Geography
advertisement

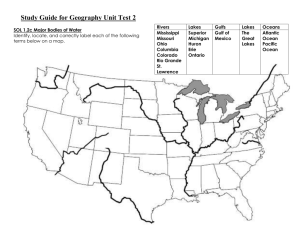
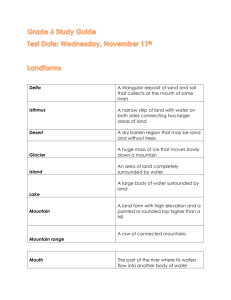
Geography Region- a geographic area with common characteristics that set is apart from surrounding areas. There are physical, political, economic, and cultural regions Physical Regions = areas with common physical features, resources, & wildlife Cultural Regions share common cultural characteristics, such as language, history, political institutions, or religion Middle East- Majority of people in speak Arabic, follow Muslim religion, wear similar clothing, enjoy similar foods Latin America- (Mexico, Central America, and South America) share a mixed Native American, European and African ancestry, have common history, and speak related languages Political Regions are countries defined by special political characteristics. Each country has its own government, borders and sovereign power Economic Regions are defined by economic characteristics European Union- EU comprised of many of the countries of Europe. It makes up a vast economic region in which people may freely travel and work, and in which goods move without paying customs duties. NAFTA- (United States, Canada, Mexico) North American Free Trade Agreement. Customs duties on many goods from with the regions are lower than they are on goods from outside it. Comparing Countries and Regions Countries with advanced economies and high standards of living are called developed countries. Countries with less advanced technology and lower standards of living are called developing countries. Demographic Data related to population. Geographers look at birth rate and death rate (often referred to mortality rate) They also look at the infant mortality rate (the number of infants out of every 1,000 births who die) A developed nation- low birth rate, a low death rate, and a low infant mortality rate A developing nation- high birthrate, death rate, and infant mortality rate Education Data Literacy rate- the percentage of people who can read and write Developed Nation- high literacy rate, high percentage of people attending colleges and universities Developing Nation- lower literacy rate and a lower percentage of people attending colleges and universities Economic Data Gross Domestic Product- indicates the total value of all goods and services produced by a nation in a year Per Capita Income- reflects the amount of money earned in a year in that nation by an average person Developed Nation- high per capita income ● Developing Nation- low per capita income How Regions Change Move and change over time Conflict and conquest Inca territory was absorbed into the much larger Spanish colonial empire Even when the boundaries of a region stay the same, its characteristics may change Settlers gradually transformed the landscape of the US which was mainly populated by Native Americanscutting down forests to create farms, building towns as centers of trade, and then expanding these urban areas to become centers of industry and technology. The Consequences of Urbanization Urbanization- refers to the movement of large numbers of people into cities Industrial cities completely altered the landscape during the IR Canals, railroads and roads were built linking these cities. The later invention of the care made it possible for people to move from city centers into suburbs Threatens environment with pollution Population Density Population Density- how many people live in a given area Dot Population Map- each dot represents a certain number of residents Population Density Map- uses patterns to show how many people live in an area. Regions of different population density are separately indicated. The map legend explains what each pattern represents. Other Human Economic Activities Changes in technology, transportation, and communications affect not only urbanization but the location of economic activities generally Such developments in steel production can transform the environment just as much as urbanization Maps can show the effects of human activity on the environment by indication which economic activities are carried out in different regions What Factors Have Influenced Human Migration Migration- the movement of people from one area to another Push Factors- are those conditions that push people out of their old location Pull Factors- are those attractions that lure migrants to a new location Social Factors (Religious or ethnic persecution) often serve as push factors Pilgrims and Puritans left England for North America in the 1600s. Ethnic strife can also lead to large-scale migration. In 1994, when the Hutu army massacred half a million Tutsis in Rwanda, millions of Tutsis fled to nearby countries Political Factors People also migrate when they are persecuted for their political beliefs Cold War – thousands of East Germans fled to democratic West Germany to avoid living under Communism. Also, after Castro imposed Communism in Cuba- Cubans fled to US Economic Factors Society suffers from extreme poverty, this pushed man to attempt to migrate Environmental Factors People also leave their homes when threatened by environmental disaster 1840s, Ireland faced disaster when it potato crop was struck by a disease which caused the potatoes to rot in the ground before they could by harvested The drought has led to erosion of the soil, forcing thousands of Africans to migrate from the Sahel region The Impact of Forces of Movement on the United States How the Characteristics of American Regions Have Changed Over Time The United States was once a vast wilderness. By the time of the American Revolution, the Atlantic Coastal Plain, stretching along he coastline and extending inland to the Appalachian Mountains, had been settled Industrial Revolution spread from Britain to America, factories arose and the population increased. The landscape changed from forest, rolling plains, small farms, & villages to the larger farms, towns & cities we have today A Shift in the US Population Until the 1970s most Americans lived in the Northeast and Midwest. The Southeast was considered too hot and humid, while the West was too dry and remote. Technology developments; air conditioning/hydroelectric plants = homes/offices/ factories cooler in summer. California and Texas are now the nation’s most populous states How Changes in Technology Transportation & Communication Have Affected the Location of American Economic Activities Improvements in transportation, communication, and specific technologies have often affected the location of American economic activities. Opened up the Great Plains to settlement and allowed farmers to ship their crops and livestock back east. Development of railroad lines and steamships made it possible to bring together Pennsylvania’s coal and