Heredity – notes - Effingham County Schools
advertisement
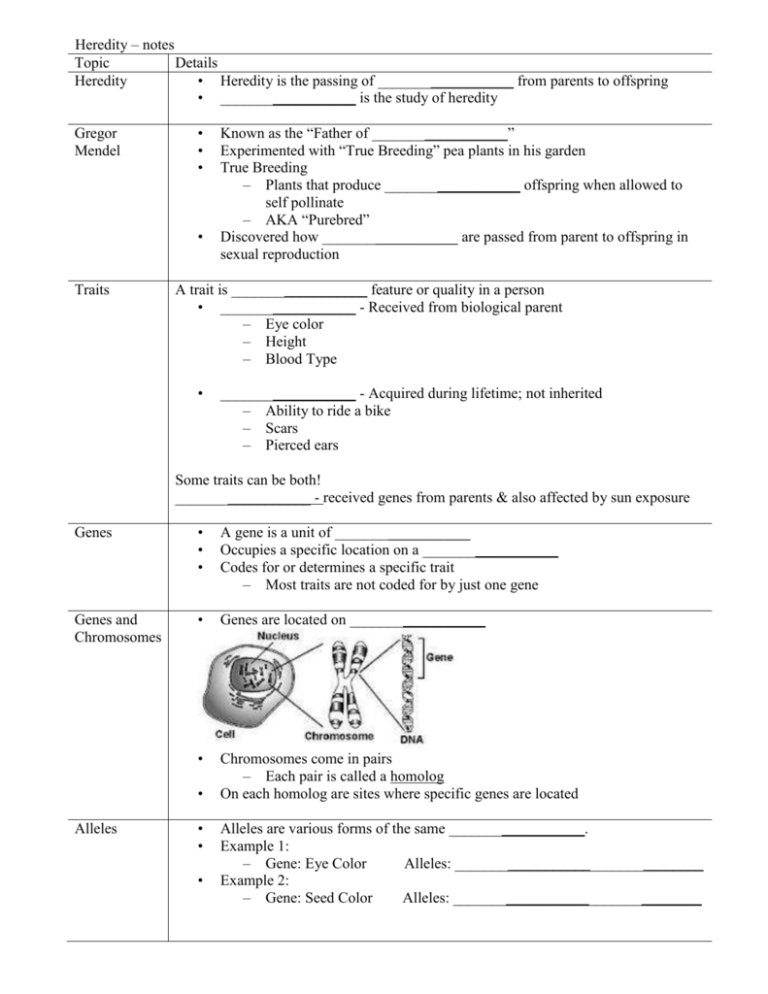
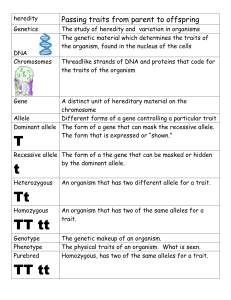
Heredity – notes Topic Details Heredity • Heredity is the passing of __________________ from parents to offspring • __________________ is the study of heredity Gregor Mendel • • • • Traits Known as the “Father of __________________” Experimented with “True Breeding” pea plants in his garden True Breeding – Plants that produce __________________ offspring when allowed to self pollinate – AKA “Purebred” Discovered how __________________ are passed from parent to offspring in sexual reproduction A trait is __________________ feature or quality in a person • __________________ - Received from biological parent – Eye color – Height – Blood Type • __________________ - Acquired during lifetime; not inherited – Ability to ride a bike – Scars – Pierced ears Some traits can be both! __________________ - received genes from parents & also affected by sun exposure Genes • • • A gene is a unit of __________________ Occupies a specific location on a __________________ Codes for or determines a specific trait – Most traits are not coded for by just one gene Genes and Chromosomes • Genes are located on __________________ • Chromosomes come in pairs – Each pair is called a homolog On each homolog are sites where specific genes are located • Alleles • • • Alleles are various forms of the same __________________. Example 1: – Gene: Eye Color Alleles: _________________________________ Example 2: – Gene: Seed Color Alleles: _________________________________ • • • • Mendel also performed experiments with __________________ plants – Hybrids - Plants that were produced by parents with different traits In these experiments, he discovered that traits are inherited by parents passing __________________ to their offspring Individuals carry __________________ alleles for each trait, but only pass down one to their offspring One __________________ is dominant over another . __________________Allele: an allele whose trait is always shows up in the organism when the allele is present – Expressed if only one is present – Example: brown eye color __________________ Allele: an allele whose trait is hidden whenever the dominant one is present – Can only be expressed if two are present – Example: blue eye color Phenotype and Genotype • Alleles are represented by symbols – Dominant represented by a _______________________________ • Example: Widows Peak =W – Recessive represented by the ___________________________letter • Example: Straight Hair Line = w • Alleles Interact to Produce Traits – Each parent contributes __________________allele for a given trait – The __________________ of alleles from parents can result in varying traits in their offspring • __________________: An organisms genetic makeup, or alleles an organism has for a trait is its genotype – Ww, Bb, bb, ww, etc __________________: An organism’s physical appearance, or visible traits is its phenotype. – Widow’s peak, brown eyes, blue eyes, straight hairline, etc • Heterozygous and Homozygous • Terms used to describe an organisms genotype – __________________ – an organism that has two different alleles for a trait is said to be heterozygous • Example: Ww, Bb – __________________– An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait is said to be homozygous • Example: WW, ww, BB, bb ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________