear plan for organizing the information as it is gathered. All students can independently explain most of this plan. Students have no clear plan for organizing the information AND/OR students in the group cannot explain their organizational plan. Ideas/Research Questions Researchers independently identify at least 4 reasonable, insightful, creative ideas/questions to pursue when doing the research. Researchers independently identify at least 4 reasonable ideas/questions to pursue when doing the research. Researchers identify, with some teacher help, at least 4 reasonable ideas/questions to pursue when doing the research. Researchers identify, with considerable teacher help, 4 reasonable ideas/questions to pursue when doing the research. Following Responsibility of Delegation Given Each student in the group can clearly explain what information is needed by the group, what information s/he is responsible for locating, and when the information is needed. Each student in the group can clearly explain what information s/he is responsible for locating. Each student in the group can, with minimal prompting from peers, clearly explain what information s/he is responsible for locating. One or more students in the group cannot clearly explain what information they are responsible for locating. CAUSE LOCATION MOUNTAIN DESCRIPTION Mountains Questions Test Our Skills Student Name: _____________________ 1. Volcanic mountains are formed by: a. the ash and smoke from a volcano b. rock on Earth’s surface melted by a volcano’s heat c. magma breaking through Earth’s crust and forming a mountain d. rock being pushed up from below Earth’s surface 2. Which type of mountain is formed by two tectonic plates colliding? a. volcanic mountains b. folded mountains c. fault-block mountains d. dome mountains 3. Which type of mountain is formed when the crust breaks and large pieces of crust are pushed up above the surrounding land? a. volcanic mountains b. folded mountains c. fault-block mountains d. dome mountains 4. Which type of mountains is formed when magma can’t break through the crust, but pushes up the rocks above it? a. volcanic mountains b. folded mountains c. fault-block mountains d. dome mountains 5. Which of these is an example of a dome mountain? a. Hawaiian Islands b. Rocky Mountains c. Sierra Nevada Mountains d. the Black Hills Mountains Questions Test Our Skills Student Name: _____________________ 6. Which of these is an example of a fault-block mountain? a. Hawaiian Islands b. Rocky Mountains c. Sierra Nevada Mountains d. the Black Hills 7. Which of these is an example of a folded mountain? a. Hawaiian Islands b. Rocky Mountains c. Sierra Nevada Mountains d. the Black Hills