Systems Review
advertisement
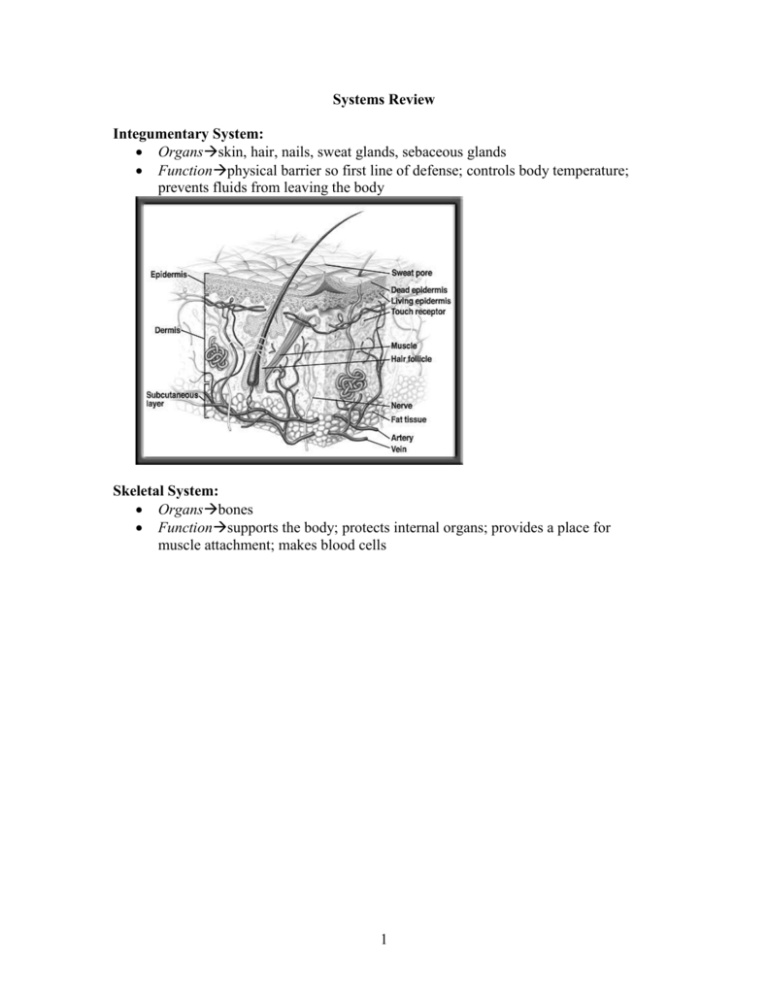
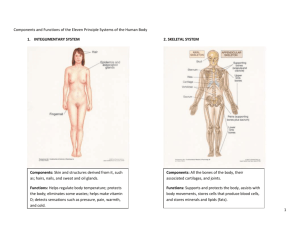
Systems Review Integumentary System: Organsskin, hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands Functionphysical barrier so first line of defense; controls body temperature; prevents fluids from leaving the body Skeletal System: Organsbones Functionsupports the body; protects internal organs; provides a place for muscle attachment; makes blood cells 1 exoskeletons are found on the outside of the body (ex: insects) endoskeletons are found on the inside of the body the place where two bones meet are called joints and allow the skeleton to move ligaments are bands of connective tissue that connect the two bones that form joints Muscular System: Organsmuscles Functionmovement Muscles attach to the skeleton and allow you to move the body. Skeletal muscles usually work in pairs. One muscle contracts while the other relaxes to create movement (ex: the biceps muscle contracts to bend the elbow while the triceps muscle is relaxed). To “undo” the movement, the 1st muscle relaxes and the 2nd muscle contracts (ex: the biceps muscle relaxes and the triceps muscle contracts to straighten out the arm). 2 there are three types of muscles: o skeletal muscle: this is voluntary (can be controlled) and makes up the muscles that move the skeleton o cardiac muscle: this is involuntary (can not be controlled) and makes up the heart muscle o smooth muscle: this is involuntary and is found in the walls of the body organs (ex: stomach, intestines, blood vessels) Cardiovascular System: Organsheart, arteries, veins, capillaries Functioncarries oxygen from the lungs to all the body cells and removes wastes The blood flows from the heart to the lungs where it receives oxygen. The newly oxygenated blood travels back to the heart and then travels out of the heart to the body. As the blood travels through the body, it loses its oxygen. The deoxygenated blood then returns to the heart and the cycle begins again. arteries are the vessels that carry blood away from the heart capillaries connect arteries and veins and are the smallest vessels in the body; this is where substances enter and leave the blood stream veins are the vessels that carry blood back to the heart this system is a closed system, because blood does not leave the vessels in an open system, blood leaves the vessels and enters open spaces that surround the body organs; simple organisms like insects have open systems Lymphatic System: Organslymph vessels, spleen, tonsils, thymus, lymph nodes Functionreturns fluid lost by cardiovascular system to the heart; cleans this fluid and works with the immune system to destroy bacteria and other foreign invaders The lymph vessels carry lymph (fluid that has leaked out of the cardiovascular system) back to the heart. As lymph is carried through the system, it goes through the lymph nodes. The nodes help clean the lymph. 