the iron ore of the Mesabi Range in Minnesota, transforming the Midwest in to America’s industrial heartland. How Geographic Processes have led to Changes in American Society Geographic processes have contributed to many changes in American society Industrialization spurred urbanization Americans migrated from rural farmlands to new industrial cities in search of work Global spread of technology Many heavy industries to relocate to Asia and Latin America where labor costs are less Forced Americans to focus more on providing services or on producing high-tech goods, which require greater skill & higher education levels Suburbs - Green comfortable, rural-like areas on the outskirts of major cities Both during the earlier phase of industrialization & in our current post-industrial era, the U.S. has benefited from labor provided by an influx of immigrants attracted to our high standards of living and democratic ideals. Other Facts on Geography = is the description of the surface of the Earth, its life and culture. The United States of America is a federal republic situated primarily in North America. It is bordered on the north by Canada and to the south by Mexico. It comprises 50 states and one federal district, and has several territories with differing degrees of affiliation. The United States shares land borders with Canada (to the north) and Mexico (to the south), and territorial water boundaries with Canada, Russia,, the Bahamas, and numerous smaller nations. It is otherwise bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean on the east, and the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Alaska borders the Pacific Ocean to the south, the Bering Strait to the west, and the Arctic Ocean to the north, while Hawaii lies far to the southwest of the mainland in the Pacific Ocean Forty-eight of the states are in the single region between Canada and Mexico, this group is referred to, with varying precision and formality, as the continental or contiguous United States, sometimes abbreviated COP/US, and as the Lower 48 Alaska, which is not included in the term contiguous United States, is at the northwestern end of North America, separated from the Lower 48 by Canada The state of Hawaii is an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean The capital city, Washington, District of Columbia, is a federal district located on land donated by the state of Maryland (Virginia had also donated land, but it was returned in 1847) The United States also has overseas territories with varying levels of independence and organization. In total area (which includes inland water and land), only Russia and Canada are larger than the United States, if inland water is excluded, China ranks second, the U.S. ranks third, and Canada ranks fourth The United Status’s total area is 3,718,711 square miles (9,631,418 km of winch land makes up 3,537,438 square miles (9,161,923 km3 and water makes up 181,273 square miles (469,495 km2 The United State’s landscape is one of the most varied among those of the world’s nations The East consists largely of rolling hills and temperate forests The Appalachian Mountains form a line of low mountains in the Eastern U S The five Great Lakes are located in the north-central portion of the country, four of them forming part of the border with Canada The Southeast largely contains subtropical forests and mangrove, especially in Florida West of the Appalachians, the Ohio and Tennessee Valleys, and the Midwest consist largely of rolling hills and productive farmland, stretching south to the Gulf Coast Stretching west from the Midwest are the Great Plains A Large portion of the country’s agricultural products are grown m this region The region consists mostly of large, heavily cultivated and very flat grassland The Great Plains come to an abrupt end at the Rocky Mountains The Rocky Mountains form a large portion of the Western U S, entering from Canada and stretching nearly to Mexico The Rocky Mountains generally contain fairly mild slopes and low peaks compared to many of the other great mountain ranges, with a few exceptions (such as the Teton Mountains in Wyoming and the Swatch Range in Colorado) In addition, instead of being one generally continuous and solid mountain range, it is broken up into a number of smaller, intermittent mountain ranges, forming a large series of basins and valleys West of the Rocky Mountains lies the Intermundane Plateaus (also known as the Intermountain West), a large, arid desert lying between the Rockies and the Cascades and Sierra Nevada ranges The large southern portion, known as the Great Basin, consists of salt flats, drainage basins, and many small north-south mountain ranges The Southwest is predominantly a low-lying desert region A portion known as the Colorado Plateau, centered around the Four Corners region, is considered to have some of the most spectacular scenery in the world It is accentuated in such national parks as Grand Canyon, Arches, and Bryce Canyon among others The Intermountain Plateaus come to an end at the Cascade Range and the Sierra Nevada The Cascades consist of largely intermittent, volcanic mountains rising prominently from the surrounding landscape The Sierra Nevada, further south, is a high, rugged, and dense mountain range It contains the highest point m the contiguous 48 states, Mount Whitney (14,505 ft, 4,421 m) These areas contain some spectacular, scenery as well, as evidenced by such national parks as Yosemite and Mount Rainer West of the Cascades and Sierra Nevada is a series of valleys, such as the Central Valley in California and the Willamette Valley in Oregon Along the coast is a series of low mountain ranges known as the Pacific Coast Ranges Much of the Pacific Northwest coast is inhabited by some of the densest vegetation outside of the Tropics, and also the tallest trees in the world (the Redwoods) Mount McKinley, Alaska, the highest point in North America at 20,320 ft (6,194 m) Alaska contains some of the most dramatic and untapped scenery m the country Tall, prominent mountain ranges rise up sharply from broad, flat tundra plains On the islands off the south and southwest coast are many volcanoes Hawaii, far to the south of Alaska in the Pacific Ocean, is a chain of tropical, volcanic islands, popular as a tourist destination for many from East Asia and the mainland Urn Led States Climate: Due to its large sin and wide range of geographic features, the United States contains just about every climate. It’s comparatively generous climate partially contributed to the country’s rise as a world power, with infrequent severe drought in the major agricultural regions, a general lack of widespread flooding, and a mainly temperate climate that receives adequate precipitation.