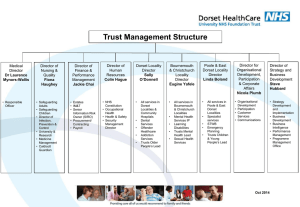
SYMBOLS EMPLOYED
advertisement

DEFINITIONS AND EXPLANATIONS 1. Population: the survey population includes the permanent (de jure) population of Israel aged 15 and over. The survey population includes: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Permanent residents living in Israel. Permanent residents living abroad for a period of less than one year. New immigrants and potential immigrants, from the moment of their arrival in Israel. Tourists, volunteers or temporary residents living in Israel continuously for one year or more. As of 1968, residents of East Jerusalem. As of 1972, the population of Jewish localities in the Golan sub-district; as of 1982, all the residents in the Golan sub-district. As of 2006, the residents of Jewish localities in the Judea and Samaria Area (from 1972 to 2005 – the Judea, Samaria and Gaza Areas). The survey population does not include: a. b. c. Permanent residents living abroad continuously for one year or more. Tourists, volunteers or temporary residents living in Israel for less than one year. Foreign diplomats and UN people. 2. Household population: the tables refer to all households except those in kibbutzim, institutions, students’ dormitories and persons living outside localities (Bedouins in the South and others). Tables relating to households according to housing density, do not include absorption centres and hotels that accommodate immigrants. 3. Household: defined as one person or a group of persons living together in a dwelling on a permanent basis, most days of the week, and who have a joint budget for food. A household may also include persons who are not relatives. A household includes: a. All the people in the survey population and children under the age of 15, who usually sleep in the dwelling at least 4 nights a week. Of those who usually sleep in the dwelling less than 4 nights a week, household members also include: b. c. d. e. f. g. A household member doing compulsory military service (including Nachal and Shalat – unpaid service – in a military framework) or serving in the permanent army, who has no other permanent civil address in Israel. A married person living away from a dwelling that is the couple’s permanent address due to work or studies, but whose spouse resides in the dwelling (not including couples who live separately). Crew members of aircraft or ships, whose permanent address is the above-mentioned dwelling, where they sleep when they are in the country. A family member residing in the dwelling at the time of the interview, and who has no other permanent address in Israel. A household member who has been staying in a hospital for less than one month. A household member who has been staying abroad continuously for less than one year. - XVII - h. i. An unmarried household member who has not been in the dwelling for less than a month, due to vacation, work or studies in a short course, and who has no other permanent address in the country. A household member studying in a military or civilian boarding school, as well as a person living in student dormitories, but at the time of the interview is at his parents’ home – if the interview is conducted during summer vacation. A household does not include: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. A married spouse who left the dwelling and does not intend to return (i.e., a spouse living apart, even if not yet divorced). A married person who resides at an address other than that of the family (spouse and children) due to work or studies, even if he or she sleeps at this address most of the week. A household member studying at a boarding school, as well as a person living in student dormitories – if the interview is conducted during the school year. A family member staying on kibbutz in a Nachal or Shalat (unpaid service) pre-military framework. A family member who temporarily resides in the sampled dwelling, but sleeps most days of the year in another dwelling, which constitutes his permanent address. A family member who has moved to a senior citizens’ home. An unmarried family member who has been away from the dwelling one month or more, and who has a different (civilian) address in the country, in which he sleeps most days of the week. A family member who has been staying in hospital for one month or more. A family member who is in prison (including an institution or work farm) or in an institution for the disabled (the blind, the deaf, the dumb, the mentally retarded) for one month or more. 4. Size of household: defined according to the number of persons included in the household, according to the above definition. 5. Labour force: In the publication on households, the definition of the labour force includes the civilian labour force, as well as the soldiers in the permanent army. 5.1 Weekly labour force: persons aged 15 and over, who were “employed” or “unemployed” in the determinant week, according to the following definitions: 5.1.1 Employed persons: persons who worked at least one hour during the determinant week, at any job, for pay, profit or other remuneration; all workers in kibbutzim (whether in services or other industries); family members who worked without pay 15 hours or more during the survey week; persons in institutions who worked 15 hours a week or more; persons who were temporarily absent from their work; soldiers in the permanent army. Employed persons are divided by the usual extent of work: - Usually full-time workers – employed persons who usually work 35 hours or more per week, and soldiers in the permanent army. - Usually part-time workers – employed persons who usually work up to 34 hours per week. - XVIII - Note: In previous publications (since 1998), data were calculated according to the extent of work in the determinant week, rather than according to the usual extent of work. Therefore, the data in Table 3 for 2002-2006 were revised and calculated according to the usual extent of work. 5.1.2 Unemployed persons: persons who did not work at all (not even one hour), who actively sought work during the last four weeks, by registering at the Labour Exchange of the Employment Service or by a personal or written application to an employer, etc., and who could have started work in the determinant week had suitable work been offered to them (“availability to work”). 