3 Respiratory System: Organsnose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs Functionprovides oxygen, removes carbon dioxide, voice production Air passes through the nose, pharynx, larynx, and trachea. The trachea divides into smaller tubes called bronchi. These tubes carry the air into the lungs into structures called alveoli. Here is where the oxygen in the air enters the bloodstream and the carbon dioxide exits. Digestive System: Organsmouth, teeth, tongue, pharynx (throat), esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Functionbreaks down food to provide nutrients and removes solid wastes Digestion of food starts in the mouth. Saliva helps to break down simple sugars. The tongue initiates swallowing and food is pushed into the esophagus. Food goes down into the stomach. The stomach “churns” the food and helps break it down into smaller pieces. The food then moves into the small intestine where the nutrients leave this system and enter the blood. The remaining contents move into the large intestine and rectum and are eliminated from the body through the anus. The liver, gallbladder and pancreas produce substances that help with the chemical breakdown of food. Immune System: 4 Organsno organs; just cells Functionprotects against foreign invaders Pathogens (ex: bacteria) enter tissues through a wound. They are attacked by macrophages at the infection site. Antigens B cell (proteins) of the pathogen Macrophage are displayed on the surface of the macrophage. Helper T cells have receptor sites that recognize and bind to the antigens on the macrophage. B cells can bind to antigens directly. Helper T cells bind to T cell Plasma cells antigens on B cells T cells release chemicals that cause B cells to produce plasma cells. Antibodies Each plasma cell secretes more than 2000 antibodies per second in the blood. Memory B cells and antibodies remain in the blood and respond to future invasions by the same pathogen. Pathogen Endocrine System: Organsovaries, testes, thyroid, adrenals, pituitary, thymus, pancreas, parathyroids Functionslow-acting control system; makes hormones The glands of this system make hormones that must enter the bloodstream to reach the organ that they will act upon. Because the hormones must travel through the bloodstream, this system takes time to cause a reaction in the body. 5 Reproductive System: Organsfemales: ovaries, vagina, uterus, cervix, Fallopian tubes males: penis, testes, urethra, ductus deferens Functionmakes hormones; produce offspring Fallopian tube ductus deferens ovary uterus penis cervix vagina urethra testis Urinary System (a.k.a. Excretory System): Organskidneys, ureter, bladder, urethra Functioncleans the blood and removes liquid wastes from blood The kidneys filter the blood and remove wastes. These wastes form the urine. Urine moves from the kidneys through the ureters and into the bladder where it is stored. Urine leaves the body through the urethra. Nervous System: Organsbrain, special senses, spinal cord, nerves Functionvision, hearing, taste, fast-acting control This system is responsible for controlling all of the other body systems. The organs of special sense (ex: eyes, ears) take in information about the environment so that this system can respond. 6 sensory neurons receive information from the external and internal environment and send it to the brain (ex: signal from the skin to the brain that lets the brain know it is cold outside) motor neurons sends signals from the nervous system to the body to cause a response (ex: signal from the brain to the muscles to cause “shivering” in response to the cold) Reflex o an automatic response to a stimulus o the nerve signal travels to the spinal cord using a sensory neuron (nerve cell) o the spinal cord sends a signal using a motor neuron to cause a response o the spinal cord also sends a signal to the brain so that it is aware of the stimulus o because the motor signal does not come from the brain, the reaction is much faster 7