5.2 Not in weekly labour force: all of those aged 15 or over, who were neither “employed” nor “unemployed” in the determinant week. This group includes students, persons employed in unpaid voluntary work, housewives who did not work for even one hour outside their homes, persons unable to work, persons living on pensions, rent, etc., who did not work for even one hour during the determinant week. In addition, this group includes soldiers on compulsory military service (excluding soldiers in the permanent army), family members who worked without pay less than 15 hours a week and persons in institutions who worked less than 15 hours during the determinant week. 6. Earners: persons aged 15 and over who are in the civilian labour force; i.e., “employed” or “unemployed”, as well as soldiers in the permanent army. 7. Head of a household: is the economic head of a household. In 1995, the definition of the head of a household was changed, and is now determined by the degree of participation in the labour force, regardless of age or sex. - The head of a household is the main earner of the household, i.e., an employed person who usually works 35 or more hours per week (including soldiers in the permanent army), and precedes an employed person who usually works up to 34 hours per week, who precedes an unemployed person. - If more than one person in the household fits the definition of the household head, the head of household is determined according to the priorities set by the interviewee. - If there is no earner in the household, the head of household is determined by the interviewee. Note: the head of the household is a person aged 18 and over (except households where the only employed person is aged 15-17 and households where there are persons aged 15-17 only). 8. Working age: men aged 15-65; women aged 15-60. Household with persons of working age: household with at least one person of working age. Household with persons above working age only (retired): entitled to old-age pension from the National Insurance Institute. 9. Children in household: includes all children up to age 17 (inclusive) in the household. Does not include those aged 15-17 who are heads of households or spouses of heads of households. - XIX - Note: In the Labour Force Surveys of 1998-2001, according to the weighting method that was used in the survey, Israeli-born children of immigrants who arrived in Israel in 1990 and after, were included in the weighting strata as "nonimmigrants”. Therefore, the estimate obtained for immigrant children was lower than their actual number. As of 2001, processing was conducted by new weighting groups. See: Central Bureau of Statistics, Labour Force Surveys 2002, Current Statistics 9/2003. 10. Number of rooms in the dwelling: includes all rooms used by the household as living quarters. The following are excluded: kitchens, bathrooms, toilets, balconies and rooms used for business or work only, as well as rooms let to tenants. Until 1979, half a room was counted as a room; since 1980, a full record of rooms and halfrooms has been made. Therefore, the data of 1980 were processed twice. 11. Number of persons per room (housing density): calculated by dividing the number of persons living in the household by the total number of rooms occupied by members of the household. 12. Average number of persons per household: calculated by dividing the total number of persons in all households by the number of households. 13. Religion and population group: the head of the household is the only household member who is questioned regarding his religion. The head of the household's religion is registered as the religion of all the members of the household. The classification according to religion includes: Jews, Moslems, Christians, Druze, and other religion (other religion also includes “no religion” or “religion unknown”). The category “Other Religions” includes all those who replied that they are not Jews. As of 2002, this group was divided into two population groups: "Arabs": a. live in non-Jewish localities; b. live in Jewish or mixed localities, and were born in Israel or arrived in Israel before 1990. "Others": live in Jewish or mixed localities, and arrived in Israel in 1990 and after. 14. Type of locality: There are two kinds of type of locality: current and permanent. A current type of locality is determined according to the estimated size of the locality’s population at the end of each year. A permanent type of locality is a current type of locality which has remained unchanged for several years in order to enable comparison of data from one year to another. The type of locality by which data are classified in the Labour Force Surveys is the permanent type of locality appearing in the list of localities. The localities are divided into two main groups, the distinction between them being according to size of locality (number of residents): a) Urban localities, in which there are 2,000 or more residents. These localities are classified into sub-groups by size; - XX - b) Rural localities, in which there are less than 2,000 residents, which are classified into three types of localities: 1. Kibbutzim; 2. Moshavim and collective moshavim; 3. Other rural localities. From 1998 until 2001 localities were classified according to their estimated population in the 1995 Census of Population and Housing. As of 2002 localities were classified according to their estimated population at the end of 2001. This was done in order to reflect the changes which occurred in population size in various localities between the censuses. Since 2007 they have been classified according to their size estimate at the end of 2005. For further details, see: Central Bureau of Statistics, List of Localities, Their Population and Codes, 31.12.2002, Technical Publication, 75. 15. Development localities: Included are the localities specified in the regularly regulations based on the “1963 Severance Pay Law”. Below are 25 localities that are included in the Labour Force Survey data: Development localities in the North: Bet She’an, Hazor HaGelilit, Tiberias, Yoqne’am Illit, Karmi’el, Migdal HaEmeq, Ma’alot-Tarshiha, Nazerat Illit, Akko, Afula, Zefat, Qiryat Shemona, Shelomi. Development localities in the South: Ofaqim, Elat, Bet Shemesh, Dimona, Yavne, Yeroham, Mizpe Ramon, Netivot, Arad, Qiryat Gat, Qiryat Mal’akhi, Sederot. For further details, see: Central Bureau of Statistics, List of Localities, Their Population and Codes, 31.12.2002, Technical Publication, 75. 16. District and Sub-District: the districts and sub-districts are defined according to the official administrative distribution of the country, according to which there are 6 districts and 15 sub-districts. For details, see: Central Bureau of Statistics, List of Localities, Their Population and Codes, 31.12.2002, Technical Publication, 75. As of 1972 the Judea, Samaria and Gaza Areas were added, in order to characterize the Jewish localities in these areas and their population. The data for 2005 relate to the residents of Judea, Samaria and the Gaza Areas, and do not reflect changes in the population following the evacuation of the Israeli localities (the Jewish localities) in the Gaza Area and northern Samaria, under the Disengagement Plan Law 2005. As of 2006 – the Judea and Samaria Area. 17. Metropolitan area: A metropolitan area is a large urban cluster, with a large number of local authorities – including local councils and rural localities – whose territories are contiguous, and who have economic, social and cultural ties, so that they form one functional unit. The metropolitan areas are divided according to their internal structure: Core: The territory of the primary city serving as the focus of activity for the population of the metropolitan area. Inner Ring: The area containing the localities surrounding the Core. - XXI - Middle Ring: The area containing the localities surrounding the Inner Ring (in the Tel Aviv metropolitan area and Be’er Sheva metropolitan area). Outer Ring: The area containing the localities surrounding the Middle Ring. Section (Northern, Eastern, Southern): Sub-divisions of the rings of each metropolitan area. As of 1999, the Labour Force Survey has used a new definition of metropolitan area, which replaced the former definition of conurbation. Two metropolitan areas were defined: the Tel Aviv Metropolitan Area and the Haifa Metropolitan Area. In 2001, the borders of the metropolitan areas were re-examined and, as a result, the borders of the Haifa Metropolitan Area were changed. The changes in the Haifa Metropolitan Area were implemented in the localities included in the outer ring of the metropolitan area: in the southern part of the metropolitan area the locality Jisr Az-Zarqa was removed, and in the northern part it was decided to maintain all of the localities up to the Nahariyya line (inclusive). In the northeastern part of the outer ring, it was decided to include all of the localities in the natural region of Karmi’el and, in addition, the localities of the Misgav regional council. The borders of the Tel Aviv Metropolitan Area were not changed. Be’er Sheva Metropolitan Area: In 2001, a plan was approved which defines the borders of a metropolitan area in the south, which is developing around the city of Be’er Sheva. The Be’er Sheva Metropolitan plan is similar to the contours of the other two metropolitan areas, in that it is also divided into rings with sections in them. The rings are defined by their distance from the center of the metropolitan area (the “core”), which is the city of Be’er Sheva. The borders of the Be’er Sheva Metropolitan Area include the Northern Negev: from the border of the Be’er Sheva sub-district in the north, up to Mizpe Ramon in the south; and from the border of the Gaza Area and Egypt in the west, up to the Dead Sea and the Jordanian border in the east. For a detailed explanation of borders of metropolitan areas, and for a list of localities included in them according to their internal structure, see: Central Bureau of Statistics, List of Localities, Publication 3, 1995 Census of Population and Housing publications. 18. Years of schooling (of head of the household): the number of years the head of the household studied in a school, excluding studying on one's own or attending irregular courses. Only completed years of schooling are considered. For persons studying at the time of the interview, that year is also counted. - XXII -